Abstract
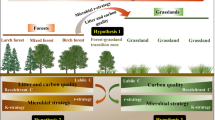
Vegetation types alter soil ecosystems by changing soil fauna community activities and soil physical–chemical properties. However, it is unclear how tree species (natural forest, native and exotic tree plantations) promote changes in the soil ecosystem, and if these changes alter functional groups of soil fauna and ecosystem services. To determine the effects of five decades of old-field vegetation on soil ecosystems in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest, field sampling of three ecosystems (exotic tree species Pinus elliottii Engelm. plantation, endangered tree species Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze plantation, and a natural ecosystem) were carried out, as well using bait-lamina tests and bioassays with collembolans, earthworms and seeds of Lactuca sativa L. Field sampling evaluated the soil fauna community and soil physical–chemical properties. The bait-lamina test in situ was carried out for 14-days to determine fauna feeding activity, and the bioassays evaluated the reproduction of Folsomia candida, the avoidance of Eisenia andrei, and germination of L. sativa in the soil from each ecosystem. The results are: (1) vegetation type altered the soil fauna community composition; (2) soil fauna feeding was reduced in the plantations compared to the natural ecosystem; (3) a physical barrier was created by recalcitrant litter that compromised fauna community structure and seed bank germination in situ; and, (4) changes in soil physical–chemical properties promoted decomposers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JN, Ingram JSI (1989) Tropical soil biology and fertility: a handbook of methods. CAB International, Wallingford
Anwar T, Ilyas N, Qureshi R, Munazir M, Rahim BZ, Qureshi H, Kousar R, Maqsood M, Abbas Q, Bhatti MI, Panni MK (2018) Allelopathic potential of Pinus roxburghii needles against selected weeds of wheat crop. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17(2):1717–1739
Ashwood F, Vanguelova EL, Benham S, Butt KR (2019) Developing a systematic sampling method for earthworms in and around deadwood. For Ecosyst 6:33
Aupic-Samain A, Baldy V, Lecareux C, Fernandez C, Santonja M (2019) Tree litter identity and predator density control prey and predator demographic parameters in a mediterranean litter-based multi-trophic system. Pedobiologia 73:1–9
Baretta D, Ferreira CS, Sousa JP, Cardoso EJBN (2008) Colêmbolos (Hexapoda: Collembola) como bioindicadores de qualidade do solo em áreas com Araucaria angustifolia. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo 32:2693–2699
Basirat M, Mousavi SM, Abbaszadesh S, Ebrahimi M, Zarebanadkouki M (2019) The rhizoshealth: a potential root trait helping plants to tolerate drought stress. Plant Soil 445:565–575
Bechara FC, Reis A, Bourscheid K, Vieira NK, Trentin BE (2013) Reproductive biology and early establishment of Pinus elliottii var. elliottii in Brazilian sandy coastal plant vegetation: implications for biological invasion. Scientia Agricola 70:89–92
Bechara FC, Reis A, Trentin BE (2014) Invasão biológica de Pinus elliottii Engelm. var. elliottii no parque estadual do rio vermelho, florianópolis. SC Floresta 44:63–72
Bezkorovaynaya IN, Egunova MN, Taskaeva AA (2017) Soil invertebrates and their trophic activity in 40-year-old forest stands. Contemp Probl Ecol 10(5):524–533
Black CA (1965) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. In: Black CA (ed) Agronomy Monograph. American Society of Agronomy, Madison
Cardinael R, Hoeffner K, Chenu C, Chevallier T, Béral C, Dewisme A, Cluzeau D (2018) Spatial variation of earthworm communities and soil organic carbon in temperate agroforestry. Biol Fertil Soils 55:171–183
Chae HM, Choi SH, Lee SH, Cha S, Yang KC, Shim JK (2019) Effect of litter quality on needle decomposition for four Pine species in Korea. Forests 10(5):371
Chen X, Hao B, Jing X, He J-S, Ma W, Zhu B (2019) Minor responses of soil microbial biomass, community structure and enzyme activities to nitrogen and phosphorus addition in three grassland ecosystems. Plant Soil 444:21–37
