Abstract
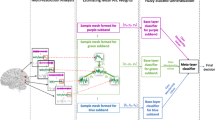
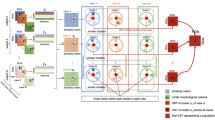
Brain connectivity networks have been shown to represent gender differences under a number of cognitive tasks. Recently, it has been conjectured that fMRI signals decomposed into different resolutions embed different types of cognitive information. In this paper, we combine multiresolution analysis and connectivity networks to study gender differences under a variety of cognitive tasks, and propose a machine learning framework to discriminate individuals according to their gender. For this purpose, we estimate a set of brain networks, formed at different resolutions while the subjects perform different cognitive tasks. First, we decompose fMRI signals recorded under a sequence of cognitive stimuli into its frequency subbands using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). Next, we represent the fMRI signals by mesh networks formed among the anatomic regions for each task experiment at each subband. The mesh networks are constructed by ensembling a set of local meshes, each of which represents the relationship of an anatomical region as a weighted linear combination of its neighbors. Then, we estimate the edge weights of each mesh by ridge regression. The proposed approach yields 2CL functional mesh networks for each subject, where C is the number of cognitive tasks and L is the number of subband signals obtained after wavelet decomposition. This approach enables one to classify gender under different cognitive tasks and different frequency subbands. The final step of the suggested framework is to fuse the complementary information of the mesh networks for each subject to discriminate the gender. We fuse the information embedded in mesh networks formed for different tasks and resolutions under a three-level fuzzy stacked generalization (FSG) architecture. In this architecture, different layers are responsible for fusion of diverse information obtained from different cognitive tasks and resolutions. In the experimental analyses, we use Human Connectome Project task fMRI dataset. Results reflect that fusing the mesh network representations computed at multiple resolutions for multiple tasks provides the best gender classification accuracy compared to the single subband task mesh networks or fusion of representations obtained using only multitask or only multiresolution data. Besides, mesh edge weights slightly outperform pairwise correlations between regions, and significantly outperform raw fMRI signals. In addition, we analyze the gender discriminative power of mesh edge weights for different tasks and resolutions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, A., Thybusch, K., Pieritz, K., Hermann, C. (2014). Gender differences in creative thinking: behavioral and fMRI findings. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 8(1), 39–51.
Barch, D.M., Burgess, G.C., Harms, M.P., Petersen, S.E., Schlaggar, B.L., Corbetta, M., Glasser, M.F., Curtiss, S., Dixit, S., Feldt, C., Nolan, D., Bryant, E., Hartley, T., Footer, O., Bjork, J.M., Poldrack, R., Smith, S., Johansen-Berg, H., Snyder, A.Z., Essen, D.C.V. (2013). Function in the human connectome: task-fmri and individual differences in behavior. NeuroImage, 80, 169–189.
Baxter, L.C., Saykin, A.J., Flashman, L.A., Johnson, S.C., Guerin, S.J., Babcock, D., Wishart, H.A. (2003). Sex differences in semantic language processing: a functional mri study. Brain and Language, 84(2), 264–272.
Behroozi, M., & Daliri, M.R. (2014). Predicting brain states associated with object categories from fmri data. Journal of Integrative Neuroscience, 13(04), 645–667.
Binder, J.R., Gross, W.L., Allendorfer, J.B., Bonilha, L., Chapin, J., Edwards, J.C., Grabowski, T.J., Langfitt, J.T., Loring, D.W., Lowe, M.J., Koenig, K., Morgan, P.S., Ojemann, J.G., Rorden, C., Szaflarski, J.P., Tivarus, M.E., Weaver, K.E. (2011). Mapping anterior temporal lobe language areas with fmri: a multicenter normative study. NeuroImage, 54(2), 1465–1475.
Biswal, B.B., Mennes, M., Zuo, X.N., Gohel, S., Kelly, C., Smith, S.M., Beckmann, C.F., Adelstein, J.S., Buckner, R.L., Colcombe, S., et al. (2010). Toward discovery science of human brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107(10), 4734–4739.
Boghi, A., Rampado, O., Bergui, M., Avidano, F., Manzone, C., Coriasco, M., Mortara, P., Orsi, L., Ropolo, R., Bradac, G. (2006). Functional mr study of a motor task and the tower of london task at 1.0 t. Neuroradiology, 48(10), 763–771.
Buckner, R.L., Krienen, F.M., Castellanos, A., Diaz, J.C., Yeo, B.T.T. (2011). The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. Journal of Neurophysiology, 106(5), 2322–2345.
Bullmore, E., Fadili, J., Maxim, V., Şendur, L, Whitcher, B., Suckling, J., Brammer, M., Breakspear, M. (2004). Wavelets and functional magnetic resonance imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage, 23, Supplement 1, S234–S249.
