Abstract
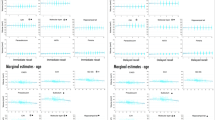
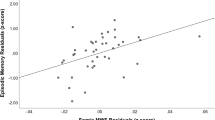
The objective of this study was to investigate the relationship of medial temporal lobe and posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) volumetrics as well as fractional anisotropy of the cingulum angular bundle (CAB) and the cingulum cingulate gyrus (CCG) bundle to performance on measures of verbal memory in non-demented older adults. The participants were 100 non-demented adults over the age of 70 years from the Einstein Aging Study. Volumetric data were estimated from T1-weighted images. The entire cingulum was reconstructed using diffusion tensor MRI and probabilistic tractography. Association between verbal episodic memory and MRI measures including volume of hippocampus (HIP), entorhinal cortex (ERC), PCC and fractional anisotropy of CAB and CCG bundle were modeled using linear regression. Relationships between atrophy of these structures and regional cingulum fractional anisotropy were also explored. Decreased HIP volume on the left and decreased fractional anisotropy of left CAB were associated with lower memory performance. Volume changes in ERC, PCC and CCG disruption were not associated with memory performance. In regression models, left HIP volume and left CAB-FA were each independently associated with episodic memory. The results suggest that microstructural changes in the left CAB and decreased left HIP volume independently influence episodic memory performance in older adults without dementia. The importance of these findings in age and illness-related memory decline require additional exploration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. American Psychiatric Association. Task Force on DSM-IV. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders : DSM-IV-TR (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Backman, L., Jones, S., Berger, A. K., Laukka, E. J., & Small, B. J. (2005). Cognitive impairment in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychology, 19(4), 520–31. doi:10.1037/0894-4105.19.4.520.
Braak, H., & Braak, E. (1991). Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica, 82(4), 239–59.
Buckner, R. L., Head, D., Parker, J., Fotenos, A. F., Marcus, D., Morris, J. C., & Snyder, A. Z. (2004). A unified approach for morphometric and functional data analysis in young, old, and demented adults using automated atlas-based head size normalization: reliability and validation against manual measurement of total intracranial volume. NeuroImage, 23(2), 724–38. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.018.
Buschke, H. (1984). Cued recall in amnesia. Journal of Clinical Neuropsychology, 6(4), 433–40.
Catani, M., & De Schotten, M. T. (2008). A diffusion tensor imaging tractography atlas for virtual in vivo dissections. Cortex, 44(8), 1105–32.
Chetelat, G., Desgranges, B., de la Sayette, V., Viader, F., Eustache, F., & Baron, J. C. (2003). Mild cognitive impairment: can FDG-PET predict who is to rapidly convert to Alzheimer’s disease? Neurology, 60(8), 1374–7.
Choo, I. H., Lee, D. Y., Oh, J. S., Lee, J. S., Lee, D. S., Song, I. C., Youn, J. C., Kim, S. G., Kim, K. W., Jhoo, J. H., & Woo, J. I. (2010). Posterior cingulate cortex atrophy and regional cingulum disruption in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 31(5), 772–9. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.06.015.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., Dekosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., Cummings, J., Delacourte, A., Galasko, D., Gauthier, S., Jicha, G., Meguro, K., O’Brien, J., Pasquier, F., Robert, P., Rossor, M., Salloway, S., Stern, Y., Visser, P. J., & Scheltens, P. (2007). Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurology, 6(8), 734–46. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70178-3.
Fellgiebel, A., Muller, M. J., Wille, P., Dellani, P. R., Scheurich, A., Schmidt, L. G., & Stoeter, P. (2005). Color-coded diffusion-tensor-imaging of posterior cingulate fiber tracts in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of Aging, 26(8), 1193–8. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.11.006.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., van der Kouwe, A., Killiany, R., Kennedy, D., Klaveness, S., Montillo, A., Makris, N., Rosen, B., & Dale, A. M. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–55.
