Abstract
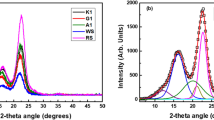
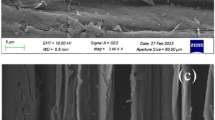
A study was conducted to test wettability changes of the wheat straw treated with different methods for the preparation of wheat straw particle board. The wheat straws were separately sprayed with two chemicals (0.6% NaOH, 0.3% H2O2) and three enzymes (lipase, xylanase, cellulase). The contact angle between water and the surface of wheat straw was measured and the spreading-penetration parameters (K-values) were also calculated with wetting model. The surfaces of treated wheat straw and control sample were scanned by means of Micro-FTIR, and their peaks arrangements were analyzed. The surface morphologies of treated wheat straw and control sample were also observed by SEM. Chemical etching was found on the exterior surfaces of the straws treated separately with 0.6% NaOH and 0.3% H2O2; furthermore, the spreading-penetration parameters (K-values) of the distilled water on the exterior surfaces of the treated wheat straw along the grain were higher than that of control. The wettability of exterior surfaces of the wheat straws treated separately with lipase, xylanase and cellulose were improved after treating for seven days, and among the three enzymes treatments, the lipase treatment showed best result. The lipase treatment and NaOH treatment were determined as better methods for improving the wettability of wheat straw surfaces. However, in the economic aspect, NaOH treatment was more practical and easier in the pretreatment for the manufacture of straw particle board.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boquillon N, Elbez G, Schonfeld U. 2004. Properties of wheat straw particleboards boned with different types of resin. Journal of Wood Science, 50: 230–235.
Fang JM, Fowler P, Tomkinson J, Hill CAS.. 2002. Preparation and characterization of methylated hemicelluloses from wheat straw. Carbohydrate Polymers, 47(3): 285–293.
Hornsby PR, Hinrichsen E, Tarverdi K. 1997. Preparation and properties of polypropylene composites reinforced with wheat and flax straw fibres: Part II Analysis of composite microstructure and mechanical properties. Jounal of Materials Science, 32(4): 1009–1015.
Huang WN, Sun XZ. 2000. Adhesive properties of soy proteins modified by urea and guanidine hydrochloride. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 77(1): 101–104.
Liu ZM, Wang FH, Wang XM. 2004. Surface structure and dynamic adhesive wettability of wheat straw. Wood and Fiber Science, 36(2): 239–249.
Liu ZM, Wang HY, Yang YM, Zhong GM, Wang XM. 2008. Wettability of wheat straw treated by three chemical reagents. In: Proceedings of IAWPS 2008 international symposium on wood science and technology. September 27–29, 2008
Morán JI, Alvarez VA, Cyras VP, Vázquez A. 2008. Extraction of cellulose and preparation of nanocellulose from sisal fibers. Cellulose. 15:149–159.
Pan MZ, Lian HL, Zhou DG. 2006. Effects of different treatment on chemical characteristics of straw fiber and properties of straw fiberboard. China Forest Products Industry, 33(4):24–26.
Shi SQ, Gardner DJ. 2001. Dynamic adhesive wettability of wood. Wood and Fiber Science, 33(1):58–68.
Sun RC, Lawther J.M., Banks WB. 1995. Influence of alkaline pre-treatments on the cell wall components wheat straw. Industrial Crops and Products, 4(2):127–145.
Sun RC, Sun XF, Sun JX, Zhu QK. 2004, Effect of tertiary amine catalysts on the acetylation of wheat straw for the production of oil sorption-active materials. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 7(2): 125–134.
Wang ZL, Wang Z, Yan HP. 2007. Study on wheat straw surface free energy and its polar and non polar. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 23(3): 207–210.
Wu ZK, Zhou DG. 2003. Surface characterization of rice straw and its fibers by FTIR and XPS. China Wood Industry, 17(6): 6–8.
Yao J, Xu XW, Feng YY. 2003. FTIR studies on the chemical composition of wheat straw in different layers. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 23(1):58–60.
Zhang Y, Hua YK. 2001. A study of moist character of wheat straw. China Wood Industry, 15(2): 6–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation project: Foundation project: This study was funded by the Scientific Research Foundation of the Bureau of Science and Technology of Heilongjiang Province (LC07C27)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Jh., Liu, Zm., Li, J. et al. Wettability changes of wheat straw treated with chemicals and enzymes. Journal of Forestry Research 22, 107–110 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-011-0134-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-011-0134-3