Abstract
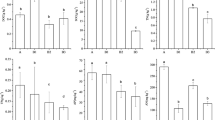
This study explores the effects of vegetation and season on soil microorganisms and enzymatic activity of different wetlands in a temperate climate. Microbial carbon metabolism diversity was assessed using community-level physiological profiles (CLPP) with 31 different carbon substrates. CLPP indicated that significant interactions occur during carbon substrate metabolism of the microorganisms. Furthermore, the different types of vegetation present in the wetland ecosystem combined with the seasonal effects to influence microbial carbon metabolism and enzymatic activity. The most significant differences occurred to carbohydrates, carboxylic acids, and amino acids. The Mantel test confirmed positive correlations between soil enzymatic activities and microbial carbon metabolism. Soil microorganisms in Betula ovalifolia and Carex schmidtii wetlands used carbon substrates more efficiently in summer than those in other forested wetlands during other periods. Enzymatic activities also showed a similar trend as microbial carbon metabolism. The results demonstrate that microbial carbon metabolism patterns can be used as biological indicators in wetland ecological alterations due to vegetation type or to seasonal factors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison SD, Vitousek PM (2005) Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs. Soil Biol Biochem 37(5):937–944
Allison VJ, Yermakov Z, Miller RM, Jastrow JD, Matamala R (2007) Using landscape and depth gradients to decouple the impact of correlated environmental variables on soil microbial community composition. Soil Biol Biochem 39(2):505–516
Anderson CJ, Lockaby BG (2011) Forested wetland communities as indicators of tidal influence along the Apalachicola River, Florida, USA. Wetlands 31(5):895–906
Andruschkewitsch M, Wachendorf C, Sradnick A, Hensgen F, Joergensen RG, Wachendorf M (2014) Soil substrate utilization pattern and relation of functional evenness of plant groups and soil microbial community in five low mountain NATURA 2000. Plant Soil 383:275–289
Baddam R, Reddy GB, Raczkowski C, Cyrus JS (2016) Activity of soil enzymes in constructed wetlands treated with swine wastewater. Ecol Eng 91:24–30
Baldrian P, Šnajdr J, Merhautová V, Dobiášová P, Cajthaml T, Valášková V (2013) Responses of the extracellular enzyme activities in hardwood forest to soil temperature and seasonality and the potential effects of climate change. Soil Biol Biochem 56:60–68
Bandick AK, Dick RP (1999) Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1471–1479
Banning NC, Lalor BM, Cookson WR, Grigg AH, Murphy DV (2012) Analysis of soil microbial community level physiological profiles in native and post-mining rehabilitation forest: which substrates discriminate? Appl Soil Ecol 56:27–34
Barreiro A, Fontúrbel MT, Lombao A, Martín A, Vega JA, Fernández C, Carballas T, Díaz-Raviña M (2015) Using phospholipid fatty acid and community level physiological profiling techniques to characterize soil microbial communities following an experimental fire and different stabilization treatments. CATENA 135:419–429
Bastida F, Barbera GG, Garcia C, Hernandez T (2008) Influence of orientation, vegetation and season on soil microbial and biochemical characteristics under semiarid conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 38(1):62–70
Bergamaschi P, Frankenberg C, Meirink JF, Krol M, Dentener F, Wagner T, Platt U, Kaplan JO, Korner S, Heimann M, Dlugokencky EJ, Goede A (2007) Satellite chartography of atmospheric methane from SCIAMACHY on board ENVISAT: 2. Evaluation based on inverse model simulations. J Geophys Res: Atmos 112:02304
Bergstrom DW, Monreal CM, King DJ (1998) Sensitivity of soil enzyme activitiesto conservation practices. Soil Sci Soc Am 62:1286–1295
Bissegger S, Rodriguez M, Brisson J, Weber KP (2014) Catabolic profiles of microbial communities in relation to plant identity and diversity in free-floating plant treatment wetland mesocosms. Ecol Eng 67:190–197
