Abstract
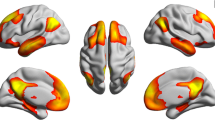
The neural mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome(IBS) are far from being completely understood. The purpose of the present study was to investigate potential white matter (WM) microstructural changes and underlying causes for WM impairment in IBS using diffusion tensor imaging. The present prospective study involved 19 patients with IBS and 20 healthy controls. Whole-brain voxel-wise analyses of fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD), and radial diffusivity (RD) were performed by tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) to localize abnormal WM regions between the 2 groups. We found that IBS patients had significantly reduced FA (P < 0.05) in the splenium of the corpus callosum, the right retrolenticular area of the internal capsule and the right superior corona radiata. We also found increased MD (P < 0.05) in the splenium and body of the corpus callosum, the right retrolenticular area of the internal capsule, the right superior corona radiata and the right posterior limb of the internal capsule. In addition, IBS patients had significantly increased AD (P < 0.05) in the splenium of the corpus callosum, the bilateral retrolenticular area of the internal capsule and the left posterior limb of the internal capsule. We conclude that the WM microstructure is changed in IBS and the underlying pathological basis may be attributed to the axonal injury and loss. These results may lead to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of IBS.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IBS:
-
irritable bowel syndrome
- TBSS:
-
tract-based spatial statistics
- DTI:
-
diffusion tensor imaging
- WM:
-
white matter
- FA:
-
fractional anisotropy
- MD:
-
mean diffusivity
- AD:
-
axial diffusivity
- RD:
-
radial diffusivity
References
Basser, P. J., Mattiello, J., & LeBihan, D. (1994). MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophysical Journal, 66(1), 259–267. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80775-1
Berman, S. M., Naliboff, B. D., Suyenobu, B., Labus, J. S., Stains, J., Ohning, G., & Mayer, E. A. (2008). Reduced brainstem inhibition during anticipated pelvic visceral pain correlates with enhanced brain response to the visceral stimulus in women with irritable bowel syndrome. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(2), 349–359. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2500-07.2008.
Blankstein, U., Chen, J., Diamant, N. E., & Davis, K. D. (2010). Altered brain structure in irritable bowel syndrome: potential contributions of pre-existing and disease-driven factors. Gastroenterology, 138(5), 1783–1789. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.043.
Breslau, N., Merikangas, K., & Bowden, C. L. (1994). Comorbidity of migraine and major affective disorders. Neurology, 44(10 Suppl 7), S17–22. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7969941
Caminiti, R., Carducci, F., Piervincenzi, C., Battaglia-Mayer, A., Confalone, G., Visco-Comandini, F., & Innocenti, G. M. (2013). Diameter, length, speed, and conduction delay of callosal axons in macaque monkeys and humans: comparing data from histology and magnetic resonance imaging diffusion tractography. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(36), 14501–14511. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0761-13.2013.
Cann, P. A., Read, N. W., Brown, C., Hobson, N., & Holdsworth, C. D. (1983). Irritable bowel syndrome: relationship of disorders in the transit of a single solid meal to symptom patterns. Gut, 24(5), 405–411. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6840614
Chang, L., Berman, S., Mayer, E. A., Suyenobu, B., Derbyshire, S., Naliboff, B., & Mandelkern, M. A. (2003). Brain responses to visceral and somatic stimuli in patients with irritable bowel syndrome with and without fibromyalgia. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 98(6), 1354–1361. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07478.x.
Chen, J. Y., Blankstein, U., Diamant, N. E., & Davis, K. D. (2011). White matter abnormalities in irritable bowel syndrome and relation to individual factors. Brain Research, 1392, 121–131. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.069
Davis, K. D., Pope, G., Chen, J., Kwan, C. L., Crawley, A. P., & Diamant, N. E. (2008). Cortical thinning in IBS: implications for homeostatic, attention, and pain processing. Neurology, 70(2), 153–154. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000295509.30630.10.
Drossman, D. A. (2006). The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology, 130(5), 1377–1390. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.03.008.
Drossman, D. A., Camilleri, M., Mayer, E. A., & Whitehead, W. E. (2002). AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology, 123(6), 2108–2131. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.37095.
