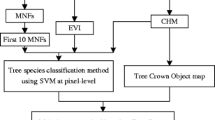
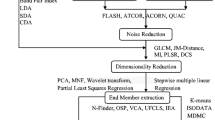
Abstract
Although airborne hyperspectral data with detailed spatial and spectral information has demonstrated significant potential for tree species classification, it has not been widely used over large areas. A comprehensive process based on multi-flightline airborne hyperspectral data is lacking over large, forested areas influenced by both the effects of bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) and cloud shadow contamination. In this study, hyperspectral data were collected over the Mengjiagang Forest Farm in Northeast China in the summer of 2017 using the Chinese Academy of Forestry’s LiDAR, CCD, and hyperspectral systems (CAF-LiCHy). After BRDF correction and cloud shadow detection processing, a tree species classification workflow was developed for sunlit and cloud-shaded forest areas with input features of minimum noise fraction reduced bands, spectral vegetation indices, and texture information. Results indicate that BRDF-corrected sunlit hyperspectral data can provide a stable and high classification accuracy based on representative training data. Cloud-shaded pixels also have good spectral separability for species classification. The red-edge spectral information and ratio-based spectral indices with high importance scores are recommended as input features for species classification under varying light conditions. According to the classification accuracies through field survey data at multiple spatial scales, it was found that species classification within an extensive forest area using airborne hyperspectral data under various illuminations can be successfully carried out using the effective radiometric consistency process and feature selection strategy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Sarria F, Valdivieso-Ros C, Gomariz-Castillo F (2019) Isolation forests to evaluate class separability and the representativeness of training and validation areas in land cover classification. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243000
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Briechle S, Krzystek P, Vosselman G (2020) Uav-based lidar data and multispectral imagery in the 3D deep neural network pointnet. ISPRS Ann Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci 2:203–210
Clark ML, Buck-Diaz J, Evens J (2018) Mapping of forest alliances with simulated multi-seasonal hyperspectral satellite imagery. Remote Sens Environ 210:490–507
Clark ML, Kilham NE (2016) Mapping of land cover in northern California with simulated hyperspectral satellite imagery. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 119:228–245
Colgan MS, Baldeck CA, Féret JB, Asner GP (2012) Mapping savanna tree species at ecosystem scales using support vector machine classification and BRDF correction on airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sens 4:3462–3480
Cross MD, Scambos T, Pacifici F, Marshall WE (2019) Determining effective meter-scale image data and spectral vegetation indices for tropical forest tree species differentiation. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 12:2934–2943
Dalponte M, Ørka HO, Gobakken T, Gianelle D, Næsset E (2013) Tree species classification in boreal forests with hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51:2632–2645
Dian YY, Li ZY, Pang Y (2015) Spectral and texture features combined for forest tree species classification with airborne hyperspectral imagery. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 43:101–107
Fassnacht FE, Latifi H, Stereńczak K, Modzelewska A, Lefsky M, Waser LT, Straub C, Ghosh A (2016) Review of studies on tree species classification from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens Environ 186:64–87
Fassnacht FE, Neumann C, Forster M, Buddenbaum H, Ghosh A, Clasen A, Joshi PK, Koch B (2014) Comparison of feature reduction algorithms for classifying tree species with hyperspectral data on three central european test sites. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 7:2547–2561
Feng BK, Zheng C, Zhang WQ, Wang LG, Yue CR (2020) Analyzing the role of spatial features when cooperating hyperspectral and LiDAR data for the tree species classification in a subtropical plantation forest area. J Appl Remote Sens 14:22213
