Abstract
Introduction
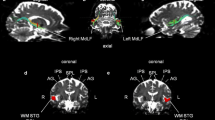
Quantitative fiber tracking with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) provides a new approach for assessing deficits in the microstructural integrity of white matter circuits that may underlie cognitive deficits associated with conditions affecting white matter, including chronic alcoholism.
Methods
Alcoholic men and women (n = 87) and healthy controls (n = 88) performed the Digit Symbol (DS) test and underwent structural and diffusion tensor imaging. Measures of fractional anisotropy (FA) of fibers passing through genu and splenium were computed, as were size of genu and splenium fiber target regions of interest (ROI).
Results
Alcoholics scored lower than controls on the DS and had even greater deficits in genu than splenium fiber FA. In alcoholics, fiber FA of the genu selectively predicted DS scores after accounting for splenium FA. Neither fiber FA measure predicted incidental recall of the symbols used in the task. Size of genu and splenium ROI, although reduced in alcoholics, did not predict DS score or incidental recall.
Conclusions
Quantitative tractography of frontal fibers connecting left and right hemispheres selectively predicted performance by alcoholics on a coordinated psychomotor task and provide support for frontally based systems in Digit Symbol performance, both of which are compromised in recovering alcoholics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, O., Masutani, Y., Aoki, S., Yamasue, H., Yamada, H., Kasai, K., et al. (2004). Topography of the human corpus callosum using diffusion tensor tractography. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 28, 533–539.
Aboitiz, F., Scheibel, A., Fisher, R., & Zaidel, E. (1992). Fiber composition of the human corpus callosum. Brain Research, 598, 143–153.
Beatty, W., Tivis, R., Stott, H., Nixon, S., & Parsons, O. (2000). Neuropsychological deficits in sober alcoholics: Influences of chronicity and recent alcohol consumption. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 24, 149–154.
Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A., & Brown, G. K. (1996). Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory—II. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
Bucur, B., Madden, D. J., Spaniol, J., Provenzale, J. M., Cabeza, R., White, L. E., et al. (2007). Age-related slowing of memory retrieval: Contributions of perceptual speed and cerebral white matter integrity. Neurobiology of Aging (in press).
Cardenas, V. A., Studholme, C., Gazdzinski, S., Durazzo, T. C., & Meyerhoff, D. J. (2007). Deformation-based morphometry of brain changes in alcohol dependence and abstinence. NeuroImage, 34, 879–887.
Crovitz, H. F., & Zener, K. A. (1962). Group test for assessing hand and eye dominance. American Journal of Psychology, 75, 271–276.
Davies, S. J., Pandit, S. A., Feeney, A., Stevenson, B. J., Kerwin, R. W., Nutt, D. J., et al. (2005). Is there cognitive impairment in clinically ‘healthy’ abstinent alcohol dependence? Alcohol and Alcoholism, 40, 498–503.
Endicott, J., Spitzer, R. L., Fleiss, J. L., & Cohen, J. (1976). The global assessment scale. A procedure for measuring overall severity of psychiatric disturbance. Archives of General Psychiatry, 33, 766–771.
Estruch, R., Nicolas, J. M., Salamero, M., Aragon, C., Sacanella, E., Fernandez-Sola, J., et al. (1997). Atrophy of the corpus callosum in chronic alcoholism. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 146, 145–151.
Fein, G., Bachman, L., Fisher, S., & Davenport, L. (1990). Cognitive impairments in abstinent alcoholics. Western Journal of Medicine, 152, 531–537.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Gibbon, M., & Williams, J. B. W. (1998). Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV Axis I disorders (SCID) version 2.0. New York, NY: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute.
Funnell, M. G., Corballis, P. M., & Gazzaniga, M. S. (2000). Insights into the functional specificity of the human corpus callosum. Brain, 123(Pt 5), 920–926.
Gazzaniga, M. S. (2005). Forty-five years of split-brain research and still going strong. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 6, 653–659.
Gerig, G., Corouge, I., Vachet, C., Krishnan, K. R., & MacFall, J. R. (2005). Quantitative analysis of diffusion properties of white matter fiber tracts: A validation study. Paper presented at the 13th Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Miami, FL.
Glosser, G., Butters, N., & Kaplan, E. (1977). Visuoperceptual processes in brain damaged patients on the digit symbol substitution test. International Journal of Neuroscience, 7, 59–66.
Gross, C. G., Bender, D. B., & Mishkin, M. (1977). Contributions of the corpus callosum and the anterior commissure to visual activation of inferior temporal neurons. Brain Research, 131, 227–239.
Harper, C. G., & Kril, J. J. (1990). Neuropathology of alcoholism. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 25, 207–216.
Harris, C. R., Albaugh, B., Goldman, D., & Enoch, M. A. (2003). Neurocognitive impairment due to chronic alcohol consumption in an American Indian community. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 64, 458–466.
Hochla, N. A., Fabian, M. S., & Parsons, O. A. (1982). Brain-age quotients in recently detoxified alcoholic, recovered alcoholic and nonalcoholic women. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38, 207–212.
