Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effects of HPV16 E6/E7 siRNAs on cervical cancer SiHa cells.
Methods
The expressions of the E6, E7, p53 and Rb genes were assayed by RT-PCR and Western-bloting respectively. The proliferation and apoptosis of the cells were evaluated by MTT and flow cytometry.
Results
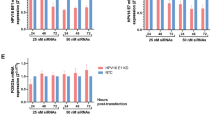
HPV 16 E6 and E7 oncogenes were selectivly downregulated by HPV 16 E6 and E7 siRNAs, which sustained at least 96 h by single dose siRNA. Furthermore, reduction of E6 and E7 oncogenes expression upregulated the expressions of P53 and RB protein and induced apoptosis in SiHa cells.
Conclusion
Introduction of HPV16 E6/E7 siRNA might be a potentially potent and specific approach to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of SiHa cervical cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002[J]. CA Cancer J Clin 2005; 55: 74–108.
Munoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjose S, et al. Epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer[J]. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 518–527.
Clifford GM, Smith Js, Plummer M, et al. Human papillomavirus types in invasive cervical cancer worldwide: a meta-analysis[J]. Br J Cancer 2003; 88: 63–73.
zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: from basic studies to clinical application[J]. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 342–350.
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, et al. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53[J]. Cell 1990; 63: 1129–1136.
Werness BA, Levine AJ, Howley PM. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53[J]. Science 1990; 248: 76–79.
Heck DV, Yee CL, Howley PM, et al. Efficiency of binding the retinoblastoma protein correlates with the transforming capacity of the E7 oncoproteins of the human papillomaviruses[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 4442–4446.
Dyson N, Guida P, Munger K, et al. Homologous sequences in adenovirus E1A and human papillomavirus E7 proteins mediate interaction with the same set of cellular proteins[J]. J Virol 1992; 66: 6893–6902.
Shillitoe EJ. Papillomaviruses as targets for cancer gene therapy[J]. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 445–450.
Caplen NJ. Gene therapy progress and prospects. Downregulating gene expression: the impact of RNA interference[J]. Gene Ther 2004; 11: 1241–1248.
Yoshinouchi M, Yamada T, Kizaki M, et al. In vitro and in vivo growth suppression of human papillomavirus 16-positive cervical cancer cells by E6 siRNA[J]. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 762–768.
Jiang M, Milner J. Selective silencing of viral gene expression in HPV-positive human cervical carcinoma cells treated with siRNA, a primer of RNA interference[J]. Oncogene 2002; 21: 6041–6048.
Butz K, Ristriani T, hengstermann A, et al. siRNA targeting of the viral E6 oncogene efficiently kills human papillomavirus- positive cancer cells[J]. Oncogene 2003; 22: 5938–5945.
Hall AH, Alexander KA. RNA interference of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 and E7 induces senescence in HeLa cells[J]. J Virol 2003; 77: 6066–6069.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells[J]. Nature 2001; 411: 494–498.
Jiang M, Milner J. Selective silencing of viral gene E6 and E7 expression in HPV-positive human cervical carcinoma cells using small interfering RNAs[J]. Methods Mol Biol 2005; 292: 401–420.
Weinberg RA. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control[J]. Cell 1995; 81: 323–330.
Koivusalo R, Krausz E, Helenius H, et al. Chemotherapy compounds in cervical cancer cells primed by reconstitution of p53 function after short interfering RNA-mediated degradation of human papillomavirus 18 E6 mRNA: opposite effect of siRNA in combination with different drugs[J]. Mol Pharmacol 2005; 68: 372–382.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No. 30660192) and the Key Project of Education Committee of Jiangxi Province (No. 2005-179).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, Cl., Gao, Gl., Han, J. et al. Human papillomavirus 16 E6, E7 siRNAs inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of SiHa cervical cancer cells. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 20, 301–306 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-008-0301-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-008-0301-z