Abstract
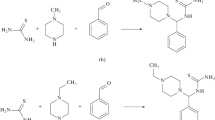
The inhibition effect of novel Mannich base 1-[morpholin-4-yl(thiophen-2-yl)methyl]thiourea on the corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M hydrochloric acid solution was investigated by potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements and surface examination through scanning electron microscope (SEM) technique. The results showed that Mannich base is an effective corrosion inhibitor and the inhibition efficiency increases with increase in concentration of the inhibitor. The corrosion behavior of mild steel in 0.5 M HCl without and with the inhibitor at various concentrations was studied at the temperature range of 303–333 K. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements showed that the Mannich base is a mixed-type inhibitor. EIS plots indicated that the presence of the inhibitor increases the charge transfer resistance of the corrosion process, increasing the inhibition efficiency. Temperature studies revealed that inhibition efficiency increased up to 323 K and beyond which inhibitor efficiency decreased because of desorption of inhibitor. The adsorption of inhibitor on mild steel surface is an endothermic reaction and is best described by the Langmuir adsorption isotherm. The surface adsorbed film was analyzed using SEM.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Ahamad, R. Prasad, M.A. Quraishi, Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acid solution by Pheniramine drug: experimental and theoretical study. Corros. Sci. 52(9), 3033–3041 (2010)
M. Gopiraman, N. Selvakumaran, D. Kesavan, I.S. Kim, R. Karvembu, Chemical and physical interactions of 1-benzoyl-3,3-disubstituted thiourea derivatives on mild steel surface: corrosion inhibition in acidic media. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(23), 7910–7922 (2012)
M.A. Amin, K.F. Khaled, Q. Mohsen, H.A. Arida, A study of the inhibition of iron corrosion in HCl solutions by some amino acids. Corros. Sci. 52(5), 1684–1695 (2010)
A. Döner, R. Solmaz, M. Özcan, G. Kardaş, Experimental and theoretical studies of thiazoles as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in sulphuric acid solution. Corros. Sci. 53(9), 2902–2913 (2011)
S. Zhang, H.J. Li, L. Wang, D.Z. Liu, E.S. Ping, P. Zou, T.L. Ma, N. Li, New pyrazine derivatives as efficient inhibitors on mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric medium. Chem. Eng. Trans. 55, 289–294 (2016)
E.S. Ferreira, C. Giacomelli, F.C. Giacomelli, A. Spinelli, Evaluation of the inhibitor effect of l-ascorbic acid on the corrosion of mild steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 83(1), 129–134 (2004)
D.K. Yadav, M.A. Quraishi, Electrochemical investigation of substituted pyranopyrazoles adsorption on mild steel in acid solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51, 8194–8210 (2012)
D. Karthik, D. Tamilvendan, G.V. Prabhu, Study on the inhibition of mild steel corrosion by 1,3-bis-(morpholin-4-yl-phenyl-methyl)-thiourea in hydrochloric acid medium. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 18(6), 835–844 (2014)
M.A. Quraishi, S.K. Shukla, Poly(aniline-formaldehyde): a new and effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113(2–3), 685–689 (2009)
A.J.A. Nasser, M.A. Sathiq, N-[morpholin-4-yl(phenyl) methyl] acetamide as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Arab. J. Chem. 9, S691–S698 (2016)
M.G. Hosseini, H. Khalilpur, S. Ershad, L. Saghatforoush, Protection of mild steel corrosion with new thia-derivative salens in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 40, 215–223 (2010)
K.C. Emregül, O. Atakol, Corrosion inhibition of iron in 1 M HCl solution with Schiff base compounds and derivatives. Mater. Chem. Phys. 83, 373–379 (2004)
A.A. Jameel, M. Palanisamy, M.S.A. Padusha, Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of metal complexes of Mannich base derived from pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde. Der Chemica Sinica 3(4), 860–863 (2012)
S. Rathakrishnanb, A.A. Jameela, M.S.A. Padushaa, Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of a chiral compound and its metal complexes. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 4(7) (2014)
M. Jeeva, G.V. Prabhu, M.S. Boobalan, C.M. Rajesh, Interactions and inhibition effect of urea-derived Mannich bases on a mild steel surface in HCl. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(38), 22025–22043 (2015)
D. Tamilvendan, S. Rajeswari, S. Ilavenil, K. Chakkaravarthy, G.V. Prabhu, Syntheses, spectral, crystallographic, antimicrobial, and antioxidant studies of few Mannich bases. Med. Chem. Res. 21, 4129–4138 (2012)
M. Yadav, S. Kumar, I. Bahadur, D. Ramjugernath, Corrosion inhibitive effect of synthesized thiourea derivatives on mild steel in a 15% HCl solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 9(11), 6529–6550 (2014)
W.H. Li, Q. He, S.T. Zhang, C.L. Pei, B.R. Hou, Some new triazole derivatives as inhibitors for mild steel corrosion in acidic medium. J. Appl. Electrochem. 38(3), 289–295 (2008)
M. Hosseini, S.F. Mertens, M. Ghorbani, M.R. Arshadi, Asymmetrical Schiff bases as inhibitors of mild steel corrosion in sulphuric acid media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 78(3), 800–808 (2003)
A.M. Fekry, The influence of chloride and sulphate ions on the corrosion behavior of Ti and Ti–6Al–4V alloy in oxalic acid. Electrochim. Acta 54(12), 3480–3489 (2009)
P.P. Kumari, P. Shetty, S.A. Rao, Electrochemical investigation of hydrazide derivative as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 23(3), 196–203 (2016)
A.K. Singh, M.A. Quraishi, Effect of Cefazolin on the corrosion of mild steel in HCl solution. Corros. Sci. 52(1), 152–160 (2010)
E.A. Noor, Temperature effects on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic solutions by aqueous extract of fenugreek leaves. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2(12), 996 (2007)
M.A. Ameer, E. Khamis, G. Al-Senani, Effect of temperature on stability of adsorbed inhibitors on steel in phosphoric acid solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 32(2), 149–156 (2002)
X. Wang, H. Yang, F. Wang, An investigation of benzimidazole derivative as corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in different concentration HCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 53(1), 113–121 (2011)
M.J. Bahrami, S.M.A. Hosseini, P. Pilvar, Experimental and theoretical investigation of organic compounds as inhibitors for mild steel corrosion in sulfuric acid medium. Corros. Sci. 52(9), 2793–2803 (2010)
S. Martinez, I. Stern, Thermodynamic characterization of metal dissolution and inhibitor adsorption processes in the low carbon steel/mimosa tannin/sulfuric acid system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 199(1–4), 83–89 (2002)
M. Bouklah, B. Hammouti, M. Lagrenee, F. Bentiss, Thermodynamic properties of 2,5-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in normal sulfuric acid medium. Corros. Sci. 48(9), 2831–2842 (2006)
M. Gholami, I. Danaee, M.H. Maddahy, M. RashvandAvei, Correlated ab initio and electroanalytical study on inhibition behavior of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and its thiole–thionetautomerism effect for the corrosion of steel (API 5L X52) in sulphuric acid solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52(42), 14875–14889 (2013)
Z. Ahmad, Principles of Corrosion Engineering and Corrosion Control (Elsevier, New York, 2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lavanya, D.K., Priya, F.V. & Vijaya, D.P. Green Approach to Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid by 1-[Morpholin-4-yl(thiophen-2-yl)methyl]thiourea. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 20, 494–502 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00850-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-020-00850-9