Hofer, S., & Frahm, J. (2006). Topography of the human corpus callosum revisited—comprehensive fiber tractography using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage, 32, 989–994.
Hollingshead, A., & Redlich, F. (1958). Social class and mental illness. New York: Wiley.
Hommer, D., Momenan, R., Rawlings, R., Ragan, P., Williams, W., Rio, D., et al. (1996). Decreased corpus callosum size among alcoholic women. Archives of Neurology, 53, 359–363.
Huang, H., Zhang, J., Jiang, H., Wakana, S., Poetscher, L., Miller, M. I., et al. (2005). DTI tractography based parcellation of white matter: Application to the mid-sagittal morphology of corpus callosum. NeuroImage, 26, 195–205.
Jokinen, H., Ryberg, C., Kalska, H., Ylikoski, R., Rostrup, E., Stegmann, M. B., et al. (2007). Corpus callosum atrophy is associated with mental slowing and executive deficits in subjects with age-related white matter hyperintensities: the LADIS Study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 78, 491–496.
Joy, S., Fein, D., & Kaplan, E. (2003a). Decoding digit symbol: speed, memory, and visual scanning. Assessment, 10, 56–65.
Joy, S., Fein, D., Kaplan, E., & Freedman, M. (2000). Speed and memory in WAIS-R-III digit symbol performance among healthy older adults. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 6, 770–780.
Joy, S., Kaplan, E., & Fein, D. (2003b). Digit symbol–incidental learning in the WAIS-III: Construct validity and clinical significance. Clinical Neuropsychology, 17, 182–194.
Kaplan, E., Fein, D., Morris, R., & Delis, D. C. (1991). WAIS-R as a neuropsychological instrument. New York: The Psychological Corporation.
Lee, S. T., Jung, Y. M., Na, D. L., Park, S. H., & Kim, M. (2005). Corpus callosum atrophy in Wernicke's encephalopathy. Journal of Neuroimaging, 15, 367–372.
Lezak, M. D. (1995). Neuropsychological assessment (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Mori, S., & van Zijl, P. C. (2002). Fiber tracking: Principles and strategies—A technical review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15, 468–480.
Oishi, M., Mochizuki, Y., & Shikata, E. (1999). Corpus callosum atrophy and cerebral blood flow in chronic alcoholics. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 162, 51–55.
Oscar-Berman, M. (2000). Neuropsychological vulnerabilities in chronic alcoholism. In A. Noronha, M. Eckardt, & K. Warren (Eds.) Review of NIAAA’s neuroscience and behavioral research portfolio, NIAAA research monograph no. 34 (pp. 437–472). Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health.
Pandya, D. N., & Seltzer, B. (1986). The topography of commissural fibers. In F. Lepore, M. Ptito, & H. H. Jasper (Eds.) Two hemispheres—one brain: Functions of the corpus callosum (pp. 47–74). New York: Alan R. Liss, Inc.
Park, H.-J., Kim, J. J., Lee, S.-K., Seok, J. H., Chun, J., Kim, D. I., et al. (2007). Corpus callosal connection mapping using cortical gray matter parcellation and DT-MRI. Human Brain Mapping (in press).
Parsons, O. A., Butters, N., & Nathan, P. E. (Eds.) (1987). Neuropsychology of alcoholism: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. New York: Guilford.
Peru, A., Beltramello, A., Moro, V., Sattibaldi, L., & Berlucchi, G. (2003). Temporary and permanent signs of interhemispheric disconnection after traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychologia, 41, 634–643.
Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E., & Sullivan, E. V. (2006a). Dysmorphology and microstructural degradation of the corpus callosum: Interaction of age and alcoholism. Neurobiology of Aging, 27, 994–1009.
Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E., & Sullivan, E. V. (2006b). Supratentorial profile of white matter microstructural integrity in recovering alcoholic men and women. Biological Psychiatry, 59, 364–372.
Pfefferbaum, A., Lim, K. O., Desmond, J. E., & Sullivan, E. V. (1996). Thinning of the corpus callosum in older alcoholic men: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 20, 752–757.
Pfefferbaum, A., Lim, K. O., Zipursky, R. B., Mathalon, D. H., Rosenbloom, M. J., Lane, B., et al. (1992). Brain gray and white matter volume loss accelerates with aging in chronic alcoholics: A quantitative MRI study. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 16, 1078–1089.
Pfefferbaum, A., Rosenbloom, M. J., Adalsteinsson, E., & Sullivan, E. V. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging with quantitative fiber tracking in HIV infection and alcoholism comorbidity: Synergistic white matter damage. Brain, 130, 48–64.
Pfefferbaum, A., Rosenbloom, M. J., Rohlfing, T., Adalsteinsson, E., Kemper, C. A., Deresinski, S., et al. (2006c). Contribution of alcoholism to brain dysmorphology in HIV infection: Effects on the ventricles and corpus callosum. NeuroImage, 33, 239–251.
Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2002). Microstructural but not macrostructural disruption of white matter in women with chronic alcoholism. NeuroImage, 15, 708–718.
Pfefferbaum, A., Sullivan, E. V., & Carmelli, D. (2001). Genetic regulation of regional microstructure of the corpus callosum in late life. Neuroreport, 12, 1677–1681.
Pfefferbaum, A., Sullivan, E. V., Hedehus, M., Adalsteinsson, E., Lim, K. O., & Moseley, M. (2000). In vivo detection and functional correlates of white matter microstructural disruption in chronic alcoholism. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 24, 1214–1221.
Rosenbloom, M. J., O’Reilly, A., Sassoon, S. A., Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2005). Persistent cognitive deficits in community-treated alcoholic men and women volunteering for research: Limited contribution from psychiatric comorbidity. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 66, 254–265.
Rosenbloom, M. J., Sullivan, E. V., Sassoon, S. A., O’Reilly, A., Fama, R., Kemper, C. A., et al. (2007). Alcoholism, HIV infection and their comorbidity: Factors affecting self-rated health-related quality of life. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 68, 115–125.
Sassoon, S. A., Fama, R., Rosenbloom, M. J., O'Reilly, A., Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2007). Component cognitive and motor processes of the digit symbol test: Differential deficits in alcoholism, HIV infection and their comorbidity. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 31, 1315–1324.
Schulte, T., Müller-Oehring, E. M., Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2007). Callosal compromise differentially affects conflict processing and attentional allocation in alcoholism, HIV infection, and their comorbidity. Brain Imaging and Behavior (in press).
Schulte, T., Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2004). Parallel interhemispheric processing in aging and alcoholism: Relation to corpus callosum size. Neuropsychologia, 42, 257–271.
Schulte, T., Sullivan, E. V., Müller-Oehring, E. M., Adalsteinsson, E., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2005). Corpus callosal microstructural integrity influences interhemispheric processing: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Cerebral Cortex, 15, 1384–1392.
Seltzer, B., & Sherwin, I. (1983). A comparison of clinical features in early and late-onset primary degenerative dementia: One entity or two. Archives of Neurology, 40, 143–146.
Skinner, H. A. (1982). Development and validation of a lifetime alcohol consumption assessment procedure. Toronto, Canada: Addiction Research Foundation.
Skinner, H. A., & Sheu, W. J. (1982). Reliability of alcohol use indices: The lifetime drinking history and the MAST. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 43, 1157–1170.
Smith, S. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17, 143–155.
Snow, W. G., & Weinstock, J. (1990). Sex differences among non-brain-damaged adults on the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scales: A review of the literature. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 12, 873–886.
Sullivan, E. V. (2003). Compromised pontocerebellar and cerebellothalamocortical systems: speculations on their contributions to cognitive and motor impairment in nonamnesic alcoholism. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 27, 1409–1419.
Sullivan, E. V., Adalsteinsson, E., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2006). Selective age-related degradation of anterior callosal fiber bundles quantified in vivo with fiber tracking. Cerebral Cortex, 16, 1030–1039.
Sullivan, E. V., Fama, R., Rosenbloom, M. J., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2002a). A profile of neuropsychological deficits in alcoholic women. Neuropsychology, 16, 74–83.
Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2005). Neurocircuitry in alcoholism: A substrate of disruption and repair. Psychopharmacology, 180, 583–594.
Sullivan, E. V., Pfefferbaum, A., Adalsteinsson, E., Swan, G. E., & Carmelli, D. (2002b). Differential rates of regional change in callosal and ventricular size: A 4-year longitudinal MRI study of elderly men. Cerebral Cortex, 12, 438–445.
Sullivan, E. V., Rosenbloom, M. J., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2000). Pattern of motor and cognitive deficits in detoxified alcoholic men. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 24, 611–621.
Tarter, R. E., & Alterman, A. I. (1984). Neuropsychological deficits in alcoholics: Etiological considerations. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 45, 1–9.
Wechsler, D. (1981). Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—Revised. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Woods, R. P., Grafton, S. T., Holmes, C. J., Cherry, S. R., & Mazziotta, J. C. (1998). Automated image registration: I. General methods and intrasubject, intramodality validation. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 22, 139–152.
Xu, D., Mori, S., Solaiyappan, M., van Zijl, P. C., & Davatzikos, C. (2002). A framework for callosal fiber distribution analysis. NeuroImage, 17, 1131–1143.
Xue, R., van Zijl, P. C., Crain, B. J., Solaiyappan, M., & Mori, S. (1999). In vivo three-dimensional reconstruction of rat brain axonal projections by diffusion tensor imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 42, 1123–1127.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (AA10723, AA12388, AA05965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenbloom, M.J., Sassoon, S.A., Fama, R. et al. Frontal Callosal Fiber Integrity Selectively Predicts Coordinated Psychomotor Performance in Chronic Alcoholism. Brain Imaging and Behavior 2, 74–83 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-007-9017-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-007-9017-9