Abstract
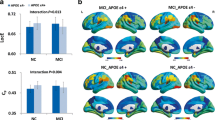
In this study, we used resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging to explore the genetic effects of amyloid precursor protein (APP) or presenilins mutation and apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 on the default-mode network (DMN) in cognitively intact young adults (24.1 ± 2.5 years). Both the APP or presenilin-1/2 group and the APOE ε4 group had significantly lower DMN functional connectivity (FC) in the some brain regions like precuneus/middle cingulate cortices (PCu/MCC) than controls (AlphaSim corrected, P < 0.05). Only a lower FC tendency was demonstrated (control < APOE ε4 < APP or presenilin-1/2 group). Moreover, lower FC in PCu/MCC is correlated with some neuropsychological assessments such as similarity test in APOE ε4 group. These findings indicate that DMN FC alteration in APP or presenilin-1/2 or APOE ε4 subjects is prior to the occurrence of neurological alterations and clinical symptoms, and DMN FC might be a valuable biomarker to detect genetic risk in the preclinical stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APOE :
-
apolipoprotein E
- APP :
-
amyloid precursor protein
- DMN:
-
default mode network
- FC:
-
functional connectivity
- MCC:
-
middle cingulate cortices
- PCC:
-
posterior cingulate cortex
- PCu:
-
precuneus
- rs-fMRI:
-
resting-state functional MR imaging
References
Barkhof, F., Haller, S., & Rombouts, S. A. (2014). Resting-state functional MR imaging: a new window to the brain. Radiology, 272(1), 29–49.
Cavanna, A. E., & Trimble, M. R. (2006). The precuneus: a review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain, 129(Pt 3), 564–583.
Cavedo, E., Pievani, M., Boccardi, M., Galluzzi, S., Bocchetta, M., Bonetti, M., et al. (2014). Medial temporal atrophy in early and late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 35(9), 2004–2012.
Chhatwal, J. P., Schultz, A. P., Johnson, K., Benzinger, T. L., Jack Jr., C., Ances, B. M., et al. (2013). Impaired default network functional connectivity in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 81(8), 736–744.
Chiu, W. Z., Papma, J. M., de Koning, I., Donker Kaat, L., Seelaar, H., Reijs, A. E., et al. (2012). Midcingulate involvement in progressive supranuclear palsy and tau positive frontotemporal dementia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 83(9), 910–915.
Cho, H., Jeon, S., Kang, S. J., Lee, J. M., Lee, J. H., Kim, G. H., et al. (2013). Longitudinal changes of cortical thickness in early- versus late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 34(7), 1921 e1929–1921 e1915.
Chouraki, V., & Seshadri, S. (2014). Genetics of Alzheimer's disease. Advances in Genetics, 87, 245–294.
Dean 3rd, D. C., Jerskey, B. A., Chen, K., Protas, H., Thiyyagura, P., Roontiva, A., et al. (2014). Brain differences in infants at differential genetic risk for late-onset Alzheimer disease: a cross-sectional imaging study. JAMA Neurol, 71(1), 11–22.
Dennis, N. A., Browndyke, J. N., Stokes, J., Need, A., Burke, J. R., Welsh-Bohmer, K. A., et al. (2010). Temporal lobe functional activity and connectivity in young adult APOE varepsilon4 carriers. Alzheimers Dement, 6(4), 303–311.
Dopper, E. G., Rombouts, S. A., Jiskoot, L. C., den Heijer, T., de Graaf, J. R., de Koning, I., et al. (2014). Structural and functional brain connectivity in presymptomatic familial frontotemporal dementia. Neurology, 83(2), e19–e26.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., Dekosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., Cummings, J., et al. (2007). Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurology, 6(8), 734–746.
Filippini, N., MacIntosh, B. J., Hough, M. G., Goodwin, G. M., Frisoni, G. B., Smith, S. M., et al. (2009). Distinct patterns of brain activity in young carriers of the APOE-epsilon4 allele. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(17), 7209–7214.
Fleisher, A. S., Chen, K., Liu, X., Ayutyanont, N., Roontiva, A., Thiyyagura, P., et al. (2013). Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 and age effects on florbetapir positron emission tomography in healthy aging and Alzheimer disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 34(1), 1–12.
Fleisher, A. S., Chen, K., Quiroz, Y. T., Jakimovich, L. J., Gomez, M. G., Langois, C. M., et al. (2012). Florbetapir PET analysis of amyloid-beta deposition in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease kindred: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurology, 11(12), 1057–1065.