Butler, T., Imperato-McGinley, J., Pan, H., Voyer, D., Cunningham-Bussel, A.C., Chang, L., Zhu, Y.S., Cordero, J.J., Stern, E., Silbersweig, D. (2007). Sex specificity of ventral anterior cingulate cortex suppression during a cognitive task. Human Brain Mapping, 28(11), 1206–1212.
Cahill, L. (2006). Why sex matters for neuroscience. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7(6), 477–484.
Castelli, F., Happé, F, Frith, U., Frith, C. (2000). Movement and mind: a functional imaging study of perception and interpretation of complex intentional movement patterns. NeuroImage, 12(3), 314–325.
Chyzhyk, D., & Graña, M. (2015). Classification of schizophrenia patients on lattice computing resting-state fmri features. Neurocomputing, 151, 151–160.
Daliri, M.R. (2012). Predicting the cognitive states of the subjects in functional magnetic resonance imaging signals using the combination of feature selection strategies. Brain Topography, 25(2), 129–135.
Delgado, M.R., Nystrom, L.E., Fissell, C., Noll, D.C., Fiez, J.A. (2000). Tracking the hemodynamic responses to reward and punishment in the striatum. Journal of Neurophysiology, 84(6), 3072–3077.
Dinov, I.D., Boscardin, J.W., Mega, M.S., Sowell, E.L., Toga, A.W. (2005). A wavelet-based statistical analysis of fmri data. Neuroinformatics, 3(4), 319–342.
Duarte-Carvajalino, J.M., Jahanshad, N., Lenglet, C., McMahon, K.L., de Zubicaray, G.I., Martin, N.G., Wright, M.J., Thompson, P.M., Sapiro, G. (2012). Hierarchical topological network analysis of anatomical human brain connectivity and differences related to sex and kinship. NeuroImage, 59(4), 3784–3804.
Feng, B., Yu, Z.L., Gu, Z., Li, Y. (2015). Analysis of fmri data based on sparsity of source components in signal dictionary. Neurocomputing, 156, 86–95.
Glasser, M.F., Sotiropoulos, S.N., Wilson, J.A., Coalson, T.S., Fischl, B., Andersson, J.L., Xu, J., Jbabdi, S., Webster, M., Polimeni, J.R., et al. (2013). The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the human connectome project. NeuroImage, 80, 105–124.
Gong, G., He, Y., Evans, A.C. (2011). Brain connectivity: gender makes a difference. The Neuroscientist, 17(5), 575–591.
Hariri, A.R., Tessitore, A., Mattay, V.S., Fera, F., Weinberger, D.R. (2002). The amygdala response to emotional stimuli: a comparison of faces and scenes. NeuroImage, 17(1), 317–323.
Hasson, U., Yang, E., Vallines, I., Heeger, D.J., Rubin, N. (2008). A hierarchy of temporal receptive windows in human cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(10), 2539–2550.
Haxby, J.V., Gobbini, M.I., Furey, M.L., Ishai, A., Schouten, J.L., Pietrini, P. (2001). Distributed and overlapping representations of faces and objects in ventral temporal cortex. Science, 293(5539), 2425–2429.
Hofer, A., Siedentopf, C.M., Ischebeck, A., Rettenbacher, M.A., Verius, M., Felber, S., Fleischhacker, W.W. (2007). Sex differences in brain activation patterns during processing of positively and negatively valenced emotional words. Psychological Medicine, 37(01), 109–119.
Kauppi, J.P., Jääskeläinen, I.P., Sams, M., Tohka, J. (2010). Inter-subject correlation of brain hemodynamic responses during watching a movie: localization in space and frequency. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics 4, 5.
Kauppi, J.P., Pajula, J., Tohka, J. (2014). A versatile software package for inter-subject correlation based analyses of fmri. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 8, 2.
Ktena, S.I., & Rueckert, D. (2016). A topological graph kernel for gender classification of functional brain networks. In OHBM.
Kulkarni, V., Pudipeddi, J.S., Akoglu, L., Vogelstein, J.T., Vogelstein, R.J., Ryman, S., Jung, R.E. (2013). Sex differences in the human connectome. In International conference on brain and health informatics (pp. 82–91): Springer.
Li, W., Li, Y., Hu, C., Chen, X., Dai, H. (2014). Point process analysis in brain networks of patients with diabetes. Neurocomputing, 145, 182–189.
Marchewka, A., Jednorog, K., Falkiewicz, M., Szeszkowski, W., Grabowska, A., Szatkowska, I. (2012). Sex, lies and fmri—gender differences in neural basis of deception. PloS one, 7(8), e43,076.
McNemar, Q. (1947). Note on the sampling error of the difference between correlated proportions or percentages. Psychometrika, 12(2), 153–157.
Onal, I., Ozay, M., Mizrak, E., Oztekin, I., Vural, F.T.Y. (2017). A new representation of fmri signal by a set of local meshes for brain decoding. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing over Networks, 3(4), 683–694.
