Abstract
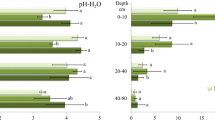
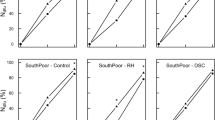
Allocation of biomass and nutrient elements including Nitrogen to above and belowground compartments of beech seedlings (Fagus sylvatica L.) treated by labeled nitrogen fertilizer in the form of 15NH4 and 15NO3 were investigated at the end of two successive growing seasons. Pot cultured beech seedlings were grown at a green house on intact soil cores sampled from three adjacent stands including beech, Norway spruce and mixed beech-spruce cultures of Solling forest, Germany. Comparing biomass allocation and nutrients concentrations of the seedlings between the control and 15N-fertilized treatments revealed no significant effect of N fertilization on nutrients uptake by seedlings over the experiment. The form of N input influenced its movement into plant pools. It was demonstrated that beech seedlings take up nitrogen mainly in the form of nitrate, which is then reduced in the leaves, although the differences between the retention of NO3 −-N and NH4 +-N in plants were not statistically significant. Percent recoveries of 15N in trees were typically greater after 15NO3 than after 15NH4 additions. It was indicated that immobilization of 15N tracer in fine roots was a slower process comparing other plant compartments such as stem and coarse roots, but a powerful sink for N during the course of study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Magill AH, Boone R, Melillo JM, Steudler P, and Bowden R. 1993. Plant and soil responses to chronic nitrogen additions at the harvard Forest, Massachusetts. Ecological Applications, 3: 156–166.
Boxman AW, Van Dam D, Van Dijk HFG, Hogervorst RF, and Koopmans CJ. 1995. Ecosystem responses to reduced nitrogen and sulfur inputs to two coniferous stands in the Netherlands. Forest Ecol and Manage, 71: 7–30.
Bredemeier M, Blanck K, and Lamersdorf N, and Wiedey GA. 1995. Response of soil water chemistry to experimental “clean rain” in the NITREX roof experiment at Solling, Germany. Forest Ecol and Manage, 71: 31–44.
Cannell MGR. 1985. Dry-matter partitioning in tree crops. In: M.G.R. Canell and J.E. Jackson (eds.), Attributes of Trees as Crop plants. Huntingdon: Institute of Terrestrial Ecology, pp. 160–193
Cromer RN and Jarvis PG. 1990. Growth and biomass partitioning in Eucalyptus grandis seedlings in response to nitrogen supply. Aust J Plant Physiol, 17: 503–515.
Davidson EA, Myrold DD, Groffman PM. 1990. Denitrification in temperate forest ecosystems. In: Sustained productivity of forest soils. Faculty of Forestry publications. University of British Colombia, Vancouver, Canada, pp 196–220
Dohrenbusch A. 1990. Verjüngungsentwicklung der Buche (Fagus sylvatica L.): Bericht einer langfristigen Beobachtung im Sollingen. Schriften aus der Forstliche Fakultät der Universität Göttingen, Bd 97. Sauerländer, Frankfurt am Main, 70 pp.
Evans JR. 1989. Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia, 78: 9–19.
Geßler A, Schneider S, Sengbusch D, Weber P, Hanemann U, Huber C, Rothe A, Kreutzer K, Rennenberg H. 1998. Field and laboratory experiments on net uptake of nitrate and ammonium by the roots of Spruce (Picea abies) and Beech (Fagus sylvatica) Trees. New Phytologist, 138: 275–285.
Glatzel G, Kazda M. 1985. Wachstum und Mineralstoffernährung von Buche (Fagus sylvatica) und Spitzahorn (Acer plantanoides) auf versauertem und schwermetallbelatetem Bodenmaterial aus dem Einsickerungsberich von Stammabflußwasser in Buchenwäldern. Z Pflanzenern u Bodenk, 148: 429–438.
Gundersen P, Rasmussen L. 1995. Nitrogen mobility in a nitrogen limited forest at Klosterhede, Denmark, Examined by NH4NO3 addition. Forest Ecol and Manage, 71: 75–88.
Johnson DW, Ball JT, Walker RF. 1997. Effects of CO2 and nitrogen fertilisation on vegetation and soil nutrient content in Juvenile ponderosa pine. Plant and Soil, 190: 29–40.
Kenk G and Fischer H. 1988. Evidence from nitrogen fertilization in the forests of Germany. Environ Pollut, 54: 199–218.
Landsberg JJ, Gower ST. 1997. Applications of physiological ecology to forest management. New York: Academic Press.
Ljungström M, and Stjernquist I. 1995. Growth and nutrient dynamics of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) seedlings in acid soils. Plant and Soil, 176: 171–181.
Matzner E. 1989. Acid precipitation: case study Solling. New York, USA: Springer Verlag, pp95–115
Minotta G, Pinzautti S. 1996. Effects of light and soil fertility on growth, leaf chlorophyll content and nutrient use efficiency of beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) seedlings. Forest Ecol and Manage, 86: 61–71.