Boyce RL, Durtsche RD, Fugal SL (2012) Impact of the invasive shrub Lonicera maackii on stand transpiration and ecosystem hydrology in a wetland forest. Biol Invasions 14(3):671–680
Brimecombe MJ, De Leij FA, Lynch JM (2007) Rhizodeposition andmicrobial populations. The rhizosphere, biochemistry and organic substances at the soil-plant interface, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 73–140
Brockett BFT, Prescott CE, Grayston SJ (2012) Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biol Biochem 44(1):9–20
Cai TJ, Xin GH, Zhang YW, Dai XX, Liu B (2010) Characteristic of soil organic carbon of the Sphagnum spp. wetland in Xiao Hinggan Mountains. Sci Soil Water Conserv 8(5):109–113
Cai XQ, Lin ZW, Penttinen P, Li YF, Li YC, Luo Y, Yue T, Jiang PK, Fu WJ (2018) Effects of conversion from a natural evergreen broadleaf forest to a Moso bamboo plantation on the soil nutrient pools, microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a subtropical area. For Ecol Manag 422:161–171
Campos A, Hernandez ME, Moreno-Casasola P, Espinosa EC, Robledo A, Mata DI (2011) Soil water retention and carbon pools in tropical forested wetlands and marshes of the Gulf of Mexico. Hydrol Sci J-J Des Sci Hydrol 56(8):1388–1406
Chavarría DN, Verdenelli RA, Muñoz EJ, Conforto C, Restovich SB, Andriulo AE, Meriles JM, Vargas-Gil S (2016) Soil microbial functionality in response to the inclusion of cover crop mixtures in agricultural systems. Span J Agric Res 14(2):e0304
Chodak M, Klimek B, Azarbad H, Jazwa M (2015) Functional diversity of soil microbial communities under Scots pine, Norway spruce, silver birch and mixed boreal forests. Pedobiologia: J Soil Ecol 58(2–3):81–88
Chodak M, Klimek B, Niklińska M (2016) Composition and activity of soil microbial communities in different types of temperate forests. Biol Fertil Soils 52:1093–1104
Chou YM, Shen FT, Chiang SC, Chang CM (2017) Functional diversity and dominant populations of bacteria in banana plantation soils as influenced by long-term organic and conventional farming. Appl Soil Ecol 110:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.11.002
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Classen AT, Boyle SI, Haskins KE, Overby ST, Hart SC (2003) Community level physiological profiles of bacteria and fungi: Plate type and incubation temperature influences on contrasting soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44:319–328
Correa-Araneda FJ, Urrutia J, Soto-Mora Y, Figueroa R, Hauenstein E (2012) Effects of the hydroperiod on the vegetative and community structure of freshwater forested wetlands. Chile J Freshw Ecol 27(3):459–470
De Deyn GB, Cornelissen JHC, Bardgett RD (2008) Plant functional traits and soil carbon sequestration in contrasting biomes. Ecol Lett 11(5):516–531
De Deyn GB, Quirk H, Bardgett RD (2011) Plant species richness, identity and productivity differentially influence key groups of microbes in grassland soils of contrasting fertility. Biol Let 7(1):75–78
De Vries FT, Manning P, Tallowin JRB, Mortimer SR, Pilgrim ES, Harrison KA, Hobbs PJ, Quirk H, Shipley B, Cornelissen JHC, Kattge J, Bardgett RD (2012) Abiotic drivers and plant traits explain landscape-scale patterns in soil microbial communities. Ecol Lett 15(11):1230–1239
Di Paola A, Valentini R, Paparella F (2012) Climate change threatens coexistence within communities of mediterranean forested wetlands. PloS One 7(10):e44727
Dick RP, Breakwell DP, Turco RF (1996) Soil enzyme activities and biodiversity measurements and integrative microbial indicators. In: Doran JW, Jones AJ (eds) Methods for assessing soil quality, vol 49. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 247–271
Eswaran HE, van den Berg E, Reich P (1993) Organic carbon pools of the world. Soil Sci Soc Am 57:192–194
Fan AN, Yang K, Liu CH, Dong Q (2009) Seasonal variations of soil enzyme activities in secondary forest communities in Montane region of eastern Liaoning province. J Northeast For Univ 37(1):52–54, 71.
