Abstract
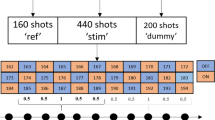
This study further investigates the influence of temporarily disrupting the blood-brain barrier (BBB) on the level of manganese used in AIM fMRI other than the recognized function of allowing that substance to enter into the activated brain regions more effectively during the BBB opening. We injected manganese into Wistar rats through ICA following the disruption of BBB with mannitol in a functional MRI test of the visual cortex. Through comparing MRI signal intensity and manganese contents in the visual cortex of rats received visual stimuli of unequal degree after the restoration of BBB, we found that the signal in the visual cortex could be further enhanced on T1WI given visual stimulation after the restoration of BBB. Temporary BBB disruption has an additional advantage in allowing Mn2+ to enter the CSF or brain for later transference to the activated brain area. So the dosage of manganese in AIM fMRI could be minimized by extending the stimulus.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, I., Naruse, S., & Tanaka, C. (2004). Manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MEMRI) of brain activity and applications to early detection of brain ischemia. NMR in Biomedicine, 17, 569–580.
Aoki, I., Wu, Y. J., Silva, A. C., Lynch, R. M., & Koretsky, A. P. (2004). In vivo detection of neuroarchitecture in the rodent brain using manganese-enhanced MRI. Neuroimage, 22, 1046–1059.
Bearer, E. L., Falzone, T. L., Zhang, X., Biris, O., Rasin, A., & Jacobs, R. E. (2007). Role of neuronal activity and kinesin on tract tracing by manganese-enhanced MRI (MEMRI). Neuroimage, 37(Suppl 1), S37–S46.
Berkowitz, B. A., Roberts, R., Goebel, D. J., & Luan, H. (2006). Noninvasive and simultaneous imaging of layer-specific retinal functional adaptation by manganese-enhanced MRI. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 47, 2668–2674.
Bhattacharjee, A. K., Nagashima, T., Kondoh, T., & Tamaki, N. (2001). Quantification of early blood-brain barrier disruption by in situ brain perfusion technique. Brain Research. Brain Research Protocols, 8, 126–131.
Bissig, D., & Berkowitz, B. A. (2009). Manganese-enhanced MRI of layer-specific activity in the visual cortex from awake and free-moving rats. Neuroimage, 44, 627–635.
Bock, N. A., Paiva, F. F., & Silva, A. C. (2008). Fractionated manganese-enhanced MRI. NMR in Biomedicine, 21, 473–478.
Bock, N. A., Kocharyan, A., & Silva, A. C. (2009). Manganese-enhanced MRI visualizes V1 in the non-human primate visual cortex. NMR in Biomedicine, 22, 730–736.
Brurok, H., SchjØtt, J., Berg, K., Karlsson, J. O., & Jynge, P. (1997). Manganese and the heart: acute cardiodepression and myocardial accumulation of manganese. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica, 159, 33–40.
Chiu, J. H., Chung, M. S., Cheng, H. C., Yeh, T. C., Hsieh, J. C., Chang, C. Y., et al. (2003). Different central manifestations in response to electroacupuncture at analgesic and nonanalgesic acupoints in rats: a manganese-enhanced functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research, 67, 94–101.
Gerdin, B., McCann, E., Lundberg, C., & Arfors, K. E. (1985). Selective tissue accumulation of manganese and its effect on regional blood flow and haemodynamics after intravenous infusion of its chloride salt in the rat. International Journal of Tissue Reactions, 7, 373–380.
Lee, J. H., Silva, A. C., Merkle, H., & Koretsky, A. P. (2005). Manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of mouse brain after systemic administration of MnCl2: dose-dependent and temporal evolution of T1 contrast. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 53, 640–648.
Leergaard, T. B., Bjaalie, J. G., Devor, A., Wald, L. L., & Dale, A. M. (2003). In vivo tracing of major rat brain pathways using manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and three-dimensional digital atlasing. Neuroimage, 20, 1591–1600.
Li, Y., Fang, F., Wang, X., & Lei, H. (2009). Neuronal projections from ventral tegmental area to forebrain structures in rat studied by manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 27, 293–299.
Lin, Y. J., & Koretsky, A. P. (1997). Manganese ion enhances T1-weighted MRI during brain activation: an approach to direct imaging of brain function. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 38, 378–388.
Liu, C. H., D’Arceuil, H. E., & de Crespigny, A. J. (2004). Direct CSF injection of MnCl(2) for dynamic manganese-enhanced MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 51, 978–987.
Lu, H., Xi, Z. X., Gitajn, L., Rea, W., Yang, Y., & Stein, E. A. (2007). Cocaine-induced brain activation detected by dynamic manganese-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MEMRI). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 2489–2494.
Lu, H., Yang, S., Zuo, Y., Demny, S., Stein, E. A., & Yang, Y. (2008). Real-time animal functional magnetic resonance imaging and its application to neuropharmacological studies. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 26, 1266–1272.
Morello, M., Canini, A., Mattioli, P., Sorge, R. P., Alimonti, A., Bocca, B., et al. (2008). Sub-cellular localization of manganese in the basal ganglia of normal and manganese-treated rats An electron spectroscopy imaging and electron energy-loss spectroscopy study. Neurotoxicology, 29, 60–72.
Paxinos, G., & Watson, C. (2004). The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates (5th ed., pp. 118–139). Orlando: Academic.
Rapoport, S. I. (2000). Osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier: principles, mechanism, and therapeutic applications. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology, 20, 217–230.
Weng, J. C., Chen, J. H., Yang, P. F., & Tseng, W. Y. (2007). Functional mapping of rat barrel activation following whisker stimulation using activity-induced manganese-dependent contrast. Neuroimage, 36, 1179–1188.
Yu, X., Wadghiri, Y. Z., Sanes, D. H., & Turnbull, D. H. (2005). In vivo auditory brain mapping in mice with Mn-enhanced MRI. Nature Neuroscience, 8, 961–968.
Yu, X., Zou, J., Babb, J. S., Johnson, G., Sanes, D. H., & Turnbull, D. H. (2008). Statistical mapping of sound-evoked activity in the mouse auditory midbrain using Mn-enhanced MRI. Neuroimage, 39, 223–230.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Funds for Key Sci-Tech Research Projects of Guangdong Province [YUECAIJIAO (2008) 258-2008A030201019, YUE KEJIBAN (2007) 05/06-7005206], and Funds for Key Sci-Tech Research Projects of Guangzhou [SUIKETIAOZI (2008)3-2008A1-E4011-6, 09B52120112-2009J1-C418-2] to Prof. Xiaodan Jiang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhiqiang Fa, Run Zhang and Peng Li, These authors contributed equally to this research
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fa, Z., Zhang, R., Li, P. et al. Effects of temporarily disrupting BBB on activity-induced manganese-dependent functional MRI. Brain Imaging and Behavior 5, 181–188 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-011-9122-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-011-9122-7