Abstract
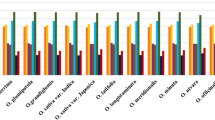
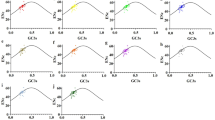
The pattern of codon usage in the chloroplast genome of Populus alba was investigated. Correspondence analysis (a commonly used multivariate statistical approach) and method of effective number of codons (ENc)-plot were conducted to analyze synonymous codon usage. The results of correspondence analysis showed that the distribution of genes on the major axis was significantly correlated with the frequency of use of G+C in synonymously variable third position of sense codon (GC3S), (r=0.349), and the positions of genes on the axis 2 and axis 3 were significantly correlated with CAI (r=−0.348, p<0.01 and r=0.602, p<0.01). The ENc for most genes was similar to that for the expected ENc based on the GC3S, but several genes with low ENC values were lying below the expected curve. All of these data indicated that codon usage was dominated by a mutational bias in chloroplast genome of P. alba. The selection in nature for translational efficiency only played a minor role in shaping codon usage in the chloroplast genome of P. alba.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashi H. 2001. Gene expression and molecular evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 11: 660–666.
Bernardi G. 1986. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol, 24: 1–11.
Bernardi G. 1993. The vertebrate genome — isochores and evolution. Mo Biol Evol, 10: 186–204.
Bonitz SG, Berlani R., Coruzzi G, Li M, Macino G. 1980. Codon recognition rules in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A., 77(6): 3167–3170.
Duret L. 2002. Evolution of synonymous codon usage in metazoans. Curr Opin Genet. Dev., 12: 640–649.
Grantham R, Gautier C, Gouy M, Mercier R, Pave A. 1980. Codon catalogue usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res, 8: r49–r62.
Hallick RB, Bairoch A. 1994. Proposals for the naming of chloroplast genes. III. Nomenclature for open reading frames encoded in chloroplast genomes. Plant Mol Biol Reptr, 12: S29–30.
Ikemura T. 1985. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol, 2: 13–34.
Kawabe A, Miyashita NT. 2003. Patterns of codon usage bias in three dicot and four monocot plant species. Genes Genet. Syst, 8: 343–352.
Klein RR, Mullet JE. 1986. Regulation of chloroplast-encoded chlorophyll-binding protein translation during higher plant chloroplast biogenesis. J. Biol. Chem., 261: 11138–11145.
Lockhart PJ, Penny D, Hendy MD, Howe CJ, Beanland TJ, Larkum AWD. 1992. Controversy on chloroplast origins. FEBS Lett., 301: 127–131.
Lu H, Zha, WM, Zheng Y, et al. 2005. Analysis of synonymous codon usage bias in Chlamydia. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinic, 37(1): 1–10.
Morton BR. 1993. Chloroplast DNA codon use: evidence for selection at the psbA locus based on tRNA availability. J Mol Evol, 37:273–280.
Morton BR. 1998. Selection on the codon bias of chloroplast and cyanelle Genes in Different Plant and Algal Lineages. J Mol Evol, 46: 449–459.
Morton BR. 1999. Strand asymmetry and codon usage bias in the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis. Proc Natl Acad. Sci USA, 96(9): 5123–5128.
Morton BR. 2003. The role of context-dependent mutations in generating compositional and codon usage bias in grass chloroplast DNA. J Mol Evol, 56(5): 616-29.
Morton BR, Levin JA. 1997. The atypical codon usage of the psbA gene may be the remnant of an ancestral bias. Proc Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 94:11434–11438.
Morton BR, So BG. 2000. Codon usage in plastid genes is correlated with context, position within the gene, and amino acid content. J Mol Evol, 50:184–193.
Mullet JE, Klein RR. 1987. Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J, 6:1571–1579.
Nussinov R. 1984. Strong doublet preferences in nucleotide sequences and DNA geometry. J Mol Evol, 20: 111–119.
Perriere G, Thioulouse J. 2002. Use and misuse of correspondence analysis in codon usgae studies. Nucleic Acids Res, 30: 4548–4555.
Pfitzinger H, Guillemaut P, Weil JH, Pillay DTN. 1987. Adjustment of the tRNA population to the codon usage of chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res, 15:137.
Sharp PM, Cowe E, Higgins DG, Shields DC, Wolfe KH, Wright F. 1988. Codon usage in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable within-species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res, 16: 8207–8711.
Sharp PM, Devine KM. 1989. Codon usage and gene-expression level in Dictyostelium discoideum — highly expressed genes do prefer optimal codons. Nucleic Acids Res., 17: 5029–5039.
Sharp, PM, Li, WH. 1987. The codon adaptation index—A measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res, 15(3): 1281–1295.
Sharp PM, Tuohy TMF, Mosurski KR. 1986. Codon usage in yeast cluster-analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res, 14: 5125–5143.
Shields DC, Sharp PM. 1987. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res, 15: 8023–8040.
Sueoka N. 1962. On the genetic basis of variation and heterogeneity of DNA base composition. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA, 48: 582–592.
Sueoka N. 1988. Directional mutational pressure and neutral pressure. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA, 85: 2653–2657.
Wang HC, Hickey DA. 2007. Rapid divergence of codon usage patterns within the rice genome. BMC Evol Bio, 7(Supp 1): S6.
Wolfe KH, Morden CW, EMS SC, Palmer JD.1992. Rapid evolution of the plastid translational apparatus in a nonphotosynthetic plant: loss or accelerated sequence evolution of tRNA and ribosomal protein genes. J Mol Evol, 35: 304–317.
Wolfe KH, Sharp PM. 1988. Identification of functional open reading frames in chloroplast genomes. Gene, 66: 215–222.
Wolfe KH, Sharp PM, Li WH. 1989. Mutation-rates differ among regions of the mammalian genome. Nature, 337: 283–285.
Wright F. 1990. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene, 87(1):23–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation project: This study was supported by the National High Tech Development Project of China, the 863 Program (Grant Nos. 2007AA02Z329) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 20060213024).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Long, W. & Li, X. Analysis of synonymous codon usage in chloroplast genome of Populus alba . Journal of Forestry Research 19, 293–297 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0052-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0052-1