Ferreira MP, Wagner FH, Aragão LEOC, Shimabukuro YE, de Souza Filho CR (2019) Tree species classification in tropical forests using visible to shortwave infrared worldview-3 images and texture analysis. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 149:119–131
Foody GM (2020) Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sens Environ 239:111630
Franklin SE, Hall RJ, Moskal LM, Maudie AJ, Lavigne MB (2000) Incorporating texture into classification of forest species composition from airborne multispectral images. Int J Remote Sens 21:61–79
Freire S, Santos T, Navarro A, Soares F, Silva JD, Afonso N, Fonseca A, Tenedório J (2014) Introducing mapping standards in the quality assessment of buildings extracted from very high resolution satellite imagery. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 90:1–9
Furniss J, Rahimzadeh-Bajgiran P, Gara TW, Daigle J, Costanza KKL (2022) Mapping ash species across a mixed forest using hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens Lett 13:441–451
Gann D (2019) Quantitative spatial upscaling of categorical information: the multi-dimensional grid-point scaling algorithm. Methods Ecol Evol 10:2090–2104
Ghorbanian A, Mohammadzadeh A (2018) An unsupervised feature extraction method based on band correlation clustering for hyperspectral image classification using limited training samples. Remote Sens Lett 9:982–991
Ghosh A, Fassnacht FE, Joshi PK, Kochb B (2014) A framework for mapping tree species combining hyperspectral and LiDAR data: role of selected classifiers and sensor across three spatial scales. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 26:49–63
Green AA, Berman M, Switzer P, Craig MD (1988) A transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 26:65–74
Gustafson KB, Coates PS, Roth CL, Chenaille MP, Ricca MA, Sanchez-Chopitea E, Casazza ML (2018) Using object-based image analysis to conduct high-resolution conifer extraction at regional spatial scales. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 73:148–155
Haralick RM (1979) Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proc IEEE 67:786–804
Immitzer M, Böck S, Einzmann K, Vuolo F, Pinnel N, Wallner A, Atzberger C (2018) Fractional cover mapping of spruce and pine at 1 ha resolution combining very high and medium spatial resolution satellite imagery. Remote Sens Environ 204:690–703
Jia W, Pang Y, Tortini R, Schläpfer D, Li ZY, Roujean JL (2020) A kernel-driven BRDF approach to correct airborne hyperspectral imagery over forested areas with rugged topography. Remote Sens 12(3):432
Jones TG, Coops NC, Sharma T (2010) Assessing the utility of airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data for species distribution mapping in the coastal Pacific Northwest, Canada. Remote Sens Environ 114:2841–2852
Ju JC, Gopal S, Kolaczyk ED (2005) On the choice of spatial and categorical scale in remote sensing land cover classification. Remote Sens Environ 96:62–77
Kang YP, Hu XL, Meng QY, Zou YF, Zhang LL, Liu M, Zhao MF (2021) Land cover and crop classification based on red edge indices features of gf-6 wfv time series data. Remote Sens 13:1–22
Kattenborn T, Lopatin J, Förster M, Braun AC, Fassnacht FE (2019) UAV data as alternative to field sampling to map woody invasive species based on combined Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens Environ 227:61–73
Kavzoglu T (2009) Increasing the accuracy of neural network classification using refined training data. Environ Model Softw 24:850–858
Ke YH, Quackenbush LJ, Im J (2010) Synergistic use of QuickBird multispectral imagery and LIDAR data for object-based forest species classification. Remote Sens Environ 114:1141–1154
Kishore BSPC, Kumar A, Saikia P, Lele N, Pandey AC, Srivastava P, Bhattacharya BK, Khan ML (2020) Major forests and plant species discrimination in mudumalai forest region using airborne hyperspectral sensing. J Asia Pac Biodivers 13:637–651
Kramm T, Hoffmeister D, Curdt C, Maleki S, Khormali F, Kehl M (2017) Accuracy assessment of landform classification approaches on different spatial scales for the iranian loess plateau. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inf 6:366