Chomel M, Fernandez C, Bousquet-Mélou A, Gers C, Monnier Y, Santonja M, Baldy V (2014) Secondary metabolites of Pinus halepensis alter decomposer organisms and litter decomposition during afforestation of abandoned agricultural zones. J Ecol 102(2):411–424
Choo J, Gill BD, Zuur AF, Zent E, Economo EP (2020) Impacts of an indigenous settlement on the taxonomic and functional structure of dung beetle communities in the venezuelan amazon. Biodivers Conserv 29:207–228
Crotty FV, Fychan JS, Sanderson R, Marley CI (2015) Assessing the impact of agricultural forage crops on soil biodiversity and abundance. Soil Biol Biochem 91:119–126
Duval BD, Curtsinger HD, Hands A, Martin J, McLaren JR, Cadol DD (2020) Greenhouse gas emissions and extracellular enzyme activity variability during decomposition of native versus invasive riparian tree litter. Plant Ecol 221:177–189
Ferreira DK, Nazareno AG, Mantovani A, Bittencourt R, Sebbenn AM, Dos Reis MS (2011) Genetic analysis of 50-year old Brazilian pine (Araucaria angustifolia) plantations: implications for conservation planning. Conserv Genet 13:435–442
Fockink GD, Pech TM, Silva M, Siminski A, Niemeyer JC (2019) Influence of aciculas deposition on natural regeneration in sub-woods of Pinus taeda L. forest stand. Floresta 50(1):1071–1080
Garcia MVB (2004) Effects of pesticides on soil fauna: development of ecotoxicological test methods for tropical regions. In: Ecology and Development Series 19. University of Bonn, Germany
Ge T, Luo Y, He X (2019) Quantitative and mechanistic insights into the key process in the rhizodeposited carbon stabilization, transformation and utilization of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in paddy soils. Plant Soil 445:1–5
Gioria M, Jarosik V, Pysec P (2014) Impact of invasive alien plants in the soil seed bank: Emerging patterns. Perspect Plant Ecol, Evolution Syst 16:132–142
Gioria M, Pysec P (2016) The legacy of plant invasions: changes in the soil seed bank of invaded plant communities. Bioscience 66:40–53
Gioria M, Pysec P, Moravcová L (2012) Soil seed banks in plant invasions: Promoting species invasiveness and long-term impact on plant community dynamics. Preslia 84:327–250
Gittleman JL, Kot M (1990) Adaptation: statistics and a null model for estimating phylogenetic effects. Syst Biol 39(3):227–241
Goss-Souza D, Mendes LM, Rodrigues JLM, Tsai SM (2019) Ecological processes shaping buld soil and rhizosphere microbiome assembly in a long-term Amazon forest-to-agriculture conversion. Microb Ecol 79:110–122
Guareschi S, Laini A, Viaroli P, Bolpagni R (2020) Integrating habitat- and species-based perspectives for wetland conservation in lowland agricultural landscapes. Biodivers Conserv 29:153–171
IITA (1979) Selected methods for soil and plant analysis. IITA (International Institute of Tropical Agriculture) Manual Series no.1, Ibadan
ISO - International Organization for Standardization (2016) ISO 18311: Soil quality—method for testing effects of soil contaminants on the feeding activity of soil dwelling organisms—bait-lamina test. ISO, Geneva
ISO - International Organization for Standardization (2008) ISO 17512–1: Soil quality e avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects on behaviour. Part 1: Test with Earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). ISO, Geneva
ISO - International Organization for Standardization (2014) ISO 11267: Soil quality e inhibition of reproduction of collembola (Folsomia candida) by soil pollutants. ISO, Geneva
Jo I, Fridley JD, Frank DA (2020) Rapid leaf litter decomposition of deciduous understory shrubs and lianas mediated by mesofauna. Plant Ecol 22:63–68
Kamau S, Barrios E, Karanja NK, Ayuke FO, Lehmann J (2020) Dominant tree species and earthworms affect soil aggregation and carbon content along a soil degradation gradient in an agricultural landscape. Geoderma 359:113983
Kimura F, Sato M, Kato-Noguchi H (2015) Allelopathy of pine litter: delivery of allelopathic substances into forest floor. J Plant Biology 58:61–67
