Abstract
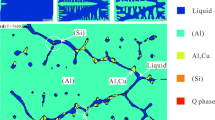
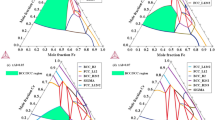
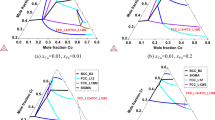
Microstructure and phase equilibria of Al2FeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy were investigated by a combination of experiments and multiscale computational materials. The CALPHAD and experimental results showed that a BCC dendritic phase formed during solidification, while a Cu-rich inter-dendritic phase with FCC structure precipitated at lower temperature. These FCC inter-dendritic phases were also surrounded by acicular precipitates with the same structure and composition. These acicular precipitates were stable during homogenization of the alloy at 550 °C, but they started to dissolve when heat-treated at 900 °C. Molecular simulation results revealed a disparate mechanism between nucleation of the FCC phase and its growth. While low annealing temperature (large undercooling of BCC) aided the nucleation process, diffusion-driven growth of the FCC crystals was faster at higher annealing temperatures.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.P. George, D. Raabe, and R.O. Ritchie, High-Entropy Alloys, Nat. Rev. Mater., 2019, 4, p 515–534.
D.B. Miracle, and O.N. Senkov, A critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts, Acta Mater., 2017, 122, p 448–511.
M.-H. Tsai, Physical Properties of High Entropy Alloys, Entropy, 2013, 15, p 5338–5345.
N.T.-C. Nguyen et al., Ultrahigh High-Strain-Rate Superplasticity in a Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloy, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, p 1–7.
Y. Shi, B. Yang, and P.K. Liaw, Corrosion-Resistant High-Entropy Alloys: A Review, Metals, 2017, 7, p 43.
W.L. Nelson et al., Superconductivity in a Uranium Containing High Entropy Alloy, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10, p 1–8.
Z. Fan, H. Wang, Y. Wu, X. Liu, and Z. Lu, Thermoelectric High-Entropy Alloys with Low Lattice Thermal Conductivity, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, p 52164–52170.
P. Sharma, V. Dwivedi, and S.P. Dwivedi, Development of High Entropy Alloys: A Review, Mater Today: Proc, 2021, 43, p 502–509.
J. Yi et al., (2020) A Novel Al0. 5CrCuNiV 3d Transition Metal High-Entropy Alloy: Phase Analysis, Microstructure and Compressive Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 846, p 156466.
J.W. Yeh et al., Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 299–303.
S. Gorsse, M. Nguyen, O.N. Senkov, and D.B. Miracle, Database on the Mechanical Properties of High Entropy Alloys and Complex Concentrated Alloys, Data Brief., 2018, 21, p 2664–2678.
Y. Zhuang, W. Liu, Z. Chen, H. Xue, and J. He, Effect of Elemental Interaction on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of FeCoNiCuAl Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 556, p 395–399.
F. Wang, and Y. Zhang, Effect of Co Addition on Crystal Structure and Mechanical Properties of Ti0. 5CrFeNiAlCo High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 2008, 496, p 214–216.
N. Krapivka, S. Firstov, M. Karpets, A. Myslivchenko, and V. Gorban, Features of Phase and Structure Formation in High-Entropy Alloys of the AlCrFeCoNiCu x System (x= 0, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0), Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2015, 116, p 467–474.
H.R. Sistla, J.W. Newkirk, and F.F. Liou, Effect of Al/Ni Ratio, Heat Treatment on Phase Transformations and Microstructure of AlxFeCoCrNi2− x (x= 0.3, 1) High Entropy Alloys, Mater. Des., 2015, 81, p 113–121.
M. López Ríos et al., Effects of Nickel Content on the Microstructure, Microhardness and Corrosion Behavior of High-Entropy AlCoCrFeNix Alloys, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10, p 1–11.
M. Beyramali Kivy, C.S. Kriewall, and M. Asle Zaeem, Formation of Chromium-Iron Carbide by Carbon Diffusion in Al X CoCrFeNiCu High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Res. Lett., 2018, 6, p 321–326.
Y. Zhang et al., Microstructures and Properties of High-Entropy Alloys, Prog. Mater Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93.
X. Fu, C.A. Schuh, and E.A. Olivetti, Materials Selection Considerations for High Entropy Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2017, 138, p 145–150.
M. Beyramali Kivy, Y. Hong, and M. Asle Zaeem, A Review of Multi-Scale Computational Modeling Tools for Predicting Structures and Properties of Multi-Principal Element Alloys, Metals, 2019, 9, p 254.
M.C. Gao, Design of high-entropy alloys, High-Entropy Alloys. Springer, Cham, 2016, p 369–398
G. Anand, R. Goodall, and C.L. Freeman, Role of Configurational Entropy in Body-Centred Cubic or Face-Centred Cubic Phase Formation in High Entropy Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2016, 124, p 90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.07.001
S. Chen et al., Simultaneously Enhancing the Ultimate Strength and Ductility of High-Entropy Alloys via Short-Range Ordering, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, p 4953. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25264-5
F. Biermair, V.I. Razumovskiy, and G. Ressel, Influence of Alloying on Thermodynamic Properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi High Entropy Alloys from DFT Calculations, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2022, 202, p 110952.
S. Chen et al., Simultaneously Enhancing the Ultimate Strength and Ductility of High-Entropy Alloys via Short-Range Ordering, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, p 1–11.
Y. Zeng, M. Man, K. Bai, and Y.-W. Zhang, Revealing High-Fidelity Phase Selection Rules for High Entropy Alloys: A combined CALPHAD and Machine Learning Study, Mater. Des., 2021, 202, p 109532.
