Abstract
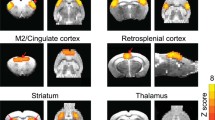
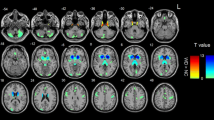
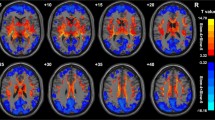
The fractional Amplitude of Low Frequency Fluctuations (fALFF) and the degree of local synchronization (Regional Homogeneity – ReHo) of resting-state BOLD signal have been suggested to map spontaneous neuronal activity and local functional connectivity, respectively. We compared voxelwise, independent of atrophy, the fALFF and ReHo patterns of 11 presymptomatic (ps-HD) and 28 symptomatic (sHD) Huntington’s disease mutation carriers, with those of 40 normal volunteers, and tested their possible correlations with the motor and cognitive subscores of the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale. In sHD patients, fALFF was mainly reduced bilaterally in parietal lobes (right precuneus being already affected in psHD), and in superior frontal gyri, and increased bilaterally in cerebellar lobules VI, VIII and IX, as well as in the right inferior temporal gyrus. In sHD, and to a lesser extent in psHD, ReHo was bilaterally reduced in putamina, cerebellar lobules III to VI, and superior medial frontal gyri, and increased in both psHD and sHD in fronto-basal cortices, and in the right temporal lobe. fALFF correlated inversely with cognitive scores in lobule IX of the cerebellum (mainly with total Stroop score, p < 0.0001), and in the medial portions of both thalami. These results are consistent with a reduced neuronal activity in the cortical components of the executive networks, known to be affected in Huntington’s Disease, and with reduced local functional integration in subcortical and cerebellar components of the sensori-motor network. Cerebellar clusters of significant correlation of fALFF with executive function scores may be related to compensatory mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolphs, R. (2002). Neural systems for recognizing emotion. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 12(2), 169–177.
Aiello, M., Salvatore, E., Cachia, A., Pappata, S., Cavaliere, C., Prinster, A., et al. (2015). Relationship between simultaneously acquired resting-state regional cerebral glucose metabolism and functional MRI: a PET/MR hybrid scanner study. NeuroImage, 113, 111–121.
Allen, P. A., Houston, J. R., Pollock, J. W., Buzzelli, C., Li, X., Harrington, A. K., et al. (2014). Task-specific and general cognitive effects in Chiari malformation type I. PloS One, 9(4), e94844.
Alonso Bde, C., Hidalgo Tobon, S., Dies Suarez, P., Garcia Flores, J., de Celis Carrillo, B., & Barragan Perez, E. (2014). A multi-methodological MR resting state network analysis to assess the changes in brain physiology of children with ADHD. PloS One, 9(6), e99119.
An, L., Cao, Q. J., Sui, M. Q., Sun, L., Zou, Q. H., Zang, Y. F., et al. (2013). Local synchronization and amplitude of the fluctuation of spontaneous brain activity in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state fMRI study. Neuroscience Bulletin, 29(5), 603–613.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. NeuroImage, 26(3), 839–851.
Ashburner, J., Neelin, P., Collins, D. L., Evans, A., & Friston, K. (1997). Incorporating prior knowledge into image registration. NeuroImage, 6(4), 344–352.
Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Woolrich, M. W., Smith, S. M., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., Boulby, P. A., et al. (2003). Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nature Neuroscience, 6(7), 750–757.
Benton, A. L., & Hamsher, K. (1989). Multilingual Aphasia Examination (2nd ed.): AJA Associates, Iowa City.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34(4), 537–541.
Bodranghien, F., Bastian, A., Casali, C., Hallett, M., Louis, E. D., Manto, M., et al. (2016). Consensus paper: revisiting the symptoms and signs of cerebellar syndrome. Cerebellum, 15(3), 369–391.
Borroni, B., Premi, E., Formenti, A., Turrone, R., Alberici, A., Cottini, E., et al. (2015). Structural and functional imaging study in dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 21(9), 1049–1055.
Bosch-Bouju, C., Hyland, B. I., & Parr-Brownlie, L. C. (2013). Motor thalamus integration of cortical, cerebellar and basal ganglia information: implications for normal and parkinsonian conditions. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 7, 163.
Casanova, R., Srikanth, R., Baer, A., Laurienti, P. J., Burdette, J. H., Hayasaka, S., et al. (2007). Biological parametric mapping: a statistical toolbox for multimodality brain image analysis. NeuroImage, 34(1), 137–143.
Chao-Gan, Y., & Yu-Feng, Z. (2010). DPARSF: a matlab toolbox for “pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 13.
Cheng, W., Ji, X., Zhang, J., & Feng, J. (2012). Individual classification of ADHD patients by integrating multiscale neuroimaging markers and advanced pattern recognition techniques. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 6, 58.