Kudela RM, Hooker SB, Houskeeper HF, McPherson M (2019) The influence of signal to noise ratio of legacy airborne and satellite sensors for simulating next-generation coastal and inland water products. Remote Sens 11:2071
Lawrence RL, Ripple WJ (1998) Comparisons among vegetation indices and bandwise regression in a highly disturbed, heterogeneous landscape: Mount St. Helens, Washington. Remote Sens Environ 64:91–102
Laybros A, Schläpfer D, Féret JB, Descroix L, Bedeau C, LefevreVincent MJ (2019) Across date species detection using airborne imaging spectroscopy. Remote Sens 11:1–24
Li JL, Pang Y, Li ZY, Jia W (2018a) Tree species classification of airborne hyperspectral image in cloud shadow area. In: International symposium of space optical instrument and application. Springer, pp 389–398
Li JL, Pang Y, Li ZY, Jia W (2019) Tree species classification by airborne hyperspectral image of forest in cloud shadow area. For Res 32:136–141
Li J, Wu ZC, Hu ZW, Li ZL, Wang YS, Molinier M (2021) Deep learning based thin cloud removal fusing vegetation red edge and short wave infrared spectral information for sentinel-2A imagery. Remote Sens 13:1–31
Li JJ, Xi BB, Li YS, Du Q, Wang KY (2018b) Hyperspectral classification based on texture feature enhancement and deep belief networks. Remote Sens 10(3):396
Li ZW, Shen HF, Li HF, Xia GS, Gamba P, Zhang LP (2017) Multi-feature combined cloud and cloud shadow detection in GaoFen-1 wide field of view imagery. Remote Sens Environ 191:342–358
Lin Y, Hyyppä J (2016) A comprehensive but efficient framework of proposing and validating feature parameters from airborne LiDAR data for tree species classification. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 46:45–55
Liu LX, Coops NC, Aven NW, Pang Y (2017) Mapping urban tree species using integrated airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 200:170–182
Liu T, Abd-Elrahman A (2018) Multi-view object-based classification of wetland land covers using unmanned aircraft system images. Remote Sens Environ 216:122–138
Luo RB, Liao WZ, Zhang HY, Zhang LP, Scheunders P, Pi YG, Philips W (2017) Fusion of hyperspectral and LiDAR data for classification of cloud-shadow mixed remote sensed scene. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 10:3768–3781
Ma L, Li MC, Ma XX, Cheng L, Du PJ, Liu YX (2017) A review of supervised object-based land-cover image classification. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 130:277–293
Man QX, Dong PL, Yang XM, Wu QY, Han RQ (2020) Automatic extraction of grasses and individual trees in urban areas based on airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sens 12:1–22
Martínez-Usó A, Pla F, Sotoca JM, García-Sevilla P (2007) Clustering-based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45:4158–4171
Maschler J, Atzberger C, Immitzer M (2018) Individual tree crown segmentation and classification of 13 tree species using airborne hyperspectral data. Remote Sens 10:1218
Meerdink SK, Roberts DA, Roth KL, King JY, Gader PD, Koltunov A (2019) Classifying california plant species temporally using airborne hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens Environ 232:111308
Modzelewska A, Fassnacht FE, Stereńczak K (2020) Tree species identification within an extensive forest area with diverse management regimes using airborne hyperspectral data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 84:101960
Modzelewska A, Kamińska A, Fassnacht FE, Stereńczak K (2021) Multitemporal hyperspectral tree species classification in the Białowieża Forest World Heritage site. For an Int J for Res 94:464–476
Mostafa Y, Abdelhafiz A (2017) Accurate shadow detection from high-resolution satellite images. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14:494–498
Nagendra H, Gadgil M (1999) Biodiversity assessment at multiple scales: linking remotely sensed data with field information. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:9154–9158
Pang Y, Li ZY, Ju HB, Lu H, Jia W, Si L, Guo Y, Liu QW, Li SM, Liu LX, Xie BB, Tan BX, Dian YY (2016) LiCHy: the CAF’s LiDAR, CCD and hyperspectral integrated airborne observation system. Remote Sens 8(5):398