Leandro LF, Cardoso MJ, Silva SD, Souza MG, Veneziani RC, Ambrosio SR, Martins CH (2014) Antibacterial activity of Pinus elliottii and its major compound, dehydroabietic acid, against multidrug-resistant strains. J Med Microbiol 63:1649–1653
Liao C, Xavier JB, Zhu Z (2020) Enhanced inference of ecological networks by parameterizing ensembles of population dynamics models constrained with prior knowledge. BMC Ecol 20:3
Liu H, Ding Y, Zhang Q, Liu X, Xu J, Li Y, Di H (2019) Heterotrophic nitrification and denitrification are the main sources of nitrous oxide in two paddy soils. Plant Soil 445:39–53
Martins C, Natal-da-Luz T, Sousa JP, Gonçalves MJ, Salgueiro L, Canhoto C (2013) Effects of essential oils from Eucalyptus globulus leaves on soil organisms involved in leaf degradation. PLoS ONE 8(4):e61233
McTavish MJ, Gorgolewski A, Murphy SD, Basiliko N (2020) Anecic earthworms (Lumbricus terrestris) facilitate the burial of surface-applied wood ash. Biol Fertil Soils 56:195–203
Melo LN, Souza TAF, Santos D (2019) Cover crop farming system affect macroarthropods community diversity of caatinga, Brazil. Biologia 74:1653–1660
Myer A, Forschler BT (2019) Evidence for the role of subterranean termites (Reticulitermes spp.) in temperate forest soil nutrient cycling. Ecosystems 22:602–618
Okalebo JR, Gathua KW, Woomer PL (1993) Laboratory methods of plant and soil analysis: a working manual. TSBF, UNESCO-ROSTA, Nairobi
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanable FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorous in soils by extraction with Sodium bicarbonate. US Department of Agriculture, Washigton DC, USA
Ortiz DC, Santos MAB, Oliveira-Filho LCI, Pompeo PN, Niemeyer JC, Klauberg-Filho O, Baretta CRDM, Sampietro JA, Baretta D (2019) Diversity of springtails (Collembola) in agricultural and forest systems in Southern Santa Catarina. Biota Neotrop 19(3):e20180720
Pielou EC (1969) An introduction to mathematical ecology. Wiley, New York
Podgaiski LR, Silveira FS, Mendonça M Jr (2011) Avaliação da atividade alimentar dos invertebrados de solo em campos do sul do Brasil – bait-lamina test. EntomoBrasilis 4(3):108–113
Pompermaier VT, Kisaka TB, Ribeiro JF, Nardoto GB (2020) Impact of exotic pastures on epigeic arthropod diversity and contribution of native and exotic plant sources to their diet in the central Brazilian savanna. Pedobiologia 78:150607
Ponge JF (1991) Succession of fungi and fauna during decomposition of needles in a small area of scots pine litter. Plant Soil 138(1):99–113
Prayogo C, Sholehuddin N, Putra EZHS, Rachmawati R (2019) Soil macrofauna diversity and structure under different management of pine-coffee agroforestry system. J Degrad Min Lands Manag 6(3):1727–1736
R Core Team (2018) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Ribeiro-Troian VR, Baldissera R, Hartz SM (2009) Effects of understory structure on the abundance, richness and diversity of collembola (Arthropoda) in Southern Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 38(3):340–345
Rożen A, Sobczyk Ł, Liszka K, Weiner J (2010) Soil faunal activity as measured by the bait-lamina test in monocultures of 14 tree species in the Siemianice common-garden experiment, Poland. Appl Soil Ecol 45:160–167
Roy S, Roy MM, Jaiswal AK, Baitha A (2018) Soil arthropods in maintaining soil health: thrust areas for sugarcane production systems. Sugar Tech 20:376–391
Santonja M, Baldy V, Fernandez C, Balesdent J, Gauquelin T (2015) Potential shift in plant communities with climate change: outcome on litter decomposition and nutrient release in a mediterranean oak forest. Ecosystems 18(7):1253–1268
Santonja M, Bousquet-Mélou A, Greff S, Ormeño E, Fernandez C (2019) Allelopathic effects of volatile organic compounds released from Pinus halepensis needles and roots. Ecol Evol 9:8201–8213
Santos MAB, Oliveira-Filho LCI, Pompeo PN, Ortiz DC, Mafra AL, Klauberg-Filho O, Baretta D (2018) Morphological diversity of springtails in land use systems. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo 42:e0170277