Gong, G., Jiang, T., Zhu, C., Zang, Y., Wang, F., Xie, S., Xiao, J., & Guo, X. (2005). Asymmetry analysis of cingulum based on scale-invariant parameterization by diffusion tensor imaging. Human Brain Mapping, 24(2), 92–8. doi:10.1002/hbm.20072.
Grober, E., Lipton, R. B., Hall, C., & Crystal, H. (2000). Memory impairment on free and cued selective reminding predicts dementia. Neurology, 54(4), 827–32.
Hua, K., Zhang, J., Wakana, S., Jiang, H., Li, X., Reich, D. S., Calabresi, P. A., Pekar, J. J., van Zijl, P. C., & Mori, S. (2008). Tract probability maps in stereotaxic spaces: analyses of white matter anatomy and tract-specific quantification. NeuroImage, 39(1), 336–47.
Jack, C. R., Jr., Shiung, M. M., Gunter, J. L., O’Brien, P. C., Weigand, S. D., Knopman, D. S., Boeve, B. F., Ivnik, R. J., Smith, G. E., Cha, R. H., Tangalos, E. G., & Petersen, R. C. (2004). Comparison of different MRI brain atrophy rate measures with clinical disease progression in AD. Neurology, 62(4), 591–600.
Jbabdi, S., Woolrich, M. W., Andersson, J. L., & Behrens, T. E. (2007). A Bayesian framework for global tractography. NeuroImage, 37(1), 116–29. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.039.
Jones, B. F., Barnes, J., Uylings, H. B., Fox, N. C., Frost, C., Witter, M. P., & Scheltens, P. (2006). Differential regional atrophy of the cingulate gyrus in Alzheimer disease: a volumetric MRI study. Cerebral Cortex, 16(12), 1701–8. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj105.
Katz, M. J., Lipton, R. B., Hall, C. B., Zimmerman, M. E., Sanders, A. E., Verghese, J., Dickson, D. W., & Derby, C. A. (2012). Age-specific and sex-specific prevalence and incidence of mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and Alzheimer dementia in blacks and whites: a report from the Einstein Aging Study. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 26(4), 335–43. doi:10.1097/WAD.0b013e31823dbcfc.
Kramer, J. H., Mungas, D., Reed, B. R., Wetzel, M. E., Burnett, M. M., Miller, B. L., Weiner, M. W., & Chui, H. C. (2007). Longitudinal MRI and cognitive change in healthy elderly. Neuropsychology, 21(4), 412–8. doi:10.1037/0894-4105.21.4.412.
Lezak, M. D. (2012). Neuropsychological assessment (5th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Lin, Y. C., Shih, Y. C., Tseng, W. Y., Chu, Y. H., Wu, M. T., Chen, T. F., Tang, P. F., & Chiu, M. J. (2014). Cingulum correlates of cognitive functions in patients with mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease: a diffusion spectrum imaging study. Brain Topography, 27(3), 393–402. doi:10.1007/s10548-013-0346-2.
Mitrushina, M. N. (2005). Handbook of normative data for neuropsychological assessment (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Monsch, A. U., Bondi, M. W., Butters, N., Salmon, D. P., Katzman, R., & Thal, L. J. (1992). Comparisons of verbal fluency tasks in the detection of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Archives of Neurology, 49(12), 1253–8.
Nestor, P. J., Fryer, T. D., Smielewski, P., & Hodges, J. R. (2003). Limbic hypometabolism in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Annals of Neurology, 54(3), 343–51. doi:10.1002/ana.10669.
Nestor, P. J., Fryer, T. D., & Hodges, J. R. (2006). Declarative memory impairments in Alzheimer’s disease and semantic dementia. NeuroImage, 30(3), 1010–20.
Nir, T. M., Jahanshad, N., Villalon-Reina, J. E., Toga, A. W., Jack, C. R., Weiner, M. W., Thompson, P. M., & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2013). Effectiveness of regional DTI measures in distinguishing Alzheimer’s disease, MCI, and normal aging. NeuroImage Clinical, 3, 180–95. doi:10.1016/j.nicl.2013.07.006.