Nadelhoffer KJ, Fry B. 1994. Nitrogen isotope studies in forest ecosystems. In: Lajtha K, Michener R (eds) Stable isotope studies in ecology and environmental science. Oxford: Blackwell, pp22–44.
Nadelhoffer KJ, Downs MR., Fry B. Aber JD., Magill AH, Melillo JM. 1995. The fate of 15N-labelled nitrate additions to a northern hardwood forest in eastern Maine, USA. Oecologia. 103: 292–301.
Nadelhoffer KJ, Downs MR, Fry B. 1999. Sinks for 15N-enriched additions to an oak forest and a red pine plantation. Ecological Applications, 9: 72–86.
Nambiar EKS, Fife DN. 1991. Nutrient retranslocation in temperate conifers. Tree Physiology, 9: 185–207.
Nilsson LO, Wiklund K. 1994. Nitrogen uptake in a Norway spruce stand following ammonium sulphate application, fertilization, irrigation, drought and nitrogen-free-fertilization. Plant and Soil, 164: 221–229.
Preston CM, Marshall VG, McCullough K, Mead DJ. 1990. Fate of 15N-labelled fertilizer applied on snow at two forest sites in British Colombia. Can J Forest Res, 20: 1583–1592.
Runion GB, Entry JA, Prior SA, Mitchell RJ, Rogers HH. 1999. Tissue chemistry and carbon allocation in seedlings of Pinus palustris subjected to elevated atmospheric CO2 and water stress. Tree Physiology, 19: 329–335.
Schmaltz J. 1966. Der Einfluß von Reservestoffen in den kotyledonen auf das wachstum von Buchensämlingen. Forstarchiv, 37: 138–139.
Skärby L, Ro-Poulsen H, Wellburn FAM, and Sheppard LJ. 1998. Impact of ozone on forests: a European perspective. New Phytologist, 139: 109–122.
Szymura TH. 2003. Differences in elemental composition of silver fir seedlings from four different populations in eastern Poland. Forest Ecol Manage, 179: 497–505.
Titema, A. 1998. Microbial carbon and nitrogen dynamics in coniferous forest floor material collected along a European nitrogen deposition gradient. Forest Ecol Manage, 101: 29–36.
Titema A, Wessel WW. 1992. Gross nitrogen transformations in the organic layer of acid forest ecosystems subjected to increased atmospheric nitrogen input. Soil Biol and Biochem, 24: 943–950.
Tietema A, Emmett BA, Gundersen P, Kjönaas OJ, Koopmans CJ. 1998. The fate of 15N-labelled nitrogen deposition in coniferous forests. Forest Ecol and Manage, 101: 19–27.
Tyrrell, LE, Boerner REJ. 1987. Larix laricina and Picea mariana relationships among leaf life-span, foliar nutrient patterns, nutrient conservation, and growth efficiency. Can J Bot, 65: 1570–1577.
Van Dijk HFG and Roelofs JGM. 1988. Effects of excessive ammonium deposition on the nutritional status and condition of pine needles. Physiol plant, 73: 494–501.
Van Hees, AFM, 1997. Growth and morphology of pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) and bech (Fagus silvatica L.) seedlings in relation to shading and drought. Annals of Forest Science, 54: 1–10.
Van Hees, AFM and Clerkx APPM. 2003. Shading and root-shoot relations in saplings of silver birch, pedunculate oak and beech. Forest Ecol and Manage, 176: 439–448.
Wallander H and Nylund J-E. 1991. Effects of excess nitrogen on carbohydrate concentration and mycorrhizal development of Pinus sylvestris L. seedlings. New Phytologist, 119: 405–411.
Wallander H and Nylund J-E. 1992. Effects of excess nitrogen and phosphorus starvation on the extramatrical myceliumof Pinus sylvestris L. ectomycorrhiza. New Phytologist, 120: 495–503.
Wright RF, Roelofs JGM, Bredemeier B, Blanck K, Boxman AW, Emmett BA, Gundersen P, Hultberg H, Kjønaas OJ, Moldman F, Tietema A, van Breemen N, van Dijk HFG. 1995. NITREX responses of coniferous forest ecosystems to experimentally changed deposition of nitrogen. Forest Ecol and Manage, 71: 163–169.
Wright RF, Titema A. 1995. Ecosystem response to 9 years of Nitrogen addition at Sogndal, Norway. Forest Ecol and Manage, 71: 133–142.
Xu XJ, and Timmer VR. 1999. Growth and nitrogen nutrition of Chinese fir seedlings exposed to nutrient loading and fertilisation. Plant and Soil, 216: 83–91.
Zech W, Suttner T, Popp E. 1985. Elemental analyses and physiological responses of forest trees in SO2-polluted areas of NE-Bavaria. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 25: 175–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation project: The study was financially supported by Institut für Bodenkunde und Waldernährung, Georg-August-Universität, Göttingen, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagherzadeh, A., Brumme, R. & Beese, F. Biomass and nutrients allocation in pot cultured beech seedlings: influence of nitrogen fertilizer. Journal of Forestry Research 19, 263–270 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0047-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-008-0047-y