Sartor LR, Adami PF, Chini NM, Thomas N, Marchese JA, Soares AB (2009) Alelopatia de acículas de Pinus taeda na germinação e no desenvolvimento de plântulas de Avena strigosa. Ciência Rural 39(6):1653–1659
Schmitz D, Schaefer CERG, Putzke J, Francelino MR, Ferrari FR, Corrêa GR, Villa PM (2020a) How does the pedoenvironmental gradient shape non-vascular species assemblages and community structures in Maritime Antarctica? Ecol Indic 108:105726
Schmitz D, Villa PM, Schaefer CEGR, Francelino MR (2020b) Avaliação de gradiante pedoambiental usando análise de components principais (PCA) na Antártica Marítima. In: Diniz ES, Villa PM (org) Aplicações da linguagem R em análises de vegetação. Atena, Ponta Grossa, Brazil
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to imageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Shannon C, CE, Weaver W, (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Shiferaw W, Bekele T, Demissew S, Aynekulu E (2019) Prosopis juliflora invasion and environmental factors on density of soil seed bank in Afar Region, Northeast Ethiopia. J Ecol Environ 43:41
Souza TAF, Andrade LA, Freitas H, Sandim AS (2017) Biological invasion influences the outcome of plant-soil feedback in the invasive plant-species from the Brazilian semi-arid. Microb Ecol 76:102–112
Souza TAF, Freitas H (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community assembly in the Brazilian tropical seasonal dry forest. Ecol Process 6:1–10
Souza TAF, Freitas H (2018) Long-term effects of fertilization on soil organism diversity. In: Gaba S, Smith B, Lichtfouse E (eds) Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 28. Springer, New York, pp 211–247
Souza TAF, Rodrígues AF, Marques LF (2016) Long-term effects of alternative and conventional fertilization on macroarthropod community composition: a field study with wheat (Triticum aestivum L) cultivated on a ferralsol. Org Agric 6:323–330
Souza TAF, Santos D, Andrade LA, Freitas H (2019) Plant-soil feedback of two legume species in semi-arid Brazil. Braz J Microbiol 50:1011–1020
Tesfaye MA, Gardi O, Anbessa TB, Blaser J (2020) Aboveground biomass, growth and yield for some selected introduced tree species, namely Cupressus lusitanica, Eucalyptus saligna, and Pinus patula in central highlands of ethiopia. J Ecol Environ 44:3
Tigre RC, Silva NH, Santos MG, Honda NK, Falcão EPS, Pereira EC (2012) Allelopathic and bioherbicidal potential of Cladonia verticillaris on the germination and growth of Lactuca sativa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:125–132
Trentini CP, Villagra M, Gómez Pámies D, Bernava Laborde V, Bedano JC, Campanello PI (2018) Effect of nitrogen addition and litter removal on understory vegetation, soil mesofauna, and litter decomposition in loblolly pine plantations in subtropical Argentina. For Ecol Manage 429:133–142
Vestgarden LS, Nilsen P, Abrahamsen G (2004) Nitrogen cycling in Pinus sylvestris stands exposed to different nitrogen inputs. Scand J for Res 19:38–47
von Torne E (1990) Assessing feeding activities of soil-living animals. I Bait-Lamina Tests Pedobiologia 34(2):89–101
WRB - IUSS Working Group (2007) World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2006, first update 2007. World Soil Resources Reports No. 103. FAO, Rome
Yang B, Zhang W, Xu H, Wang S, Xu X, Fan H, Chen HYH, Ruan H (2018) Effects of soil fauna on leaf litter decomposition under different land used in eastern coast of China. J for Res 29:973–982
Ziller SR, Galvão F (2003) Environmental degradation of a grassland ecosystem in Parana state with biological invasions of Pinus elliottii and P. taeda. Floresta 32:41–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project Funding: This project has no funding.
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Yanbo Hu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz, D.C., de Souza, T.A.F., Pech, T.M. et al. Soil ecosystem changes by vegetation on old-field sites over five decades in the Brazilian Atlantic forest. J. For. Res. 33, 667–677 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-021-01368-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-021-01368-y