Fleisher, A. S., Chen, K., Quiroz, Y. T., Jakimovich, L. J., Gutierrez Gomez, M., Langois, C. M., et al. (2015). Associations between biomarkers and age in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease kindred: a cross-sectional study. JAMA Neurol, 72(3), 316–324.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., Van Essen, D. C., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(27), 9673–9678.
Fransson, P., & Marrelec, G. (2008). The precuneus/posterior cingulate cortex plays a pivotal role in the default mode network: evidence from a partial correlation network analysis. NeuroImage, 42(3), 1178–1184.
Frisoni, G. B., Pievani, M., Testa, C., Sabattoli, F., Bresciani, L., Bonetti, M., et al. (2007). The topography of grey matter involvement in early and late onset Alzheimer's disease. Brain, 130(Pt 3), 720–730.
Gauthier, C. T., Duyme, M., Zanca, M., & Capron, C. (2009). Sex and performance level effects on brain activation during a verbal fluency task: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Cortex, 45(2), 164–176.
Goldberg, I. I., Harel, M., & Malach, R. (2006). When the brain loses its self: prefrontal inactivation during sensorimotor processing. Neuron, 50(2), 329–339.
Hascup, K. N., & Hascup, E. R. (2015). Altered neurotransmission prior to cognitive decline in AbetaPP/PS1 mice, a model of Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 44(3), 771–776.
Heise, V., Filippini, N., Trachtenberg, A. J., Suri, S., Ebmeier, K. P., & Mackay, C. E. (2014). Apolipoprotein E genotype, gender and age modulate connectivity of the hippocampus in healthy adults. NeuroImage, 98, 23–30.
Kapogiannis, D., Reiter, D. A., Willette, A. A., & Mattson, M. P. (2013). Posteromedial cortex glutamate and GABA predict intrinsic functional connectivity of the default mode network. NeuroImage, 64, 112–119.
Kim, J., Kim, Y. H., & Lee, J. H. (2013). Hippocampus-precuneus functional connectivity as an early sign of Alzheimer's disease: a preliminary study using structural and functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Brain Research, 1495, 18–29.
Knoferle, J., Yoon, S. Y., Walker, D., Leung, L., Gillespie, A. K., Tong, L. M., et al. (2014). Apolipoprotein E4 produced in GABAergic interneurons causes learning and memory deficits in mice. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(42), 14069–14078.
Koch, W., Teipel, S., Mueller, S., Benninghoff, J., Wagner, M., Bokde, A. L., et al. (2012). Diagnostic power of default mode network resting state fMRI in the detection of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(3), 466–478.
Lim, H. K., Nebes, R., Snitz, B., Cohen, A., Mathis, C., Price, J., et al. (2014). Regional amyloid burden and intrinsic connectivity networks in cognitively normal elderly subjects. Brain, 137(Pt 12), 3327–3338.
Matura, S., Prvulovic, D., Jurcoane, A., Hartmann, D., Miller, J., Scheibe, M., et al. (2014). Differential effects of the ApoE4 genotype on brain structure and function. NeuroImage, 89, 81–91.
Mormino, E. C., Smiljic, A., Hayenga, A. O., Onami, S. H., Greicius, M. D., Rabinovici, G. D., et al. (2011). Relationships between beta-amyloid and functional connectivity in different components of the default mode network in aging. Cerebral Cortex, 21(10), 2399–2407.
Patel, K. T., Stevens, M. C., Pearlson, G. D., Winkler, A. M., Hawkins, K. A., Skudlarski, P., et al. (2013). Default mode network activity and white matter integrity in healthy middle-aged ApoE4 carriers. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 7(1), 60–67.
Procyk, E., Wilson, C. R., Stoll, F. M., Faraut, M. C., Petrides, M., & Amiez, C. (2016). Midcingulate motor map and feedback detection: converging data from humans and monkeys. Cerebral Cortex, 26(2), 467–476.
Raichle, M. E., & Snyder, A. Z. (2007). A default mode of brain function: a brief history of an evolving idea. NeuroImage, 37(4), 1083–1090 discussion 1097-1089.
Rami, L., Sala-Llonch, R., Sole-Padulles, C., Fortea, J., Olives, J., Llado, A., et al. (2012). Distinct functional activity of the precuneus and posterior cingulate cortex during encoding in the preclinical stage of Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 31(3), 517–526.
