Abstract
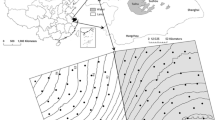
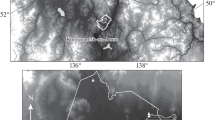
Agroforestry is a ubiquitous landscape on the slopes in Loess Plateau, where soil moisture is a limiting factor for plant growth and development. The spatial and temporal characteristics of soil moisture were studied in three types of agroforestry boundaries: forest-grassland, forest-cropland and shelterbelt-cropland. The result shows that soil moisture content decreased with soil depth increasing from the surface to 110 cm. Soil moisture content differed significantly among the three boundaries all in the rainy season (July–September), dry season (May–June) and spring (March–April). The horizontal distribution of soil moisture in different soil layers in the three types of boundaries showed different patterns with line form, wave form, scoop form or “W” form. The distance of edge influence (DEI) of soil moisture in different types of landscape boundaries was estimated by variance analysis and multiple comparisons. In dry season the DEI in 0–10 cm soil layer was 0.4 H (H, average height of trees), which ranged from 0.2 H in grassland or in cropland to 0.2 H in forest field for both forest-grassland and forest- cropland boundaries, and 0.7 H (ranged from 0.2 H in cropland to 0.5 H in forest field) for shelterbelt-cropland boundary. In rainy season the DEI at soil depth of 0–110 cm was 0.7 H for the three boundaries. The results indicated that agroforestry type should be carefully selected to maintain soil moisture in land management, especially in restoring degraded land in Loess Plateau.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belnap J, Hawkes CV, Firestone MK. 2003. Boundaries in miniature: Two examples from soil. BioScience, 53: 739–749.
Bider JR. 1968. Animal activity in uncontrolled terrestrial communities as determined by a sand transect technique. Ecol Monogr, 38: 269–308.
Cadenasso ML, Pickett STA, Weathers KC, Jones CG. 2003. A framework for a theory of ecological boundaries. BioScience, 53: 750–758.
Cadenasso ML, Pickett STA. 2001. Effect of edge structure on the flux of species into forest interiors. Conserv Biol, 15(1): 91–97.
Cadenasso ML, Traynor MM, Pickett STA. 1997. Functional location of forest edges: Gradients of multiple physical factors. Can J Forest Res, 27: 774–782.
Cancino J. 2005. Modeling the edge effect in even-aged Monterey pine (Pinus radiata D. Don) stands. For Ecol Manag, 210: 159–172.
Chen Habin, Sun Changzhong, An Feng, Dang Kunliang. 2003. A study on forest soil water features of Loess Plateau gully and hilly region (I). J Northwest For Univ, 18(4): 13–16. (in Chinese)
Chen J, Franklin JF, Lowe JS. 1996. Comparison of abiotic and structurally defined patch patterns in a hypothetical forest landscape. Conserv Biol, 10: 854–862.
Chisci GC, Bazzoffi P, Pagliai M, Papini R, Pellegrini S, Vignozzi N. 2001. Association of sulla and atriplex shrub for the physical improvement of clay soils and environmental protection in central Italy. Agr Ecosyst Environ, 84: 45–53.
Choesin D, Boerner REJ. 2002. Vegetation boundary detection: a comparison of two approaches applied to field data. Plant Ecology, 158: 85–96.
Das NN, Mohanty BP. 2008. Temporal dynamics of PSR-based soil moisture across spatial scales in an agricultural landscape during SMEX02: A wavelet approach. Remote Sens. Enviro, 112(2): 522–534.
English NB, Weltzin JF, Fravolini A, Thomas L, Williams DG. 2005. The influence of soil texture and vegetation on soil moisture under rainout shelters in a semi-desert grassland. J Arid Environ, 63(1): 324–343.
Fagan WF, Fortin MJ, Soykan C. 2003. Integrating edge detection and dynamic modeling in quantitative analyses of ecological boundaries. BioScience, 53: 730–738.
Famiglietti JS, Wood EF. 1995. Effects of spatial variability and scale on a really averaged evapotranspiration. Water Resour Res, 31: 699–712.
Farahani HJ, Bausch WC. 1995. Performance of evapotranspiration models for maize-bare soil to closed canopy. Trans Amer Soc Agric Eng, 38: 1049–1059.
Fraver S. 1994. Vegetation responses along edge-to-interior gradients in the mixed hardwood forests of the Roanoke River Basin, North Carolina. Conserv Biol, 8: 822–832.
Fu Bojie, Ma Keming, Zhou Huafeng, Chen Liding. 1998. The effect of land use structure on the distribution of soil nutrients in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Chin Sci Bull, 43(22): 2444–2447. (in Chinese)
Fu Bojie, Wang Jun, Ma Keming. 1999. Effect of land use on soil water in Loess hill area. Science Foundation in China, 4: 225–227. (in Chinese)
Gholz H. 1987. Agroforestry: Realities, Possibilities and Potential. Dordrecht: Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, pp.1–3.
Huo Zhu, Shao Mingan, Horton R. 2008. Impact of gully on soil moisture of shrubland in wind-water erosion crisscross region of the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere, 18(5): 674–680.
Ingmar M, Chen LD, Hessel R. 2003. Soil conditions in a small catchment on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena, 54: 45–58.