Ellingson, B. M., Mayer, E., Harris, R. J., Ashe-McNally, C., Naliboff, B. D., Labus, J. S., & Tillisch, K. (2013). Diffusion tensor imaging detects microstructural reorganization in the brain associated with chronic irritable bowel syndrome. Pain, 154(9), 1528–1541. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.04.010.
Fields, R. D. (2008). White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends in Neurosciences, 31(7), 361–370. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2008.04.001
Frokjaer, J. B., Olesen, S. S., Gram, M., Yavarian, Y., Bouwense, S. A., Wilder-Smith, O. H., & Drewes, A. M. (2011). Altered brain microstructure assessed by diffusion tensor imaging in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gut, 60(11), 1554–1562. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.236620.
Fukudo, S. (2013). Stress and visceral pain: focusing on irritable bowel syndrome. Pain, 154(Suppl 1), S63–S70. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.09.008.
Jarman, J., Fernandez, M., Davies, P. T., Glover, V., Steiner, T. J., Thompson, C., Sandler, M. (1990). High incidence of endogenous depression in migraine: confirmation by tyramine test. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 53(7), 573–575. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2391520
Labus, J. S., Naliboff, B. D., Berman, S. M., Suyenobu, B., Vianna, E. P., Tillisch, K., & Mayer, E. A. (2009). Brain networks underlying perceptual habituation to repeated aversive visceral stimuli in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. NeuroImage, 47(3), 952–960. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.078
Labus, J. S., Gupta, A., Coveleskie, K., Tillisch, K., Kilpatrick, L., Jarcho, J., et al. (2013). Sex differences in emotion-related cognitive processes in irritable bowel syndrome and healthy control subjects. Pain, 154(10), 2088–2099. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.024.
Li, X. L., Fang, Y. N., Gao, Q. C., Lin, E. J., Hu, S. H., Ren, L., & Luo, B. N. (2011). A diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study of corpus callosum from adult patients with migraine complicated with depressive/anxious disorder. Headache, 51(2), 237–245. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01774.x.
Lieberman, G., Shpaner, M., Watts, R., Andrews, T., Filippi, C. G., Davis, M., & Naylor, M. R. (2014). White matter involvement in chronic musculoskeletal pain. The Journal of Pain, 15(11), 1110–1119. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2014.08.002
Longstreth, G. F., Thompson, W. G., Chey, W. D., Houghton, L. A., Mearin, F., & Spiller, R. C. (2006). Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology, 130(5), 1480–1491. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.11.061.
Ma, X., Li, S., Tian, J., Jiang, G., Wen, H., Wang, T., & Xu, Y. (2015). Altered brain spontaneous activity and connectivity network in irritable bowel syndrome patients: a resting-state fMRI study. Clinical Neurophysiology, 126(6), 1190–1197. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2014.10.004.
Mayer, E. A., Naliboff, B. D., Chang, L., & Coutinho, S. V. (2001). V. Stress and irritable bowel syndrome. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 280(4), G519–524. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11254476
Meleine, M., & Matricon, J. (2014). Gender-related differences in irritable bowel syndrome: potential mechanisms of sex hormones. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20(22), 6725–6743. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6725
Mertz, H., Morgan, V., Tanner, G., Pickens, D., Price, R., Shyr, Y., & Kessler, R. (2000). Regional cerebral activation in irritable bowel syndrome and control subjects with painful and nonpainful rectal distention. Gastroenterology, 118(5), 842–848. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10784583
Moayedi, M., Weissman-Fogel, I., Salomons, T. V., Crawley, A. P., Goldberg, M. B., Freeman, B. V., et al. (2012). White matter brain and trigeminal nerve abnormalities in temporomandibular disorder. Pain, 153(7), 1467–1477. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2012.04.003.