Reiman, E. M., Quiroz, Y. T., Fleisher, A. S., Chen, K., Velez-Pardo, C., Jimenez-Del-Rio, M., et al. (2012). Brain imaging and fluid biomarker analysis in young adults at genetic risk for autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease in the presenilin 1 E280A kindred: a case-control study. Lancet Neurology, 11(12), 1048–1056.
Rieck, J. R., Rodrigue, K. M., Kennedy, K. M., Devous Sr., M. D., & Park, D. C. (2015). The effect of beta-amyloid on face processing in young and old adults: a multivariate analysis of the BOLD signal. Human Brain Mapping, 36(7), 2514–2526.
Rombouts, S. A., Barkhof, F., Goekoop, R., Stam, C. J., & Scheltens, P. (2005). Altered resting state networks in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer's disease: an fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 26(4), 231–239.
Ryan, N. S., Biessels, G. J., Kim, L., Nicholas, J. M., Barber, P. A., Walsh, P., et al. (2015). Genetic determinants of white matter hyperintensities and amyloid angiopathy in familial Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 36(12), 3140–3151.
Ryman, D. C., Acosta-Baena, N., Aisen, P. S., Bird, T., Danek, A., Fox, N. C., et al. (2014). Symptom onset in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology, 83(3), 253–260.
Scheff, S. W., Price, D. A., Schmitt, F. A., Roberts, K. N., Ikonomovic, M. D., & Mufson, E. J. (2013). Synapse stability in the precuneus early in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 35(3), 599–609.
Sheline, Y. I., Raichle, M. E., Snyder, A. Z., Morris, J. C., Head, D., Wang, S., et al. (2010). Amyloid plaques disrupt resting state default mode network connectivity in cognitively normal elderly. Biological Psychiatry, 67(6), 584–587.
Shima, K., Matsunari, I., Samuraki, M., Chen, W. P., Yanase, D., Noguchi-Shinohara, M., et al. (2012). Posterior cingulate atrophy and metabolic decline in early stage Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 33(9), 2006–2017.
Shinohara, M., Fujioka, S., Murray, M. E., Wojtas, A., Baker, M., Rovelet-Lecrux, A., et al. (2014). Regional distribution of synaptic markers and APP correlate with distinct clinicopathological features in sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease. Brain, 137(Pt 5), 1533–1549.
Su, Y. Y., Liang, X., Schoepf, U. J., Varga-Szemes, A., West, H. C., Qi, R., et al. (2015). APOE polymorphism affects brain default mode network in healthy young adults: a STROBE article. Medicine (Baltimore), 94(52), e1734.
Taylor, K. S., Seminowicz, D. A., & Davis, K. D. (2009). Two systems of resting state connectivity between the insula and cingulate cortex. Human Brain Mapping, 30(9), 2731–2745.
Tiwari, V., & Patel, A. B. (2012). Impaired glutamatergic and GABAergic function at early age in AbetaPPswe-PS1dE9 mice: implications for Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 28(4), 765–769.
Wang, L., Roe, C. M., Snyder, A. Z., Brier, M. R., Thomas, J. B., Xiong, C., et al. (2012). Alzheimer disease family history impacts resting state functional connectivity. Annals of Neurology, 72(4), 571–577.
Wood, H. (2014). Alzheimer disease: functional connectivity changes show similar trajectories in autosomal dominant and sporadic Alzheimer disease. Nature Reviews. Neurology, 10(9), 483.
Yu, J. T., Tan, L., & Hardy, J. (2014). Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease: an update. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 37, 79–100.
Zhao, W., Dumanis, S. B., Tamboli, I. Y., Rodriguez, G. A., Jo Ladu, M., Moussa, C. E., et al. (2014). Human APOE genotype affects intraneuronal Abeta1-42 accumulation in a lentiviral gene transfer model. Human Molecular Genetics, 23(5), 1365–1375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the local Medical Research Ethics Committee of Jinling Hospital (China).
Funding
This study was funded by the grants from Natural Scientific Foundation of China (81,322,020, 81,230,032, and 81,171,313 to L.J.Z.) and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0260 to L.J.Z.).
Competing financial interests
Dr. Schoepf is a consultant for and receives research support from Astellas, Bayer, Bracco, GE, Medrad, and Siemens. The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y.Y., Zhang, X.D., Schoepf, U.J. et al. Lower functional connectivity of default mode network in cognitively normal young adults with mutation of APP, presenilins and APOE ε4 . Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 818–828 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9556-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9556-z