Jia Zhiqing, Song Guiping, Li Qinghe, Sun Baoping, Li Changzhe. 1997. Study on soil moisture dynamic variation law of typical watershed in the southern mountainous area of Ningxia Hui Autonomous region. J. Beijing For Univ, 19(3): 15–20. (in Chinese)
Krummel JR, Gardner RH, Sugihara G, Coleman PR. 1987. Landscape patterns in a disturbed environment. Oikos, 48: 321–324.
Laurance WF, Didham RK, Power ME. 2001. Ecological boundaries: A search for synthesis. Trends Ecol Evol, 16: 70–71.
Li H. 2001. Spatial pattern analysis in plant ecology. Forest Sci, 47: 119–121.
Li Liguang, He Xingyuan, Li Xiuzhen, Wen Qingchun, He Hong S. 2007. Depth of edge influence of the agricultural-forest landscape boundary, Southwestern China. Ecol Res, 22: 774–783.
Li Liguang, He Xingyuan, Li Xiuzhen, Wen Qingchun, Zhao Yonghua. 2005. Distribution and depth of edge influence on surface soil moisture in field-forest boundary in arid valley of up reaches of Minjiang river. J Liaoning Tech Uni, 24(6): 940–942. (in Chinese)
Liu Guangcai, Tian Guanglong, Shu Dongcai, Lin Sanyi, Liu Shuzhen. 2004. Streamflow and soil moisture of agroforestry and grass watersheds in hilly area. Pedosphere, 14(2): 263–268.
Liu Guobin, Xu Mingxiang, Coen R. 2003. A study of soil surface characteristics in a small watershed in the hilly, gullied area on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena, 54: 31–44.
Matlack GR. 1993. Microenvironment variation within and among forest edge sites in the eastern united states. Conserv Biol, 66: 185–194.
Meng Ping, Song Zhaoming, Zhang Jinsong, Lu Guangming. 1995. Study on water efficiency of agroforestry. Forest Research, 9(5): 443–448. (in Chinese)
Meng Ping, Zhang Jinsong, Fan Wei. 2003. Research on agroforestry in China. Beijing: China Forestry Press, pp.155–161. (in Chinese)
Moreno, G. 2008. Response of understorey forage to multiple tree effects in Iberian dehesas. Agr Ecosyst Environ, 123(1): 239–244.
Muthuri, CW, Ong, CK, Craigon, J, Mati, BM, Ngumi, VW, Black, CR.2009. Gas exchange and water use efficiency of trees and maize in agroforestry systems in semi-arid Kenya. AgrEcosyst Environ, 129(4): 497–507.
Peterjohn WT, Correll DL. 1984. Nutrient dynamics in an agricultural watershed: Observations on the role of a riparian forest. Ecology, 65: 1466–1475.
Qiu Yang, Fu Bojie, Wang Jun, Chen Liding. 2001. Soil moisture variation in relation to topography and land use in a hillslope catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. J Hydrol, 240: 243–263.
Saunders SC, Chen J, Drummer TD, Crow TR. 1999. Modeling temperature gradients across edges over time in a managed landscape. For Ecol Manag, 117: 17–31.
Schlesinger WH, Raikes JA, Hartley AE, Cross AE. 1996. On the spatial pattern of soil nutrients in desert ecosystems. Ecology, 77: 364–374.
Strayer DL, Power ME, Fagan WF, Pickett STA, Belnap J. 2003. A classification of ecological boundaries. Bioscience, 53: 723–729.
Wang Mengben, Li Hongjian. 1995. Quantitative study on the soil water dynamics of various forestry plantations in the Loess Plateau region in northwestern Shanxi. Acta Ecol Sin, 15(2): 178–184. (in Chinese)
Wang Yan, Wang Qingli, Dai Limin, Wang Miao, Zhou Li, Dai Baoqing. 2004. Effect of soil moisture gradient on structure of broad-leaved/Korean pine forest in Changbai Mountain. Journal of Forestry Research, 15(2): 119–123.
Weathers K, Cadenasso ML, Pickett STA. 2001. Forest edges as nutrient and pollutant concentrators: Potential synergisms between fragmentation, forest canopies, and the atmosphere. Conserv. Biol, 15: 1506–1514.
Whittaker RH, Niering WA, Crisp MD. 1979. Structure, pattern, and diversity of a mallee community in New South Wales. Vegetatio, 39: 65–76.
Wiens JA. 1989. Spatial scaling in ecology. Funct Eco, 3: 385–397.
Wierenga PJ, Hendrickx JMH, Nash MH, Ludwig JA, Daugherty LA. 1987. Variation of soil and vegetation with distance along a transect in the Chihuahuan Desert. J Arid Environ, 13: 53–63.
Wilson MV, Mohler CL. 1983. Measuring compositional change along gradients. Vegetatio, 54: 129–141.
You Wenzhong, Zeng Dehui, Liu Mingguo, Song Xide, Ye Yanhui, Zhang Yong. 2005. Spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture at forest-grassland landscape boundary after raining in hilly area of Loess Plateau. Chin J Appl Ecol, 16(9): 1591–1596. (in Chinese)
Zhang Xingchang, Lu Zongfan. 1993. Study on the dynamic change of soil water and yield-increasing mechanism about level trench tillage in slope land. J Soil Water Conserv, 7(3): 58–66. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation project: This work is supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (No. 2006BAD03A0502) and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (No. 2002CB111506).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, Wz., Zeng, Dh., Liu, Mg. et al. Spatial and temporal variations of soil moisture in three types of agroforestry boundaries in the Loess Plateau, China. Journal of Forestry Research 21, 415–422 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-010-0091-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-010-0091-2