Abstract
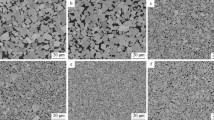
In this paper, several major factors affecting the erosion wear of WC–Co cemented carbide were tested and analyzed by the cemented carbide solid particle erosion test. In addition to the erosion angle, the impact velocity, the hardness and dimensions of the abrasive and the degree of fracture of the abrasive after impacting the target material also have a significant effect on the erosion wear results. Abrasives with a high degree of fragmentation after erosion have lower erosion wear efficiency for cemented carbides. The increase in Co content and WC grain size will lead to the decline of erosion resistance of cemented carbide. After the energy spectrum analysis of the target material after erosion, it was found that Co particles were first detached during the erosion process. Later, due to the instability of the entire microstructure, a series of erosion wears was caused.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Furberg, R. Arvidsson, S. Molander, Environmental life cycle assessment of cemented carbide (WC–Co) production. J. Clean. Prod. 209, 1126–1138 (2019)
I. Finnie, Erosion of surfaces by solid particle. Wear 3(2), 87–103 (1960)
I. Hussainova, M. Anton, A. Zikin, Erosive wear of advanced composites based on WC. Tribol. Int. 46(1), 254–260 (2012)
A. Sharma, A. Kumar, R. Tyagi, Erosive wear analysis of medium carbon dual phase steel under dry ambient condition. Wear 334, 91–98 (2015)
M. Antonov, R. Veinthal, D.-L. Yung, D. Katušin, I. Hussainova, Mapping of impact-abrasive wear performance of WC–Co cemented carbides[J]. Wear 332, 971–978 (2015)
K. Bonny, P. De Baets, O. Van der Biest, J. Vleugels, B. Lauwers, Edge effects in sliding wear behavior of ZrO2–WC composites and WC–Co cemented carbides. Mater. Sci. Forum 561–565, 503–506 (2007)
G. Pezzotti, T. Nishida, Elastic after-effect in WC–Co cemented carbide. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19(4), 419–425 (1999)
J.D. Gates, M.S. Dargusch, J.J. Walsh, S.L. Field, M.J.-P. Hermand, B.G. Delaup, J.R. Saad, Effect of abrasive mineral on alloy performance in the ball mill abrasion test. Wear 265(5–6), 865–870 (2008)
ISO 6507-1:2018, Metallic Materials Vickers Hardness Test Part 1: Test Methods
D. Wang, J. Zhao, A. Li, X. Cui, X. Chen, Microstructure level modelling for properties prediction of WC–Co cemented carbides. Mater. Res. Innov. 17, 40–55 (2013)
R.J. John, J. Bijwe, B. Venkataraman, V.B. Tewari, Effect of impinging velocity on the erosive wear behaviour of polyamides. Tribol. Int. 37(3), 219–226 (2004)
Z.L. Ding, J.M. Deng, X.H. Zen, J.P. Wu, Y.S. Zou, Thermal erosion of WC-based cemented carbide nozzles by coal water slurry. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 26(4), 334–339 (2008)
D. Ciampini, J.K. Spelt, M. Papini, Simulation of interference effects in particle streams following impact with a flat surface. Part 1: theory and analysis. Wear 254(3), 237–249 (2003)
J.G.A. Bitter, A study of erosion phenomena: part l. Wear 6(3), 5–21 (1963)
J.G.A. Bitter, A study of erosion phenomena: part 2. Wear 6(3), 169–190 (1963)
J. Barber, B.G. Mellor, R.J.K. Wood, The development of sub-surface damage during high energy solid particle erosion of a thermally sprayed WC–C0–Cr coating. Wear 259(1–6), 125–134 (2005)
M. Liebhard, A.V. Levy, The effect of erodent particle characteristics on the erosion of metals. Wear 151(2), 381–390 (1991)
J. Abenojar, J. Tutor, Y. Ballesteros, J.C. del Real, M.A. Martínez, Erosion-wear, mechanical and thermal properties of silica filled epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. B Eng. 120, 42–53 (2017)
R.M. Brach, Impact dynamics with applications to solid particle erosion. Int. J. Impact Eng. 7(1), 37–53 (1988)
V.B. Nguyen, Q.B. Nguyen, Y.W. Zhang, C.Y.H. Lim, B.C. Khoo, Effect of particle size on erosion characteristics. Wear 348, 126–137 (2016)
J. Heinrichs, H. Mikado, A. Kawakami, U. Wiklund, S. Kawamura, S. Jacobson, Wear mechanisms of WC–Co cemented carbide tools and PVD coated tools used for shearing Cu-alloy wire in zipper production. Wear 420, 96–107 (2019)
R.G. Wellman, C. Allen, The effect of angle of impact and material properties on the erosion rate of ceramics. Wear 186–187(Part 1), 117–122 (1995)
Y. Torres, R. Bermejo, F.J. Gotor, E. Chicardi, L. Llanes, Analysis on the mechanical strength of WC–Co cemented carbides under uniaxial and biaxial bending. Mater. Des. 55, 851–856 (2014)
I. Cha Seung, H. Lee Kyong, J. Ryu Ho, H. Hong Soon, Effect of size and location of spherical pores on transverse rupture strength of WC–Co cemented carbides. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 486(1–2), 404–408 (2008)
U. Beste, L. Hammerstrom, H. Engqvist, S. Rimlinger, S. Jacobson, Particle erosion of cemented carbides with low Co content. Wear 250(1), 809–817 (2001)
S. Hiroyuki, I. Akira, S. Tomoharu, Effects of Co content and WC grain size on wear of WC cemented carbide. Wear 261(2), 126–132 (2006)
H. Hosokawa, K. Shimojima, M. Kawakami, Role of the Co phase in superplasticity for WC–Co cemented carbides. Mater. Trans. 45(4), 1391–1394 (2004)
J. Weidow, H.-O. André, APT analysis of WC–Co based cemented carbides. Ultramicroscopy 111(6), 595–599 (2011)
Y. Torres, M. Anglada, L. Llanes, Fatigue limit estimation for WC–Co cemented carbides on the basis of linear elastic fracture mechanics. Boletin de la Sociedad Espanola de Ceramica y Vidrio 43(2), 273–276 (2004)
A. Laukkanen, T. Pinomaa, K. Holmberg, T. Andersson, Effective interface model for design and tailoring of WC–Co microstructures. Powder Metall. 59(1), 20–30 (2016)
V.A. Pugsley, C. Allen, Microstructure/property relationships in the cavitation erosion of tungsten carbide–cobalt. Wear 233–235, 93–103 (1999)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Open Fund (OGE201702-05) of the Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Equipment, Ministry of Education (Southwest Petroleum University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, C., Chen, D., Xu, M. et al. Study of Solid Particle Erosion Wear Resistance of WC–Co Cemented Carbide. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 20, 543–554 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00861-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00861-6