Dogan, I., Eickhoff, C. R., Fox, P. T., Laird, A. R., Schulz, J. B., Eickhoff, S. B., et al. (2015). Functional connectivity modeling of consistent cortico-striatal degeneration in Huntington’s disease. NeuroImage: Clinical, 7, 640–652.
Dumas, E. M., van den Bogaard, S. J., Hart, E. P., Soeter, R. P., van Buchem, M. A., van der Grond, J., et al. (2013). Reduced functional brain connectivity prior to and after disease onset in Huntington’s disease. NeuroImage: Clinical, 2, 377–384.
Friston, K. J., Ashburner, J., Frith, C. D., Poline, J. B., Heather, J. D., & Frackowiak, R. S. J. (1995). Spatial registration and normalization of images. Human Brain Mapping, 3(3), 165–189.
Fryer, S. L., Roach, B. J., Ford, J. M., Turner, J. A., van Erp, T. G., Voyvodic, J., et al. (2015). Relating intrinsic low-frequency BOLD cortical oscillations to cognition in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology, 40(12), 2705–2714.
Gao, B., Wang, Y., Liu, W., Chen, Z., Zhou, H., Yang, J., et al. (2015). Spontaneous activity associated with delusions of schizophrenia in the left medial superior frontal gyrus: a resting-state fMRI study. PloS One, 10(7), e0133766.
Goldman, R. I., Stern, J. M., Engel Jr., J., & Cohen, M. S. (2002). Simultaneous EEG and fMRI of the alpha rhythm. Neuroreport, 13(18), 2487–2492.
Haag, L. M., Heba, S., Lenz, M., Glaubitz, B., Hoffken, O., Kalisch, T., et al. (2015). Resting BOLD fluctuations in the primary somatosensory cortex correlate with tactile acuity. Cortex, 64, 20–28.
Habas, C., Kamdar, N., Nguyen, D., Prater, K., Beckmann, C. F., Menon, V., et al. (2009). Distinct cerebellar contributions to intrinsic connectivity networks. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(26), 8586–8594.
Harrington, D. L., Rubinov, M., Durgerian, S., Mourany, L., Reece, C., Koenig, K., et al. (2015). Network topology and functional connectivity disturbances precede the onset of Huntington’s disease. Brain, 138(Pt 8), 2332–2346.
Hoptman, M. J., Zuo, X. N., Butler, P. D., Javitt, D. C., D’Angelo, D., Mauro, C. J., et al. (2010). Amplitude of low-frequency oscillations in schizophrenia: a resting state fMRI study. Schizophrenia Research, 117(1), 13–20.
Huntington Study Group (1996). Unified Huntington’s disease rating scale: reliability and consistency. Huntington study group. Movement Disorders, 11(2), 136–142.
Iwabuchi, S. J., Krishnadas, R., Li, C., Auer, D. P., Radua, J., & Palaniyappan, L. (2015). Localized connectivity in depression: a meta-analysis of resting state functional imaging studies. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 51, 77–86.
Jiang, L., Xu, T., He, Y., Hou, X. H., Wang, J., Cao, X. Y., et al. (2015). Toward neurobiological characterization of functional homogeneity in the human cortex: regional variation, morphological association and functional covariance network organization. Brain Structure & Function, 220(5), 2485–2507.
Kendall, M. G., & Gibbons, J. D. (1990). Rank correlation methods (5th ed.). London, UK: Edward Arnold.
Kloppel, S., Stonnington, C. M., Petrovic, P., Mobbs, D., Tuscher, O., Craufurd, D., et al. (2010). Irritability in pre-clinical Huntington’s disease. Neuropsychologia, 48(2), 549–557.
Koenig, K. A., Lowe, M. J., Harrington, D. L., Lin, J., Durgerian, S., Mourany, L., et al. (2014). Functional connectivity of primary motor cortex is dependent on genetic burden in prodromal Huntington disease. Brain Connectivity, 4(7), 535–546.
Koziol, L. F., Budding, D., Andreasen, N., D’Arrigo, S., Bulgheroni, S., Imamizu, H., et al. (2014). Consensus paper: the cerebellum’s role in movement and cognition. Cerebellum, 13(1), 151–177.
Kucyi, A., Hove, M. J., Biederman, J., Van Dijk, K. R., & Valera, E. M. (2015). Disrupted functional connectivity of cerebellar default network areas in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Human Brain Mapping, 36(9), 3373–3386.
Li, Z., Kadivar, A., Pluta, J., Dunlop, J., & Wang, Z. (2012a). Test-retest stability analysis of resting brain activity revealed by blood oxygen level-dependent functional MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 36(2), 344–354.