Mulak, A., Tache, Y., & Larauche, M. (2014). Sex hormones in the modulation of irritable bowel syndrome. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 20(10), 2433–2448. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2433
Naliboff, B. D., Derbyshire, S. W., Munakata, J., Berman, S., Mandelkern, M., Chang, L., & Mayer, E. A. (2001). Cerebral activation in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and control subjects during rectosigmoid stimulation. Psychosomatic Medicine, 63(3), 365–375. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11382264
Nichols, T. E., & Holmes, A. P. (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Human Brain Mapping, 15(1), 1–25. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11747097
Pae, C. U., Masand, P. S., Ajwani, N., Lee, C., & Patkar, A. A. (2007). Irritable bowel syndrome in psychiatric perspectives: a comprehensive review. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 61(10), 1708–1718. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01409.x
Prasko, J., Jelenova, D., & Mihal, V. (2010). Psychological aspects and psychotherapy of inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome in children. Biomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 154(4), 307–314. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21293541
Rotarska-Jagiela, A., Schonmeyer, R., Oertel, V., Haenschel, C., Vogeley, K., & Linden, D. E. (2008). The corpus callosum in schizophrenia-volume and connectivity changes affect specific regions. NeuroImage, 39(4), 1522–1532. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.063
Schmulson, M. J. (2001). Brain-gut interaction in irritable bowel syndrome: new findings of a multicomponent disease model. The Israel Medical Association Journal, 3(2), 104–110. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11347592
Scholz, J., Klein, M. C., Behrens, T. E., & Johansen-Berg, H. (2009). Training induces changes in white-matter architecture. Nature Neuroscience, 12(11), 1370–1371. doi:10.1038/nn.2412
Silverman, D. H., Munakata, J. A., Ennes, H., Mandelkern, M. A., Hoh, C. K., & Mayer, E. A. (1997). Regional cerebral activity in normal and pathological perception of visceral pain. Gastroenterology, 112(1), 64–72. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8978344
Smith, S. M. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17(3), 143–155. doi:10.1002/hbm.10062
Smith, S. M., & Nichols, T. E. (2009). Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage, 44(1), 83–98. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.061
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E., Johansen-Berg, H., Matthews, P. M. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage, 23 Suppl 1, S208–S219. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Johansen-Berg, H., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Mackay, C. E.,. .. Behrens, T. E. (2006). Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. NeuroImage, 31(4), 1487–1505. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.02.024
Smith, S. M., Johansen-Berg, H., Jenkinson, M., Rueckert, D., Nichols, T. E., Miller, K. L., & Behrens, T. E. (2007). Acquisition and voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data with tract-based spatial statistics. Nature Protocols, 2(3), 499–503. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.45.
Stanghellini, V., Tosetti, C., Barbara, G., De Giorgio, R., Cogliandro, L., Cogliandro, R., & Corinaldesi, R. (2002). Dyspeptic symptoms and gastric emptying in the irritable bowel syndrome. The American Journal of Gastroenterology, 97(11), 2738–2743. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.07062.x
Szabo, N., Kincses, Z. T., Pardutz, A., Tajti, J., Szok, D., Tuka, B., et al. (2012). White matter microstructural alterations in migraine: a diffusion-weighted MRI study. Pain, 153(3), 651–656. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2011.11.029.
Tillisch, K., Mayer, E. A., & Labus, J. S. (2011). Quantitative meta-analysis identifies brain regions activated during rectal distension in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology, 140(1), 91–100. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.07.053.
Yuan, Y. Z., Tao, R. J., Xu, B., Sun, J., Chen, K. M., Miao, F., Xu, J. Y. (2003). Functional brain imaging in irritable bowel syndrome with rectal balloon-distention by using fMRI. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 9(6), 1356–1360. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12800256
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Natural Scientific Foundation of China (grant no. 81471639) and Guangdong Provincial Natural Scientific Foundation (grant no. 2015 A030313723). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
Author Jin Fang, Shumei Li, Meng Li, Queenie Chan, Xiaofen Ma, Huanhuan Su, Tianyue Wang, Wenfeng Zhan, Jianhao Yan, Ming Xu, Yaxi Zhang, Luxian Zeng, Junzhang Tian, Guihua Jiang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Jin Fang and Shumei Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J., Li, S., Li, M. et al. Altered white matter microstructure identified with tract-based spatial statistics in irritable bowel syndrome: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1110–1116 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9573-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9573-y