Pontius J, Hanavan RP, Hallett RA, Cook BD, Corp LA (2017) High spatial resolution spectral unmixing for mapping ash species across a complex urban environment. Remote Sens Environ 199:360–369
Pontius RG, Millones M (2011) Death to kappa: birth of quantity disagreement and allocation disagreement for accuracy assessment. Int J Remote Sens 32:4407–4429
Pu RL (2021) Mapping tree species using advanced remote sensing technologies: a state-of-the-art review and perspective. J Remote Sens 2021:1–26
Pu RL, Landry S, Yu QY (2018) Assessing the potential of multi-seasonal high resolution Pléiades satellite imagery for mapping urban tree species. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 71:144–158
Puissant A, Hirsch J, Weber C (2005) The utility of texture analysis to improve per-pixel classification for high to very high spatial resolution imagery. Int J Remote Sens 26:733–745
Qi YJ (2012) Random forest for bioinformatics. In: Ensemble machine learning. Springer, Boston, MA, pp 307–323
Queally N, Ye ZW, Zheng T, Chlus A, Schneider F, Pavlick RP, Townsend PA (2022) FlexBRDF: A flexible BRDF correction for grouped processing of airborne imaging spectroscopy flightlines. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 127:e2021JG006622
Rahimzadeh-Bajgiran P, Hennigar C, Weiskittel A, Lamb S (2020) Forest potential productivity mapping by linking remote-sensing-derived metrics to site variables. Remote Sens 12:2056
Roth KL, Roberts DA, Dennison PE, Peterson SH, Alonzo M (2015) The impact of spatial resolution on the classification of plant species and functional types within imaging spectrometer data. Remote Sens Environ 171:45–57
Roujean JL, Leroy M, Deschamps PY (1992) A bidirectional reflectance model of the Earth’s surface for the correction of remote sensing data. J Geophys Res 97:20455
Sánchez de Miguel A, Kyba CCM, Aubé M, Zamorano J, Cardiel N, Tapia C, Bennie J, Gaston KJ (2019) Colour remote sensing of the impact of artificial light at night (I): the potential of the International Space Station and other DSLR-based platforms. Remote Sens Environ 224:92–103
Schläpfer D, Hueni A, Richter R (2018) Cast shadow detection to quantify the aerosol optical thickness for atmospheric correction of high spatial resolution optical imagery. Remote Sens 10 (2): 200
Schlapfer D, Richter R, Feingersh T (2015) Operational BRDF effects correction for wide-field-of-view optical scanners (BREFCOR). IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53:1855–1864
Shang C, Treitz P, Caspersen J, Jones T (2017) Estimating stem diameter distributions in a management context for a tolerant hardwood forest using ALS height and intensity data. Can J Remote Sens 43:79–94
Shao GF, Tang LN, Liao JF (2019) Overselling overall map accuracy misinforms about research reliability. Landsc Ecol 34:2487–2492
Shao GF, Tang LN, Zhang H (2021) Introducing image classification efficacies. IEEE. Access 9:134809–134816
Shen X, Cao L (2017) Tree-species classification in subtropical forests using airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sens 9(11):1180
Shen X, Cao L, Coops NC, Fan HC, Wu XQ, Liu H, Wang GB, Cao FL (2020) Quantifying vertical profiles of biochemical traits for forest plantation species using advanced remote sensing approaches. Remote Sens Environ 250:112041
Shi YF, Skidmore AK, Wang TJ, Holzwarth S, Heiden U, Pinnel N, Zhu X, Heurich M (2018) Tree species classification using plant functional traits from LiDAR and hyperspectral data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 73:207–219
Stehman SV, Wickham JD (2011) Pixels, blocks of pixels, and polygons: Choosing a spatial unit for thematic accuracy assessment. Remote Sens Environ 115:3044–3055
Sun H, Ren JC, Zhao HM, Sun GY, Liao WZ, Fang ZY, Zabalza J (2022) Adaptive distance-based band hierarchy (ADBH) for effective hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans Cybern 52:215–227
Sun WW, Du Q (2019) Hyperspectral band selection: A review. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Mag 7:118–139
Tane Z, Roberts D, Koltunov A, Sweeney S, Ramirez C (2018) A framework for detecting conifer mortality across an ecoregion using high spatial resolution spaceborne imaging spectroscopy. Remote Sens Environ 209:195–210
