Abstract
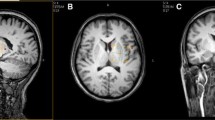
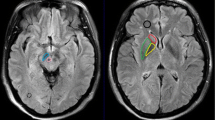
This study investigates changes in substantia nigra metabolites in Parkinson’s disease (PD) using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H- MRS). Thirty patients with asymmetric PD and 20 normal controls were included in this study. Substantia nigra metabolites were detected in all subjects using 3D-multimer 1H-MRS with a 3.0 T MRI scanner. The relative ratios of NAA/Cr, NAA/Cho, NAA/(Cho + Cr) in the substantia nigra were compared between two sides of asymmetric PD patients as well as between PD patients and controls. Significant differences in NAA/Cr, NAA/Cho, NAA/(Cho + Cr) were observed between PD patients and healthy controls (P < 0.05) as well as between the ipsilateral and contralateral of affected extremity in PD patients (P < 0.05). Significant differences in NAA/Cr, NAA/Cho, NAA/(Cho + Cr) were also observed between patients with mild and severe PD. Thus, we found that 1H-MRS can be used to detect substantia nigra metabolites in PD patients, which may be useful for early diagnosis and evaluation of PD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarsland, D., Zaccai, J., & Brayne, A. (2005). Systematic review of prevalence studies of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders, 20, 1255–1263.
Barker, P. B., & Lin, D. D. M. (2006). In vivo proton MR spectroscopy of the human brain. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, 49, 99–128.
Bmak, H., Bold, J. R., Muller, C. M., et al. (2006). Stanley Fahn Lecture 2005:The Stagira procedure for the inclusion body pathology associated with sporadic Parkinson’s disease reconsidered. Movement Disorders, 21, 2042–2051.
Brooks, D. J. (2012). Parkinson’s disease: diagnosis. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 18(Suppl 1), S31–S33.
Burlina, A. P., Aureli, T., Bracco, F., Conti, F., & Battistin, L. (2000). MR spectroscopy: a powerful tool for investigating brain function and neurological diseases. Neurochemical Research, 25, 1365–1372.
Choi, C., Bhardwaj, P. P., Seres, P., Kalra, S., Tibbo, P. G., & Coupland, N. J. (2008). Measurement of glycine in human brain by triple refocusing 1H-MRS in vivo at 3.0T. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 59, 59–64.
Ellis, C. M., Lemmens, G., Williams, S. C., Simmons, A., Dawson, J., Leigh, P. N., et al. (1997). Changes in putamen N-acetylaspartate and choline ratios in untreated and levodopa-treated Parkinson’s disease: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neurology, 49, 438–444.
Gallagher, D. A., & Schapira, A. H. (2009). Etiopathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry, 9, 860–868.
Gensanne, D., Josse, G., Lagarde, J. M., & Vincensini, D. (2006). High spatial resolution quantitative MR images: an experimental study of dedicated surface coils. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 51, 2843–2855.
Goetz, C. G., Poewe, W., Rascol, O., Sampaio, C., Stebbins, G. T., Counsell, C., et al. (2004). Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: status and recommendations. Movement Disorders, 19, 1020–1028.
Govindaraju, V., Young, K., & Maudsley, A. A. (2000). Proton NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants for brain metabolites. NMR in Biomedicine, 13, 129–153.
Monza, D., Soliveri, P., Radice, D., Fetoni, V., Testa, D., Caffarra, P., et al. (1998). Cognitive dysfunction and impaired organization of complex motility in degenerative parkinsonian syndromes. Archives of Neurology, 55, 372–378.
Rango, M., Arighi, A., Biondetti, P., Barberis, B., Bonifati, C., Blandini, F., et al. (2007). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonian syndromes. Functional Neurology, 22, 75–79.
Seppi, K. (2008). MRI for the differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative parkinsonism in clinical practice. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 13(Suppl 3), S400–S4005.
Tka´cˇ, I. (2008). Refinement of simulated basis set for LCModel analysis.Proceedings 16th Scientific Meeting, International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Toronto. pp 1624.
Wood, L. D., Neumiller, J. J., Setter, S. M., & Dobbins, E. K. (2010). Clinical review of treatment options for select nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The American Journal of Geriatric Pharmacotherapy, 8, 294–315.
Acknowledgments
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bing Zhou and Fangzhen Yuan contributed equally to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, B., Yuan, F., He, Z. et al. Application of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy on substantia nigra metabolites in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior 8, 97–101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-013-9251-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-013-9251-2