C. Wen et al., Machine Learning Assisted Design of High Entropy Alloys with Desired Property, Acta Mater., 2019, 170, p 109–117.
P. Mandal, A. Choudhury, A.B. Mallick M. Ghosh, Phase Prediction in High Entropy Alloys by Various Machine Learning Modules Using Thermodynamic and Configurational Parameters. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, p 38–52.
Thermo-Calc Software TCHEA6: High Entropy Alloy v4.2 2022.
J.P. Perdew et al., Atoms, Molecules, Solids, and Surfaces: Applications of the Generalized Gradient Approximation for Exchange and Correlation, Phys. Rev. B, 1992, 46, p 6671.
D. Vanderbilt, Soft Self-Consistent Pseudopotentials in a Generalized Eigenvalue Formalism, Phys. Rev. B, 1990, 41, p 7892.
P. Giannozzi et al., Quantum ESPRESSO Toward the Exascale, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, p 154105.
P. Giannozzi et al., Advanced Capabilities for Materials Modelling with Quantum ESPRESSO, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter., 2017, 29, p 465901.
Q. Espresso, A modular and Open-Source Software Project for Quantum Simulations of Materials/P Giannozzi [et al.], J. Phys. Condens. Matter., 2009, 21, p 395502.
A. Van De Walle, M. Asta, and G. Ceder, The Alloy Theoretic Automated Toolkit: A User Guide, Calphad, 2002, 26, p 539–553.
S. Tripathi, R.A. Cotter, S. Utamsing, M. Islam, M.B. Kivy, A. Strachan, Random and Special Quasirandom Structure Generator. 2019. https://nanohub.org/resources/sqsatat
P. Hirel, Atomsk: A Tool for Manipulating and Converting Atomic Data Files, Comput. Phys. Commun., 2015, 197, p 212–219.
M. Parrinello, and A. Rahman, Polymorphic Transitions in Single Crystals: A New Molecular Dynamics Method, J. Appl. Phys., 1981, 52, p 7182–7190.
S. Plimpton, Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics, J. Comput. Phys., 1995, 117, p 1–19.
M.S. Daw, S.M. Foiles, and M.I. Baskes, The Embedded-Atom Method: A Review of Theory and Applications, Mater. Sci. Rep., 1993, 9, p 251–310.
A. Stukowski, Visualization and Analysis of Atomistic Simulation Data with OVITO–the Open Visualization Tool, Modell. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2009, 18, p 015012.
H. Tsuzuki, P.S. Branicio, and J.P. Rino, Structural Characterization of Deformed Crystals by Analysis of Common Atomic Neighborhood, Comput. Phys. Commun., 2007, 177, p 518–523.
A. Rodriguez-Lopez, B. Savoini, M. Monge, A. Muñoz, and P. Pérez, Exploring CuCrFeVTi System to Produce High Entropy Alloys for High Heat Flux Applications, Nucl. Mater. Energy, 2021, 29, p 101065.
H. Zheng et al., Microstructure Evolution, Cu Segregation and Tensile Properties of CoCrFeNiCu High Entropy Alloy During Directional Solidification, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 38, p 19–27.
Y. Ye et al., Elemental Segregation in Solid-Solution High-Entropy Alloys: Experiments and Modeling, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 681, p 167–174.
C.-W. Tsai et al., Deformation and Annealing Behaviors of High-Entropy Alloy Al0. 5CoCrCuFeNi, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 486, p 427–435.
C.-J. Tong et al., Microstructure Characterization of Al x CoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy System with Multiprincipal Elements, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2005, 36, p 881–893.
M.-H. Tsai et al., Morphology, Structure and Composition of Precipitates in Al0. 3CoCrCu0. 5FeNi High-Entropy Alloy, Intermetallics, 2013, 32, p 329–336.
G. Parker, Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology. Elsilver, Amsterdam, 2001.
C.-F. Lee, and T.-T. Shun, Age Heat Treatment of Al0. 5CoCrFe1.5NiTi0.5 High-Entropy Alloy, Metals, 2021, 11, p 91.
A. Asabre et al., Effect of Al, Ti and C Additions on Widmanstätten Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Cast Al0. 6CoCrFeNi Compositionally Complex Alloys, Mater. Des., 2019, 184, p 108201.
A.S. Sabau, Predicting Interdendritic Cavity Defects During Casting Solidification, JOM, 2004, 56, p 54–56.
M.B. Kivy, M.A. Zaeem, and S. Lekakh, Investigating Phase Formations in Cast AlFeCoNiCu High Entropy Alloys by Combination of Computational Modeling and Experiments, Mater. Des., 2017, 127, p 224–232.
W.-R. Wang et al., Effects of Al Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Property of AlxCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2012, 26, p 44–51.
X. Yan et al., Al0 3CrxFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloys with High Corrosion Resistance and Good Mechanical Properties, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 860, p 158436.
S. Yang et al., Effect of Cr Content on Corrosion Behavior of AlCrxFeNi2Cu16 High Entropy Alloys, Mater. Res. Exp., 2019, 6, p 076501.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Trevor Harding, Dr. Ryan Smith, Mr. Eric Beaton, Mrs. Caitlin Kriewall, and the NACE club of the Materials Engineering Department for their assistance and/or inputs in this project. We are also thankful to ASM Materials Genome Toolkits award (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MBK, RT, JPJ, MK, LH performed all the experiments. MBK performed the CALPHAD and DFT calculations. AKM performed the MD simulations. MBK, AKM, RT, JPJ, MK, LH wrote the manuscript, and MBK coordinated the whole work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kivy, M.B., Mahata, A.K., Thompson, R. et al. Experimental and Computational Study of Microstructure of Al2FeCoNiCu High-Entropy Alloy. J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 44, 76–85 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-023-01024-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11669-023-01024-4