German DP, Weintraub MN, Grandy AS, Lauber CL, Rinkes ZL, Allison SD (2011) Optimization of hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme methods for ecosystem studies. Soil Biol Biochem 43(7):1387–1397
Godin AM, Lidher KK, Whiteside MD, Jones MD (2015) Control of soil phosphatase activities at millimeter scales in a mixed paper birch-Douglas-fir forest: the importance of carbon and nitrogen. Soil Biol Biochem 80:62–69
He B, Wen YG, Yuan X, Liang HW (2002) Studies on soil physical and chemical properties and enzyme activities of different mangrove communities in Yingluo bay of Guangxi. Scientia Silvae Sinicae 38(2):21–26
Helbig M, Chasmer LE, Desai AR, Kljun N, Quinton WL, Sonnentag O (2017) Direct and indirect climate change effects on carbon dioxide fluxes in a thawing boreal forest-wetland landscape. Glob Change Biol 23(8):3231–3248
Jefferies RL, Walker NA, Edwards KA, Dainty J (2010) Is the decline of soil microbial biomass in late winter coupled to changes in the physical state of cold soils? Soil Biol Biochem 42(2):129–135
Kader MA, Yeasmin S, Akter M, Sleutel S (2017) Response of hydrolytic enzyme activities and nitrogen mineralization to fertilizer and organic matter application in subtropical paddy soils. Eur J Soil Biol 80:27–34
Klimek B, Chodak M, Jazwa M, Solak A, Tarasek A, Niklinska M (2016) The relationship between soil bacteria substrate utilisation patterns and the vegetation structure in temperate forests. Eur J For Res 135(1):179–189
Krauss KW, Whitbeck JL (2012) Soil greenhouse gas fluxes during wetland forest retreat along the Lower Savannah River, Georgia (USA). Wetlands 32(1):73–81
Kumar U, Shahid M, Tripathi R, Mohanty S, Kumar A, Bhattacharyya P, Lal B, Gautam P, Raja R, Panda BB, Jambhulkar NN, Shukla AK, Nayak AK (2017) Variation of functional diversity of soil microbial community in sub-humid tropical rice-rice cropping system under long-term organic and inorganic fertilization. Ecol Ind 73:536–543
Legay N, Grassein F, Binet MN, Arnoldi C, Personeni E, Perigon S, Poly F, Pommier T, Puissant J, Clement JC, Lavorel S, Mouhamadou B (2016) Plant species identities and fertilization influence on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal colonisation and soil bacterial activities. Appl Soil Ecol 98:132–139
Lemanceau P, Maron PA, Mazurier S, Mougel C, Pivato B, Plassart P, Ranjard L, Revellin C, Tardy V, Wipf D (2015) Understanding and managing soil biodiversity: a major challenge in agroecology. Agron Sustain Dev 35(1):67–81
Li X, Zhang HH, Yue BB, Jin WW, Xu N, Zhu WX, Sun GY (2012) Effects of mulberry-soybean intercropping on carbon-metabolic microbial diversity in salinealkaline soil. Chin J Appl Ecol 23(7):1825–1831
Lorenz K, Lal R (2005) The depth distribution of soil organic carbon in relation to land use and management and the potential of carbon sequestration in subsoil horizons. Adv Agron 88:35–66
Luna L, Pastorelli R, Bastida F, Hernández T (2016) The combination of quarry restoration strategies in semiarid climate induces different responses in biochemical and microbiological soil properties. Appl Soil Ecol 107:33–47
Maharjan M, Sanaullah M, Razavi BS, Kuzyakov Y (2017) Effect of land use and management practices on microbial biomass and enzyme activities in subtropical top-and sub-soils. Appl Soil Ecol 113:22–28
Maltby E, Immirzi P (1993) Carbon dynamics in peatlands and other wetland soils regional and global perspectives. Chemosphere 27:999–1023
Mayor ÁG, Goirán SB, Vallejo VR, Bautista S (2016) Variation in soil enzyme activity as a function of vegetation amount, type, and spatial structure in fire-prone Mediterranean shrublands. Sci Total Environ 573:1209–1216
Michele I, Elisa N, Rosaria D, Tiziana D, Primo P, Luigi N, Luca R, Simona C, Antonietta F (2017) Effects of olive pomace amendment on soil enzyme activities. Appl Soil Ecol 119:242–249
Moghimian N, Hosseini SM, Kooch Y, Darki BZ (2017) Impacts of changes in land use/cover on soil microbial and enzyme activities. CATENA 157:407–414