Li, Z., Zhu, Y., Childress, A. R., Detre, J. A., & Wang, Z. (2012b). Relations between BOLD fMRI-derived resting brain activity and cerebral blood flow. PloS One, 7(9), e44556.
Liu, H., Liu, Z., Liang, M., Hao, Y., Tan, L., Kuang, F., et al. (2006). Decreased regional homogeneity in schizophrenia: a resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroreport, 17(1), 19–22.
Liu, Y., Wang, K., Yu, C., He, Y., Zhou, Y., Liang, M., et al. (2008). Regional homogeneity, functional connectivity and imaging markers of Alzheimer’s disease: a review of resting-state fMRI studies. Neuropsychologia, 46(6), 1648–1656.
Logothetis, N. K., Pauls, J., Augath, M., Trinath, T., & Oeltermann, A. (2001). Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal. Nature, 412(6843), 150–157.
Lu, H., Zuo, Y., Gu, H., Waltz, J. A., Zhan, W., Scholl, C. A., et al. (2007). Synchronized delta oscillations correlate with the resting-state functional MRI signal. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(46), 18265.
Lui, S., Huang, X., Chen, L., Tang, H., Zhang, T., Li, X., et al. (2009). High-field MRI reveals an acute impact on brain function in survivors of the magnitude 8.0 earthquake in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(36), 15412–15417.
Mantini, D., Perrucci, M. G., Del Gratta, C., Romani, G. L., & Corbetta, M. (2007). Electrophysiological signatures of resting state networks in the human brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(32), 13170–13175.
Masterton, R. A., Carney, P. W., & Jackson, G. D. (2012). Cortical and thalamic resting-state functional connectivity is altered in childhood absence epilepsy. Epilepsy Research, 99(3), 327–334.
McGill, M. L., Devinsky, O., Wang, X., Quinn, B. T., Pardoe, H., Carlson, C., et al. (2014). Functional neuroimaging abnormalities in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. NeuroImage: Clinical, 6, 455–462.
Moosmann, M., Ritter, P., Krastel, I., Brink, A., Thees, S., Blankenburg, F., et al. (2003). Correlates of alpha rhythm in functional magnetic resonance imaging and near infrared spectroscopy. NeuroImage, 20(1), 145–158.
Novak, M. J., Warren, J. D., Henley, S. M., Draganski, B., Frackowiak, R. S., & Tabrizi, S. J. (2012). Altered brain mechanisms of emotion processing in pre-manifest Huntington’s disease. Brain, 135(Pt 4), 1165–1179.
Odish, O. F., Leemans, A., Reijntjes, R. H., van den Bogaard, S. J., Dumas, E. M., Wolterbeek, R., et al. (2015a). Microstructural brain abnormalities in Huntington’s disease: a two-year follow-up. Human Brain Mapping, 36(6), 2061–2074.
Odish, O. F., van den Berg-Huysmans, A. A., van den Bogaard, S. J., Dumas, E. M., Hart, E. P., Rombouts, S. A., et al. (2015b). Longitudinal resting state fMRI analysis in healthy controls and premanifest Huntington’s disease gene carriers: a three-year follow-up study. Human Brain Mapping, 36(1), 110–119.
Pelled, G., & Goelman, G. (2004). Different physiological MRI noise between cortical layers. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 52(4), 913–916.
Poudel, G. R., Egan, G. F., Churchyard, A., Chua, P., Stout, J. C., & Georgiou-Karistianis, N. (2014). Abnormal synchrony of resting state networks in premanifest and symptomatic Huntington disease: the IMAGE-HD study. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 39(2), 87–96.
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2142–2154.
Quarantelli, M., Salvatore, E., Giorgio, S. M., Filla, A., Cervo, A., Russo, C. V., et al. (2013). Default-mode network changes in Huntington’s disease: an integrated MRI study of functional connectivity and morphometry. PloS One, 8(8), e72159.
Rees, E. M., Farmer, R., Cole, J. H., Haider, S., Durr, A., Landwehrmeyer, B., et al. (2014). Cerebellar abnormalities in Huntington’s disease: a role in motor and psychiatric impairment? Movement Disorders, 29(13), 1648–1654.
Rub, U., Hoche, F., Brunt, E. R., Heinsen, H., Seidel, K., Del Turco, D., et al. (2013). Degeneration of the cerebellum in Huntington’s disease (HD): possible relevance for the clinical picture and potential gateway to pathological mechanisms of the disease process. Brain Pathology, 23(2), 165–177.
Sang, L., Qin, W., Liu, Y., Han, W., Zhang, Y., Jiang, T., et al. (2012). Resting-state functional connectivity of the vermal and hemispheric subregions of the cerebellum with both the cerebral cortical networks and subcortical structures. NeuroImage, 61(4), 1213–1225.
