Abstract
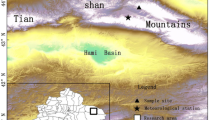
As one of the regions most affected by global climate warming, the Tianshan mountains has experienced several ecological crises, including retreating glaciers and water deficits. Climate warming in these mountains is considered mainly to be caused by increases in minimum temperatures and winter temperatures, while the influence of maximum temperatures is unclear. In this study, a 300-year tree-ring chronology developed from the Western Tianshan Mountains was used to reconstruct the summer (June–August) maximum temperature (Tmax6–8) variations from 1718 to 2017. The reconstruction explained 53.1% of the variance in the observed Tmax6–8. Over the past 300 years, the Tmax6–8 reconstruction showed clear interannual and decadal variabilities. There was a significant warming trend (0.18 °C/decade) after the 1950s, which was close to the increasing rates of the minimum and mean temperatures. The increase in maximum temperature was also present over the whole Tianshan mountains and its impact on climate warming has increased. The Tmax6-8 variations in the Western Tianshan mountains were influenced by frequent volcanic eruptions combined with the influence of solar activity and the summer North Atlantic Oscillation. This study reveals that climate warming is significantly influenced by the increase in maximum temperatures and clarifies possible driving mechanisms of temperature variations in the Western Tianshan mountains which should aid climate predictions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babst F, Wright WE, Szejner P, Wells L, Belmecheri S, Monson RK (2016) Blue intensity parameters derived from Ponderosa pine tree rings characterize intra-annual density fluctuations and reveal seasonally divergent water limitations. Trees-Struct Funct 30(4):1403–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-016-1377-6
Butler PG, Richardson CA, Scourse JD, Wanamaker AD, Shammon TM, Bennell JD (2010) Marine climate in the Irish Sea: analysis of a 489-year marine master chronology derived from growth increments in the shell of the clam Arctica islandica. Quat Sci Rev 29(13–14):1614–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.07.010
Byrne MP (2021) Amplified warming of extreme temperatures over tropical land. Nat Geosci 14(11):837–841. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-021-00828-8
Cai QF, Liu Y, Duan BC, Sun CF (2018) Regional difference of the start time of the recent warming in Eastern China: prompted by a 165-year temperature record deduced from tree rings in the Dabie mountains. Clim Dyn 50(5–6):2157–2168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-017-3741-7
Carrasco VMS (2021) Number of Sunspot groups and individual sunspots recorded by Tevel for the period 1816–1836 in the Dalton minimum. Astrophys J 922(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/ac24a5
Chen W, Zhou Q (2012) Modulation of the arctic oscillation and the east Asian winter climate relationships by the 11-year solar cycle. Adv Atmos Sci 29(2):217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-011-1095-3
Chen J, Wang LL, Zhu HF, Wu P (2009) Reconstructing mean maximum temperature of growing season from the maximum density of the Schrenk Spruce in Yili, Xinjiang, China. Chin Sci Bull 54(09):2300–2308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0051-4
Chen F, Yuan YJ, Yu SL, Chen FH (2019) A 391-year summer temperature reconstruction of the Tien Shan, reveals far-reaching summer temperature signals over the midlatitude Eurasian Continent. J Geophys Res-Atmos 124(22):11850–11862. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD030301
Cohen AS, Gergurich EL, Kraemer BM, McGlue MM, Mclntyre PB, Russell JM, Simmons JD, Swarzenski PW (2016) Climate warming reduces fish production and benthic habitat in lake Tanganyika, one of the most biodiverse freshwater ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(34):9563–9568. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603237113
Cook ER, Meko DM, Stahle DW, Cleaveland MK (1999) Drought reconstructions for the continental United States. J Clim 12(4):1145–1162
Cook ER (1985) A time series approach to tree-ring standardization. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Arizona
Cuny HE, Rathgeber CBK, Frank D, Fonti P, Fournier M (2014) Kinetics of tracheid development explain conifer tree-ring structure. New Phytol 203(4):1231–1241. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12871
Du YB, Zhang J, Zhao SW, Chen HS (2020) Impact of the eastward shift in the negative-phase NAO on extreme drought over northern China in summer. J Geophys Res-Atmos 125(16):e2019JD032019. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032019
Durbin J, Watson GS (1950) Testing for serial correlation in least squares regression. Biometrika 37(3–4):409–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4380-9_20
Fritts HC (1976) Tree rings and climate. Academic Press, New York, pp 162–164
Gao CC, Gao YJ, Zhang Q, Shi CM (2017) Climatic aftermath of the 1815 Tambora eruption in China. J Meteorol Res 31(1):28–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-017-6091-9