Moseman-Valtierra SM, Armaiz-Nolla K, Levin LA (2010) Wetland response to sedimentation and nitrogen loading: diversification and inhibition of nitrogen-fixing microbes. Ecol Appl 20(6):1556–1568
Mu C (2003) Succession of Larix olgensis and Betula platyphlla-marsh ecotone communities in Changbai Mountain. J Appl Ecol 14(11):1813–1819
Mu CC, Wang B, Lu HC, Bao X, Cui W (2013) Carbon storage of natural wetland ecosystem in Daxing’anling of China. Acta Ecol Sin 33:4956–4965
Nayak DR, Babu YJ, Adhya TK (2007) Long-term application of compost influences microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a tropical Aeric Endoaquept planted to rice under flooded condition. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1897–1906
Pan FJ, Zhang W, Liang YM, Liu SJ, Wang KL (2018) Increased associated effects of topography and litter and soil nutrients on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass along vegetation successions in karst ecosystem, southwestern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2:1–12
Pierce ML, Ward JE, Dobbs FC (2014) False positives in Biolog EcoPlates (TM) and MT2 MicroPlates (TM) caused by calcium. J Microbiol Methods 97:20–24
Pietrzykowski M, Daniels WL, Koropchak SC (2015) Microtopographic effects on growth of young bald cypress (Taxodium distichum L.) in a created freshwater forested wetland in southeastern Virginia. Ecol Eng 83:135–143
Prasse CE, Baldwin AH, Yarwood SA (2015) Site history and edaphic features override the influence of plant species on microbial communities in restored tidal freshwater wetlands. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:3482–3491
Qian X, Gu J, Sun W, Li YD, Fu QX, Wang XJ, Gao H (2014) Changes in the soil nutrient levels, enzyme activities, microbial community function, and structure during apple orchard maturation. Appl Soil Ecol 77:18–25
Rogers BF, Tate RL III (2001) Temporal analysis of the soil microbial community along a toposequence in Pineland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33(10):1389–1401
Salomo S, Munch C, Roske I (2009) Evaluation of the metabolic diversity of microbial communities in four different filter layers of a constructed wetland with vertical flow by Biolog (TM) analysis. Water Res 43(18):4569–4578
Sardans J, Peñuelas J, Estiarte M (2006) Warming and drought alter soil phosphatase activity and soil P availability in a Mediterranean shrubland. Plant Soil 289:227–238
Sharma S, Szele Z, Schilling R, Munch JC, Schloter M (2006) Influence of freeze-thaw stress on the structure and function of microbial communities and denitrifying populations in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(3):2148–2154
Siles JA, Cajthaml T, Minerbi S, Margesin R (2016) Effect of altitude and season on microbial activity, abundance and community structure in Alpine forest soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92:fiw008
Sims A, Zhang YY, Galaraj S, Brown PB, Hu ZQ (2013) Toward the development of microbial indicators for wetland assessment. Water Res 47:1711–1725
Sinsabaugh RL, Lauber CL, Weintraub MN, Ahmed B, Allison SD, Crenshaw C, Contosta AR, Cusack D, Frey S, Gallo ME, Gartner TB, Hobbie SE, Holland K, Keeler BL, Powers JS, Stursova M, Takacs-Vesbach C, Waldrop MP, Wallenstein MD, Zak DR, Zeglin LH (2008) Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol Lett 11(11):1252–1264
Stark S, Mannisto MK, Eskelinen A (2014) Nutrient availability and pH jointly constrain microbial extracellular enzyme activities in nutrient-poor tundra soils. Plant Soil 383(1–2):373–385
Steinweg JM, Dukes J, Wallenstein M (2012) Modeling the effects of temperature and moisture on soil enzyme activity: Linking laboratory assays to continuous field data. Soil Biol Biochem 55:85–92
Sun XX, Mu CC, Song CC, Wu YX (2011) Effects of cutting on methane flux from forested swamps in Xiaoxing’an Mountains, Northeast China. J Soil Sci 42:190–194
