Abstract
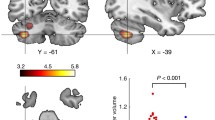
Complex tasks require the learning and integration of multiple cognitive, sensory, and psychomotor skills for correct execution. Driving-related skills are developed step by step through the increase of mileage driven and the accumulation of practice in different traffic situations. The acquisition of these skills should be reflected in the brain structure. However, no previous studies have explored brain structural variations associated with driving experience. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether driving frequency, defined as average annual driving mileage, is related to neuroanatomical variations in gray matter (GM) volume and white matter (WM) integrity using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and DTI-based fractional anisotropy (FA), respectively. We recruited 83 drivers with variable range of annual driving mileage and controlled for age, sex, handedness, IQ, time since the acquisition of driving license, use of motorcycles/mopeds and bicycles, perceived driving skills, and subjective probability of having an accident. Our results showed variations in white matter FA as a function of mileage driven. Driving experience was related to a significant increase of FA in parts of the right hemisphere superior and inferior longitudinal fasciculus, anterior thalamic radiation, forceps majors, inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, and corticospinal tract. No significant differences were observed in gray matter volumes. FA variations were found in brain regions that have been associated with cognitive, visual, and motor processes necessary for skilled performance in driving. These results suggest that variations in white matter diffusivity can underlie the development of driving skills and safer driving.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almairac, F., Herbet, G., Moritz-Gasser, S., de Champfleur, N. M., & Duffau, H. (2015). The left inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus subserves language semantics: A multilevel lesion study. Brain Structure and Function, 220(4), 1983–1995.
Ashburner, J. (2010). VBM tutorial. Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging. London: UK.
Ashburner, J., Barnes, G., Chen, C., Daunizeau, J., Flandin, G., Friston, K., Kiebel, S., Kilner, J., Litvak, V., Moran, R., Penny, W., Stephan, K., Gitelman, D., Henson, R., Hutton, C., Glauche, V., Mattout, H., & Phillips, C. (2012). SPM8 manual. Institute of Neurology, London: Functional Imaging Laboratory.
Beaulieu, C. (2002). The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15, 435–455.
Bengtsson, S. L., Nagy, Z., Skare, S., Forsman, L., Forssberg, H., & Ullén, F. (2005). Extensive piano practicing has regionally specific effects on white matter development. Nature Neuroscience, 8(9), 1148–1150.
Bernardi, G., Cecchetti, L., Handjaras, G., Sani, L., Gaglianese, A., Ceccarelli, R., et al. (2014). It's not all in your car: Functional and structural correlates of exceptional driving skills in professional racers. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 888.
Bjørnskau, T., & Sagberg, F. (2005). What do novice drivers learn during the first months of driving? Improved handling skills or improved road user interaction? In G. Underwood (Ed.), Traffic and transport psychology: Theory and application (pp. 129–140). Oxford: Elsevier.
Blumenfeld-Katzir, T., Pasternak, O., Dagan, M., & Assaf, Y. (2011). Diffusion MRI of structural brain plasticity induced by a learning and memory task. PloS One, 6(6), e20678.
Catani, M., & De Schotten, M. T. (2008). A diffusion tensor imaging tractography atlas for virtual in vivo dissections. Cortex, 44(8), 1105–1132.
Catani, M., Howard, R. J., Pajevic, S., & Jones, D. K. (2002). Virtual in vivo interactive dissection of white matter fasciculi in the human brain. NeuroImage, 17(1), 77–94.
Cavallo, V., Brun-Dei, M., Laya, O., & Neboit, M. (1988). Perception and anticipation in negotiating curves: The role of driving experience. In A. G. Gale, M. H. Freeman, C. M. Haslegrave, P. Smith, & S. P. Taylor (Eds.), Vision in vehicles II (pp. 365–374). North-Holland: Elsevier.
Caverzasi, E., Papinutto, N., Amirbekian, B., Berger, M. S., & Henry, R. G. (2014). Q-ball of inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and beyond. PloS One, 9(6), e100274.