Onal Ertugrul, I., Ozay, M., Yarman Vural, F.T. (2018a). Encoding the local connectivity patterns of fmri for cognitive task and state classification. Brain Imaging and Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9901-5.
Onal Ertugrul, I. , Ozay, M., Yarman Vural, F.T. (2018b). Hierarchical multi-resolution mesh networks for brain decoding. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 12(4), 1067–1083.
Ozay, M., & Yarman-Vural, F.T. (2016). Hierarchical distance learning by stacking nearest neighbor classifiers. Information Fusion, 29, 14–31.
Parhizi, B., Daliri, M.R., Behroozi, M. (2018). Decoding the different states of visual attention using functional and effective connectivity features in fmri data. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 12(2), 157–170.
Piefke, M., Weiss, P.H., Markowitsch, H.J., Fink, G.R. (2005). Gender differences in the functional neuroanatomy of emotional episodic autobiographical memory. Human Brain Mapping, 24(4), 313–324.
Richiardi, J., Eryilmaz, H., Schwartz, S., Vuilleumier, P., Ville, D.V.D. (2011). Decoding brain states from fmri connectivity graphs. NeuroImage, 56(2), 616–626.
Richiardi, J., Achard, S., Bunke, H., De Ville, D.V. (2013). Machine learning with brain graphs: predictive modeling approaches for functional imaging in systems neuroscience. IEEE Signal Process Mag.
Satterthwaite, T.D., Wolf, D.H., Roalf, D.R., Ruparel, K., Erus, G., Vandekar, S., Gennatas, E.D., Elliott, M.A., Smith, A., Hakonarson, H., et al. (2014). Linked sex differences in cognition and functional connectivity in youth. Cerebral cortex p bhu036.
Schmithorst, V.J., & Holland, S.K. (2006). Functional mri evidence for disparate developmental processes underlying intelligence in boys and girls. NeuroImage, 31(3), 1366–1379.
Schmithorst, V.J., & Holland, S.K. (2007). Sex differences in the development of neuroanatomical functional connectivity underlying intelligence found using bayesian connectivity analysis. NeuroImage, 35(1), 406–419.
Smith, R., Keramatian, K., Christoff, K. (2007). Localizing the rostrolateral prefrontal cortex at the individual level. NeuroImage, 36(4), 1387–1396.
Thompson, W.H., & Fransson, P. (2015). The frequency dimension of fmri dynamic connectivity: network connectivity, functional hubs and integration in the resting brain. NeuroImage, 121, 227–242.
Tian, L., Wang, J., Yan, C., He, Y. (2011). Hemisphere-and gender-related differences in small-world brain networks: a resting-state functional mri study. NeuroImage, 54(1), 191–202.
Van De Ville, D., Blu, T., Unser, M. (2006). Surfing the brain—an overview of wavelet-based techniques for fMRI data analysis. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 25(2), 65–78.
Vogelstein, J.T., Roncal, W.G., Vogelstein, R.J., Priebe, C.E. (2013). Graph classification using signal-subgraphs: applications in statistical connectomics. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(7), 1539–1551.
Wang, L., Shen, H., Tang, F., Zang, Y., Hu, D. (2012). Combined structural and resting-state functional mri analysis of sexual dimorphism in the young adult human brain: an mvpa approach. NeuroImage, 61 (4), 931–940.
Wheatley, T., Milleville, S.C., Martin, A. (2007). Understanding animate agents: distinct roles for the social network and mirror system. Psychological Science, 18(6), 469–474.
Wu, K., Taki, Y., Sato, K., Hashizume, H., Sassa, Y., Takeuchi, H., Thyreau, B., He, Y., Evans, A.C., Li, X., et al. (2013). Topological organization of functional brain networks in healthy children: differences in relation to age, sex, and intelligence. PloS one, 8(2), e55,347.
Xu, Z., & Chan, A.K. (2002). Encoding with frames in mri and analysis of the signal-to-noise ratio. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 21(4), 332–342.
Zhang, Q., & Lee, M. (2009). Analysis of positive and negative emotions in natural scene using brain activity and gist. Neurocomputing, 72(4), 1302–1306.
Acknowledgments
This work was completed when Itir Onal Ertugrul was with the Department of Computer Engineering, METU.
Funding
This work was supported by CREST, JST, Grant Number JPMJCR14D1, the ImPACT Program of the Council for Science, Technology, and Innovation (Cabinet Office, Government of Japan) and TUBITAK Project No 116E091. Itir Onal Ertugrul was supported by TUBITAK 2211E.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Itir Onal Ertugrul, Mete Ozay and Fatos Yarman Vural declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Data used in this study were previously collected.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onal Ertugrul, I., Ozay, M. & Yarman Vural, F.T. Gender classification using mesh networks on multiresolution multitask fMRI data. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 460–476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-0021-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-0021-z