Trier ØD, Salberg AB, Kermit M, Rudjord Ø, Gobakken T, Næsset E, Aarsten D (2018) Tree species classification in Norway from airborne hyperspectral and airborne laser scanning data. Eur J Remote Sens 51:336–351
van Aardt JAN, Wynne RH (2007) Examining pine spectral separability using hyperspectral data from an airborne sensor: An extension of field-based results. Int J Remote Sens 28:431–436
Wang MY, Zheng Y, Huang CQ, Meng R, Pang Y, Jia W, Zhou J, Huang ZH, Fang LC, Zhao F (2022) Assessing Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 spectral-temporal features for mapping tree species of northern plantation forests in Heilongjiang Province, China. For Ecosyst 9:100032
Waser LT, Ginzler C, Rehush N (2017) Wall-to-Wall tree type mapping from countrywide airborne remote sensing surveys. Remote Sens 9(8):766
Waser LT, Küchler M, Jütte K, Stampfer T (2014) Evaluating the potential of worldview-2 data to classify tree species and different levels of ash mortality. Remote Sens 6:4515–4545
Wetherley EB, Roberts DA, McFadden JP (2017) Mapping spectrally similar urban materials at sub-pixel scales. Remote Sens Environ 195:170–183
Whiteside TG, Maier SW, Boggs GS (2014) International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation Area-based and location-based validation of classified image objects. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 28:117–130
Wietecha M, Jełowicki Ł, Mitelsztedt K, Miścicki S, Stereńczak K (2019) The capability of species-related forest stand characteristics determination with the use of hyperspectral data. Remote Sens Environ 231:111232
Wu YS, Zhang XL (2020) Object-Based tree species classification using airborne hyperspectral images and LiDAR data. Forests 11(1):32
Xiao CW, Li P, Feng ZM, Liu YY, Zhang XZ (2020) Sentinel-2 red-edge spectral indices (RESI) suitability for mapping rubber boom in Luang Namtha Province, northern Lao PDR. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 93:102176
Xu NX, Tian J, Tian QJ, Xu KJ, Tang SF (2019) Analysis of vegetation red edge with different illuminated/shaded canopy proportions and to construct normalized difference canopy shadow index. Remote Sens 11:1–16
Zhai H, Zhang HY, Zhang LP, Li PX (2018) Cloud/shadow detection based on spectral indices for multi/hyperspectral optical remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 144:235–253
Zhang B, Zhao L, Zhang XL (2020a) Three-dimensional convolutional neural network model for tree species classification using airborne hyperspectral images. Remote Sens Environ 247:111938
Zhang GC, Cerra D, Müller R (2020b) Shadow detection and restoration for hyperspectral images based on nonlinear spectral unmixing. Remote Sens 12:1–22
Zhang YL, Bai YL, Li CH (2014) Topographic normalization of Landsat TM images in rugged terrain. In: Proceeding of 2014 7th international congress on image and signal processing CISP, pp 580–585
Zhou WQ, Huang GL, Troy A, Cadenasso ML (2009) Object-based land cover classification of shaded areas in high spatial resolution imagery of urban areas: a comparison study. Remote Sens Environ 113:1769–1777
Zhu Z, Wang SX, Woodcock CE (2015) Improvement and expansion of the Fmask algorithm: cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection for Landsats 4–7, 8, and Sentinel 2 images. Remote Sens Environ 159:269–277
Acknowledgements
The Mengjiagang Forest Farm provides the forest inventory data and access to their forests. We thank the graduate students (Junling Li, Xiaoyun Xia, Xiaojun Liang, Hao Xiong and Yu Bai) from Chinese Academy of Forestry and Prof. Weiwei Jia from Northeast Forestry University for their help in the fieldwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project Funding: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42101403), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFD0600404).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, W., Pang, Y. Tree species classification in an extensive forest area using airborne hyperspectral data under varying light conditions. J. For. Res. 34, 1359–1377 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01593-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01593-z