Ceci, S. J. (1991). How much does schooling influence general intelligence and its cognitive components? A reassessment of the evidence. Developmental Psychology, 27(5), 703.
Cooper, P. J., Pinili, M., & Chen, W. (1995). An examination of the crash involvement rates of novice drivers aged 16 to 55. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 27(1), 89–104.
Crinson, L. F., & Grayson, G. B. (2005). Profile of the British learner driver. In G. Underwood (Ed.), Traffic and transport psychology: Theory and application (pp. 157–170). Oxford: Elsevier.
Crundall, D., & Underwood, G. (1998). Effects of experience and processing demands on visual information acquisition in drivers. Ergonomics, 41, 448–458.
Dayan, E., & Cohen, L. G. (2011). Neuroplasticity subserving motor skill learning. Neuron, 72(3), 443–454.
Deery, H., Kowadlo, N., Westphal-Wedding, T., & Fildes, B. (1998). Identifying subtypes of young novice drivers: Implications for matching training to the needs of the driver, Report no. 142. Accident Research Center, Australia: Monash University.
DeJoy, D. M. (1989). The optimism bias and traffic accident risk perception. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 21(4), 333–340.
Di Stasi, L. L., Contreras, D., Cándido, A., Cañas, J. J., & Catena, A. (2011). Behavioral and eye-movement measures to track improvements in driving skills of vulnerable road users: First-time motorcycle riders. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 14, 26–35.
Engel, A., Hijmans, B. S., Cerliani, L., Bangert, M., Nanetti, L., Keller, P. E., & Keysers, C. (2014). Inter-individual differences in audio-motor learning of piano melodies and white matter fiber tract architecture. Human Brain Mapping, 35(5), 2483–2497.
Ferreira, D., Molina, Y., Machado, A., Westman, E., Wahlund, L. O., Nieto, A., et al. (2014). Cognitive decline is mediated by gray matter changes during middle age. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(5), 1086–1094.
Fields, R. D. (2010). Change in the brain’s white matter: The role of the brain’s white matter in active learning and memory may be underestimated. Science, 330(6005), 768.
Fjell, A. M., Westlye, L. T., Amlien, I. K., & Walhovd, K. B. (2012). A multi-modal investigation of behavioral adjustment: Post-error slowing is associated with white matter characteristics. NeuroImage, 61(1), 195–205.
Forsyth, E., Maycock, G., & Sexton, B. (1995). Cohort study of learner and novice drivers: Part 3, accidents, offences and driving experience in the first three years of driving, TRL report PR 111. Crowthorne: Department of Transport. Transport Research Laboratory.
Gregersen, N. P., Berg, H. Y., Engström, I., Nolén, S., Nyberg, A., & Rimmö, P. A. (2000). Sixteen years age limit for learner drivers in Sweden-an evaluation of safety effects. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 32(1), 25–35.
Harik, L. M. (2015). The impact of pediatric traumatic brain injury on written expression: a diffusion tensor imaging study utilizing tract-based spatial statistics (doctoral dissertation). University of Houston.
Hofstetter, S., Tavor, I., Moryosef, S. T., & Assaf, Y. (2013). Short-term learning induces white matter plasticity in the fornix. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(31), 12844–12850.
Hong, Y. H., Lim, T. S., Yong, S. W., & Moon, S. Y. (2010). Ipsilateral visual illusion after unilateral posterior cerebral artery infarction: A report of two cases. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 295(1), 114–116.
Huang, P., & Winston, F. K. (2011). Young Drivers. In B. E. Porter (Ed.), Handbook of traffic psychology. London: Academic Press.
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S. M. (2012). Fsl. Neuroimage, 62(2), 782–790.
Jones, D. K., Knösche, T. R., & Turner, R. (2013). White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: The do's and don'ts of diffusion MRI. NeuroImage, 73, 239–254.
Kan, K., Schweizer, T. A., Tam, F., & Graham, S. J. (2013). Methodology for functional MRI of simulated driving. Medical Physics, 40(1), 012301.