Trettin CC, Jurgensen MF (2003) Carbon cycling in wetland forest soils. In: Kimble J, Birdsie R, Lal R (eds) The potential of US forest soils to sequester carbon and mitigate the greenhouse effect. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 311–331
Vanhala P (2002) Seasonal variation in the soil respiration rate in coniferous forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 34(9):1375–1379
Wang X, Chen C, Wang JL (2016) Bioremediation of cesium-contaminated soil by sorghum bicolor and soil microbial community analysis. Geomicrobiol J 33(3–4):216–221
Ward BB (2005) Molecular approaches to marine microbial cology and the marine nitrogen cycle. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 33:301–333
Watson RT, Noble LR, Bolin B, Ravindranath NH, Verardo DJ, Dokken DJ (2000) IPCC special report: land use, land-use change, and forestry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Watts AC, Kobziar LN (2015) Hydrology and fire regulate edge influence on microclimate in wetland forest patches. Freshw Sci 34(4):1383–1393
Whittaker RH, Likens GE (1973) Primary production, the biosphere and man. Hum Ecol 1:357–369
Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Clement L, Balloi A, Daffonchio D, Heylen K, De Vos P, Versraete W, Boon N (2009) Initial community evenness favors functionality under selective stress. Nature 458:623–626
Wollenberg ALVD (1977) Redundancy analysis an alternative for canonical correlation analysis. Psychometrika 42(2):207–219
Xie XF, Pu LJ, Wang QQ, Zhu M, Xu Y, Zhang M (2017) Response of soil physicochemical properties and enzyme activities to long-term reclamation of coastal saline soil, Eastern China. Sci Total Environ 607:1419–1427
Yang WJ, Cheng HG, Hao FH, Ouyang W, Liu SQ, Lin CY (2012) The influence of land-use change on the forms of phosphorus in soil profiles from the Sanjiang Plain of China. Geoderma 189:207–214
Yin R, Deng H, Wang HL, Zhang B (2014) Vegetation type affects soil enzyme activities and microbial functional diversity following re-vegetation of a severely eroded red soil in sub-tropical China. CATENA 115:96–103
Yu Y, Wang H, Liu J, Wang Q, Shen TL, Guo WH, Wang RQ (2012) Shifts in microbial community function and structure along the successional gradient of coastal wetlands in Yellow River Estuary. Eur J Soil Biol 49:12–21
Yuan L, Zhao YS, Nie YZ (2006) Spatial distribution pattern of community biomass in the forest-wetland interlaced zone of Daxing’an Mountains. J Northeast For Univ 34:11–14
Zelles L (1999) Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterization of microbial communities in soil: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 29:111–129
Zeng J, Liu XJ, Song L, Lin XG, Zhang HY, Shen CC, Chu HY (2016) Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biol Biochem 92:41–49
Zhang C, Liu GB, Xue S, Wang GL, Wang J, Song ZL (2018a) Effects of rhizosphere interactions of grass interspecies on the soil microbial properties during the natural succession in the Loess Plateau. Eur J Soil Biol 85:79–88
Zhang L, Wang A, Yang WQ, Xu ZF, Wu FZ, Tan B, Liu Y, Chen LH (2017) Soil microbial abundance and community structure vary with altitude and season in the coniferous forests, China. J Soils Sediments 17(9):2318–2328
Zhang WJ, Li RR, Ai XY, Chen J, Xu WN, Li W, Ai YW (2018b) Enzyme activity and microbial biomass availability in artificial soils on rock-cut slopes restored with outside soil spray seeding (OSSS): Influence of topography and season. J Environ Manag 211:287–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31500508), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2572020BD02), and Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. LH2020C041).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Chi, Q., Sui, X. et al. Metabolic diversity and seasonal variation of soil microbial communities in natural forested wetlands. J. For. Res. 32, 2619–2631 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-021-01326-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-021-01326-8