Schroeder, C. E., Lakatos, P., Kajikawa, Y., Partan, S., & Puce, A. (2008). Neuronal oscillations and visual amplification of speech. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 12(3), 106–113.
Sommer, M. A. (2003). The role of the thalamus in motor control. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 13(6), 663–670.
Sui, J., Pearlson, G. D., Du, Y., Yu, Q., Jones, T. R., Chen, J., et al. (2015). In search of multimodal neuroimaging biomarkers of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 78(11), 794–804.
Takeuchi, H., Taki, Y., Nouchi, R., Sekiguchi, A., Hashizume, H., Sassa, Y., et al. (2015). Degree centrality and fractional amplitude of low-frequency oscillations associated with Stroop interference. NeuroImage, 119, 197–209.
Treisman, A., & Fearnley, S. (1969). The Stroop test: selective attention to colours and words. Nature, 222(5192), 437–439.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15(1), 273–289.
Van Dijk, K. R., Sabuncu, M. R., & Buckner, R. L. (2012). The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. NeuroImage, 59(1), 431–438.
Walker, F. O. (2007). Huntington’s disease. Lancet, 369(9557), 218–228.
Wang, X., Jiao, Y., Tang, T., Wang, H., & Lu, Z. (2013). Altered regional homogeneity patterns in adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. European Journal of Radiology, 82(9), 1552–1557.
Wechsler, D. (1981). Manual for the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale - Revised. New York: Psychological Corporation.
Werner, C. J., Dogan, I., Sass, C., Mirzazade, S., Schiefer, J., Shah, N. J., et al. (2014). Altered resting-state connectivity in Huntington’s disease. Human Brain Mapping, 35(6), 2582–2593.
Wolf, R. C., Sambataro, F., Vasic, N., Depping, M. S., Thomann, P. A., Landwehrmeyer, G. B., et al. (2014). Abnormal resting-state connectivity of motor and cognitive networks in early manifest Huntington’s disease. Psychological Medicine, 44(15), 3341–3356.
Wu, T., Zang, Y., Wang, L., Long, X., Li, K., & Chan, P. (2007). Normal aging decreases regional homogeneity of the motor areas in the resting state. Neuroscience Letters, 423(3), 189–193.
Wu, T., Long, X., Zang, Y., Wang, L., Hallett, M., Li, K., et al. (2009). Regional homogeneity changes in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Human Brain Mapping, 30(5), 1502–1510.
Yan, C. G., Cheung, B., Kelly, C., Colcombe, S., Craddock, R. C., Di Martino, A., et al. (2013). A comprehensive assessment of regional variation in the impact of head micromovements on functional connectomics. NeuroImage, 76, 183–201.
Yang, T., Fang, Z., Ren, J., Xiao, F., Li, Q., Liu, L., et al. (2014). Altered spontaneous activity in treatment-naive childhood absence epilepsy revealed by regional homogeneity. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 340(1–2), 58–62.
Yu, R., Chien, Y. L., Wang, H. L., Liu, C. M., Liu, C. C., Hwang, T. J., et al. (2014). Frequency-specific alternations in the amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations in schizophrenia. Human Brain Mapping, 35(2), 627–637.
Zang, Y., Jiang, T., Lu, Y., He, Y., & Tian, L. (2004). Regional homogeneity approach to fMRI data analysis. NeuroImage, 22(1), 394–400.
Zeng, H., Ramos, C. G., Nair, V. A., Hu, Y., Liao, J., La, C., et al. (2015). Regional homogeneity (ReHo) changes in new onset versus chronic benign epilepsy of childhood with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): a resting state fMRI study. Epilepsy Research, 116, 79–85.
Zhong, Y., Zhang, R., Li, K., Qi, R., Zhang, Z., Huang, Q., et al. (2015). Altered cortical and subcortical local coherence in PTSD: evidence from resting-state fMRI. Acta Radiologica, 56(6), 746–753.
Zou, Q. H., Zhu, C. Z., Yang, Y., Zuo, X. N., Long, X. Y., Cao, Q. J., et al. (2008). An improved approach to detection of amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) for resting-state fMRI: fractional ALFF. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 172(1), 137–141.
Zuo, X. N., Xu, T., Jiang, L., Yang, Z., Cao, X. Y., He, Y., et al. (2013). Toward reliable characterization of functional homogeneity in the human brain: preprocessing, scan duration, imaging resolution and computational space. NeuroImage, 65, 374–386.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a grant from the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research, project PRIN 2010-2011 20108WT59Y_007 to G.D.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The study was supported by a grant from the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research, project PRIN 2010–2011 20108WT59Y_007 to G.D.M.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarappa, C., Salvatore, E., Filla, A. et al. Functional MRI signal fluctuations highlight altered resting brain activity in Huntington’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1459–1469 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9630-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9630-6