Karni, A., Meyer, G., Rey-Hipolito, C., Jezzard, P., Adams, M. M., Turner, R., & Ungerleider, L. G. (1998). The acquisition of skilled motor performance: Fast and slow experience-driven changes in primary motor cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 95(3), 861–868.
Klauer, S. G., Guo, F., Simons-Morton, B. G., Ouimet, M. C., Lee, S. E., & Dingus, T. A. (2014). Distracted driving and risk of road crashes among novice and experienced drivers. New England Journal of Medicine, 370(1), 54–59.
Kwon, M. S., Vorobyev, V., Moe, D., Parkkola, R., & Hämäläinen, H. (2014). Brain structural correlates of risk-taking behavior and effects of peer influence in adolescents. PloS One, 9, e112780.
Lajunen, T., & Summala, H. (1995). Driving experience, personality, and skill and safety-motive dimensions in drivers' self-assessments. Personality and Individual Differences, 19(3), 307–318.
Langford, J., Koppel, S., McCarthy, D., & Srinivasan, S. (2008). In defence of the ‘low-mileage bias’. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 40(6), 1996–1999.
Langford, J., Methorst, R., & Hakamies-Blomqvist, L. (2006). Older drivers do not have a high crash risk-a replication of low mileage bias. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 38(3), 574–578.
Lappi, O. (2015). The racer’s brain–how domain expertise is reflected in the neural substrates of driving. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 635.
Lehtonen, E., Lappi, O., Koirikivi, I., & Summala, H. (2014). Effect of driving experience on anticipatory look-ahead fixations in real curve driving. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 70, 195–208.
Maguire, E. A., Woollett, K., & Spiers, H. J. (2006). London taxi drivers and bus drivers: A structural MRI and neuropsychological analysis. Hippocampus, 16(12), 1091–1101.
Makris, N., Kennedy, D. N., McInerney, S., Sorensen, A. G., Wang, R., Caviness, V. S., & Pandya, D. N. (2005). Segmentation of subcomponents within the superior longitudinal fascicle in humans: A quantitative, in vivo, DT-MRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 15(6), 854–869.
Mamah, D., Conturo, T. E., Harms, M. P., Akbudak, E., Wang, L., McMichael, A. R., et al. (2010). Anterior thalamic radiation integrity in schizophrenia: A diffusion-tensor imaging study. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 183(2), 144–150.
Martino, J., Brogna, C., Robles, S. G., Vergani, F., & Duffau, H. (2010). Anatomic dissection of the inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus revisited in the lights of brain stimulation data. Cortex, 46(5), 691–699.
Maycock, G., Lockwood, C. R., & Lester, J. F. (1991). The accident liability of car drivers, TRL research report 315. Transport Research Laboratory, Crowthorne: Department of Transport.
McKnight, A. J., & McKnight, A. S. (2003). Young novice drivers: Careless or clueless? Accident Analysis & Prevention, 35(6), 921e925.
Megías, A., Maldonado, A., Catena, A., Di Stasi, L. L., Serrano, J., & Cándido, A. (2011). Modulation of attention and urgent decisions by affect-laden roadside advertisement in risky driving scenarios. Safety Science, 49(10), 1388–1393.
Megías, A., Navas, J. F., Petrova, D., Cándido, A., Maldonado, A., Garcia-Retamero, R., & Catena, A. (2015). Neural mechanisms underlying urgent and evaluative behaviors: An fMRI study on the interaction of automatic and controlled processes. Human Brain Mapping, 36(8), 2853–2864.
Moffat, S. D., Kennedy, K. M., Rodrigue, K. M., & Raz, N. (2007). Extrahippocampal contributions to age differences in human spatial navigation. Cerebral Cortex, 17(6), 1274–1282.
Mori, S., Kaufmann, W. E., Davatzikos, C., Stieltjes, B., Amodei, L., Fredericksen, K., et al. (2002). Imaging cortical association tracts in the human brain using diffusion-tensor-based axonal tracking. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 47(2), 215–223.