Ge QS, Liu LL, Zheng JY, Hao ZX (2016) Spatial patterns of drought/flood over eastern China in the periods of anomalous solar activity during the past millennium. Acta Geogr Sin 71(05):707–717. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb201605001
Gessler A, Brandes E, Buchmann N, Helle G, Rennenberg H, Barnard RL (2009) Tracing carbon and oxygen isotope signals from newly assimilated sugars in the leaves to the tree-ring archive. Plant Cell Environ 32(7):780–795. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01957.x
Gou X, Peng J, Chen F, Yang M, Levia DF, Li J (2008) A dendrochronological analysis of maximum summer half-year temperature variations over the past 700 years on the northeastern Tibetan plateau. Theor Appl Climatol 93(3–4):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0336-y
Hao XM, Li C, Li WH, Zhao RF (2011) Response of climate and hydrology change to North Atlantic and Arctic Oscillation in the west of Northern Xinjiang during the last fifty years. J Desert Res 31(01):191–198 ((in Chinese))
Holmes RL (1983) Computer-assisted quality control in tree-ring dating and measurement. Tree-Ring Bull 43:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1006/biol.1999.0214
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2013–the physical science basis: working group i contribution to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324
Jiang LL, Jiapaer GL, Bao AM, Guo H, Ndayisaba FL (2017) Vegetation dynamics and responses to climate change and human activities in Central Asia. Sci Total Environ 599:967–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.012
Jin LY, Qin NS, Gou XH, Chen FH, Li J (2005) Series of spring maximum temperature in southern Qinghai Plateau and analysis of its variations during the last 450 years. Quat Sci 25(2):193–201. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.02.009
Kagawa A, Sugimoto A, Maximov TC (2006) 13CO2 pulse-labelling of photoassimilates reveals carbon allocation within and between tree rings. Plant Cell Environ 29(8):1571–1584. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01533.x
Kuptz D, Fleischmann F, Matyssek R, Grams TEE (2011) Seasonal patterns of carbon allocation to respiratory pools in 60-yr-old deciduous (Fagus sylvatica) and evergreen (Picea abies) trees assessed via whole-tree stable carbon isotope labeling. New Phytol 191(1):160–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03676.x
Li Q, Liu Y, Nakatsuka T, Liu RS, Cai QF, Song HM, Wang SJ, Sun CF, Fang CX (2020) Delayed warming in Northeast China: insights from an annual temperature reconstruction based on tree-ring δ18O. Sci Total Environ 749:141432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141432
Li P, Song HM, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Fang CX, Li Q, Cai QF, Zeng XL, Ma YF (2022) Maximum july–august temperatures for the middle of the southern Tien Shan inferred from tree-ring latewood maximum densities. Int J Biometeorol 67(2):321–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-022-02408-w
Liu HC, Li M, Shi PH, Liu L, Sun JY (2015) Statistical diagnosis of the relationship between NAO and Bipolar oscillation of summer precipitation over Qinghai-Xizang plateau in multi-time scales. Plateau Meteorol 34(3):633–641. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2015.00031
Liu Y, Li CY, Sun CF, Song HM, Li Q, Cai QF, Liu RS (2020) Temperature variation at the low-latitude regions of East Asia recorded by tree rings during the past six centuries. Int J Climatol 40(3):1561–1570. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6287
Mann ME, Fuentes JD, Rutherford S (2012) Underestimation of volcanic cooling in tree-ring-based reconstructions of hemispheric temperatures. Nat Geosci 5(3):202–205. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1394
Ols C, Hofgaard A, Bergeron Y, Drobyshev I (2016) Previous growing season climate controls the occurrence of black spruce growth anomalies in boreal forests of Eastern Canada. Can J for Res 46(5):696–705. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2015-0404
Panshin AJ, Zeeuw C (1964) Textbook of wood technology. McGraw Hill Book Company Inc, New York
Piovesan G, Biondi F, Di Filippo A, Alessandrini A, Maugeri M (2008) Drought-driven growth reduction in old beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) forests of the central Apennines, Italy. Glob Chang Biol 14(6):1265–1281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01570.x
Rahmanifard F, Wet WC, Schwadron NA, Owens MJ, Jordan AP, Wilson JK, Joyce CJ, Spence HE, Smith CW, Townsend LW (2020) Galactic cosmic radiation in the interplanetary space through a modern secular minimum. Space Weather 18(9):e2019SW002428. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019SW002428
Robock A (2000) Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev Geophys 45(3):RG3005. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998RG000054