Pennanen, C., Kivipelto, M., Tuomainen, S., Hartikainen, P., Hanninen, T., Laakso, M. P., Hallikainen, M., Vanhanen, M., Nissinen, A., Helkala, E. L., Vainio, P., Vanninen, R., Partanen, K., & Soininen, H. (2004). Hippocampus and entorhinal cortex in mild cognitive impairment and early AD. Neurobiology of Aging, 25(3), 303–10. doi:10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00084-8.
Sasson, E., Doniger, G. M., Pasternak, O., Tarrasch, R., & Assaf, Y. (2013). White matter correlates of cognitive domains in normal aging with diffusion tensor imaging. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 32. doi:10.3389/fnins.2013.00032.
Sexton, C. E., Kalu, U. G., Filippini, N., Mackay, C. E., & Ebmeier, K. P. (2011). A meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 32(12), 2322 e5–18. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.019.
Sperling, R. A., Dickerson, B. C., Pihlajamaki, M., Vannini, P., LaViolette, P. S., Vitolo, O. V., Hedden, T., Becker, J. A., Rentz, D. M., Selkoe, D. J., & Johnson, K. A. (2010). Functional alterations in memory networks in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Medicine, 12(1), 27–43. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8109-7.
Strauss, E., Sherman, E. M. S., Spreen, O., & Spreen, O. (2006). A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration, norms, and commentary (3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Van Petten, C. (2004). Relationship between hippocampal volume and memory ability in healthy individuals across the lifespan: review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia, 42(10), 1394–413. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2004.04.006.
Wakana, S., Caprihan, A., Panzenboeck, M. M., Fallon, J. H., Perry, M., Gollub, R. L., Hua, K., Zhang, J., Jiang, H., Dubey, P., Blitz, A., van Zijl, P., & Mori, S. (2007). Reproducibility of quantitative tractography methods applied to cerebral white matter. NeuroImage, 36(3), 630–44. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.02.049.
Wilson, R. S., Barnes, L. L., Krueger, K. R., Hoganson, G., Bienias, J. L., & Bennett, D. A. (2005). Early and late life cognitive activity and cognitive systems in old age. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society: JINS, 11(4), 400–7.
Wolk, D. A., Dickerson, B. C., & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. (2011). Fractionating verbal episodic memory in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 54(2), 1530–9. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.005.
Yendiki, A., Panneck, P., Srinivasan, P., Stevens, A., Zollei, L., Augustinack, J., Wang, R., Salat, D., Ehrlich, S., Behrens, T., Jbabdi, S., Gollub, R., & Fischl, B. (2011). Automated probabilistic reconstruction of white-matter pathways in health and disease using an atlas of the underlying anatomy. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics, 5, 23. doi:10.3389/fninf.2011.00023.
Zago, L., Petit, L., Turbelin, M. R., Andersson, F., Vigneau, M., & Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. (2008). How verbal and spatial manipulation networks contribute to calculation: an fMRI study. Neuropsychologia, 46(9), 2403–14.
Zammit, A. R., Katz, M. J., Lai, J. Y., Zimmerman, M. E., Bitzer, M., & Lipton, R. B. (2014). Association between renal function and cognitive ability domains in the Einstein aging study: a cross-sectional analysis. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. doi:10.1093/gerona/glu185.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there are no financial, personal, or other potential conflicts of interest to report.
Funding
This research was supported by National Institute on Aging Grant AG03949 and AG026728.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Movie 1
Demontration of coronal view of posterior probability distributions of CCG (upper bundle) and CAB (lower bundle) pathways reconstructed with TRACULA in both hemispheres, while superimposed on T1 image of the subject. CCG= cingulum cingulate gyrus bundle, CAB= cingulum angular bundle. (MPG 1482 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezzati, A., Katz, M.J., Lipton, M.L. et al. Hippocampal volume and cingulum bundle fractional anisotropy are independently associated with verbal memory in older adults. Brain Imaging and Behavior 10, 652–659 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9452-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9452-y