Owsley, C., & McGwin, G. (2010). Vision and driving. Vision Research, 50(23), 2348–2361.
Power, C., Frank, J., Hertzman, C., Schierhout, G., & Li, L. (2001). Predictors of low back pain onset in a prospective British study. American Journal of Public Health, 91(10), 1671–1678.
Ridgway, G. (2007). Get_totals.M. [computer software]. Retrieved April 19, 2016, from http://www.cs.ucl.ac.uk/staff/G.Ridgway/vbm/.
Sagberg, F., & Bjørnskau, T. (2006). Hazard perception and driving experience among novice drivers. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 38(2), 407–414.
Sagi, Y., Tavor, I., Hofstetter, S., Tzur-Moryosef, S., Blumenfeld-Katzir, T., & Assaf, Y. (2012). Learning in the fast lane: New insights into neuroplasticity. Neuron, 73(6), 1195–1203.
Sampaio-Baptista, C., Khrapitchev, A. A., Foxley, S., Schlagheck, T., Scholz, J., Jbabdi, S., et al. (2013). Motor skill learning induces changes in white matter microstructure and myelination. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(50), 19499–19503.
Schoenen, J., & Grant, G. (2004). Spinal cord: Connections (pp. 233–249). Amsterdam: The human nervous system. Elsevier Academic Press.
Scholz, J., Klein, M. C., Behrens, T. E., & Johansen-Berg, H. (2009). Training induces changes in white-matter architecture. Nature Neuroscience, 12(11), 1370–1371.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E., et al. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31(4), 1487–1505.
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23, S208–S219.
Spiers, H. J., & Maguire, E. A. (2007). Neural substrates of driving behaviour. NeuroImage, 36(1), 245–255.
Summala, H., Lamble, D., & Laakso, M. (1998). Driving experience and perception of the lead car's braking when looking at in-car targets. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 30(4), 401–407.
Tang, Y. Y., Lu, Q., Fan, M., Yang, Y., & Posner, M. I. (2012). Mechanisms of white matter changes induced by meditation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(26), 10570–10574.
Taylor, D. H. (1964). Drivers' galvanic skin response and the risk of accident. Ergonomics, 7(4), 439–451.
Wang, L., Liu, Q., Shen, H., Li, H., & Hu, D. (2015). Large-scale functional brain network changes in taxi drivers: Evidence from resting-state fMRI. Human Brain Mapping, 36(3), 862–871.
Wechsler, D. (1997). WAIS-III: Wechsler adult intelligence scale. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
Wikman, A. S., Nieminen, T., & Summala, H. (1998). Driving experience and time-sharing during in-car tasks on roads of different width. Ergonomics, 41(3), 358–372.
Winter, J. D., Stanton, N. A., Price, J. S., & Mistry, H. (2016). The effects of driving with different levels of unreliable automation on self-reported workload and secondary task performance. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 70(4), 297–324.
World Medical Association. (2008). Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Ferney-Voltaire: World Medical Association.
Zhao, G., & Wu, C. (2012). The effects of driver identity on driving safety in a retrospective feedback system. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 45, 354–365.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Spanish MICINN PSI2016-80558-R and PSI2012-39292 grant to A. Catena, and Spanish General Directorate of Traffic (DGT) SPIP2014-01341 grant to A.Cándido. Dafina Petrova is supported by Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (PSI2014-51842-R). Alberto Megías is supported by Juan de la Cierva postdoctoral fellowship from the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alberto Megías declares that he has no conflict of interest. Dafina Petrova declares that she has no conflict of interest. Juan Francisco Navas declares that he has no conflict of interest. Antonio Cándido declares that he has no conflict of interest. Antonio Maldonado declares that he has no conflict of interest. Andrés Catena declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Megías, A., Petrova, D., Navas, J.F. et al. Neuroanatomical variations as a function of experience in a complex daily task: A VBM and DTI study on driving experience. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 653–662 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9725-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9725-8