Rohde R, Muller RA, Jacobsen R, Muller EA, Perlmutter S, Rosenfeld AH, Wurtele JS, Groom DE, Wickham C (2013) A new estimate of the average earth surface land temperature spanning 1753 to 2011. Geoinfor Geostat: Overv 1:1–7. https://doi.org/10.4172/2327-4581.1000101
Shao XM, Huang L, Liu HB, Liang EY, Fang XQ, Wang LL (2005) Reconstruction of precipitation variation from tree rings in recent 1000 years in Delingha, Qinghai. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 48(7):939–949. https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd0146
Shen XC, Masahide K (2007) Studies of the interannual variability of springtime Eurasian surface air temperature. Chin J Atmos Sci 31(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.01.02
Shi F, Yang B, Gunten L, Qin C, Wang ZY (2012) Ensemble empirical mode decomposition for tree-ring climate reconstructions. Theor Appl Climatol 109(1–2):233–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0576-8
Sorg A, Bolch T, Stofel M, Solomina O, Beniston M (2012) Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat Clim Chang 2:725–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1592
Tao H, Fischer T, Su BD, Mao WY, Jiang T, Fraedrich K (2017) Observed changes in maximum and minimum temperatures in Xinjiang autonomous region. China Int J Climatol 37(15):5120–5128. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5149
Thompson DWJ, Wallace JM (2001) Regional climate impacts of the Northern Hemisphere annular mode. Science 293(5527):85–89. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1058958
Voosen P (2022) Use of ‘too hot’ climate models exaggerates impacts of global warming. Science 376(6594):685. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adc9453
Wang CY, Li M (1990) Analysis of cooling and warming characteristics in Barkol during the last 500 years. Meteorol Xinjiang 13(12):19–22 ((in Chinese))
Wang A, Gao XR, Zhou ZY, Yang H, Zhao XH, Wang YM, Li M, Zhao XN (2022) Dynamic responses of tree-ring growth to drought over Loess plateau in the past three decades. Ecol Indic 143:109423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109423
Wigley TML, Briffa KR, Jones PD (1984) On the average value of correlated time series, with applications in dendroclimatology and hydrometeorology. J Appl Meteorol Clim 23(2):201–213. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0450(1984)023%3c0201:OTAVOC%3e2.0.CO;2
Wu XL, Zhang TX, Wang H, Yu XJ, Zheng XN, Li HY (2020) Characteristics of temperature and precipitation change in Xinjiang during 1961–2017. Desert Oasis Meteorol 14(4):27–34. https://doi.org/10.12057/j.issn.1002-0799.2020.04.004
Wu GL, Cheng Z, Alatalo JM, Zhao JX, Liu Y (2021) Climate warming consistently reduces grassland ecosystem productivity. Earths Future 9(6):e2020EF001837. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020EF001837
Yonenobu H, Eckstein D (2006) Reconstruction of early spring temperature for central Japan from the tree-ring widths of Hinoki cypress and its verification by other proxy records. Geophys Res Lett 33(10):L10701. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL026170
Yu SL, Yuan YJ, Jin HL, Cui Y, Liu B, Lin CL (2005) A 379-year july–august precipitation series reconstructed from tree-ring on the midwestern part of the northern slopes of Tianshan mountains. J Glaciol Geocryol 27(3):404–410. https://doi.org/10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2005.0060
Zhang DE, Liang YY (2010) A long lasting and extensive drought event over China in 1876–1878. Adv Clim Chang Res 1(2):91–99. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1248.2010.00091
Zhang RB, Wei WS, Yuan YJ, Yu SL, Chen F, Zhang TW (2008) Development and climatic significance of the chronologies of tree-ring samples from the Huocheng region, West Tianshan mountains. Arid Zone Res 25(5):716–722. https://doi.org/10.1386/j.azr.2008.05.006
Zhang C, Zhao C, Yu SL, Yang XD, Cheng J, Zhang XJ, Xue B, Shen J, Chen FH (2022) Seasonal imprint of Holocene temperature reconstruction on the Tibetan plateau. Earth Sci Rev 226(71):103927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103927
Zhang L (2010) The dendroclimatological reconstruction and analysis of the south slope on the north Tianshan mountain in Yili, Xinjiang. Master’s dissertation, Xinjiang Normal University (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: This study was supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (2019QZKK0101); the China Desert Meteorological Science Research Foundation (Sqj2022012); the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (2023-JC-QN-0307); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42361144712); the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB40010300); and the State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, CAS (SKLLQG2022).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, M., Liu, Y., Cai, Q. et al. Climate warming is significantly influenced by rising summer maximum temperatures: insights from tree-ring evidence of the Western Tianshan Mountains, China. J. For. Res. 35, 63 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-024-01715-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-024-01715-9