Abstract
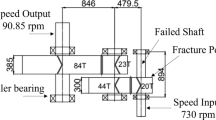
A systematic and practical methodology was adopted to determine the root cause(s) of the premature failure of a pelletizer mixer timing gear. The investigation activities covered all possible causes of failure and included field examination, interview of engineers and operators, lubrication analysis, metallurgical examination. Fracture surfaces and microstructure of gear material were examined, and hardness profiles were developed. Analyses of shaft misalignment and teeth profiles were performed and found to be within acceptable limits. Results clearly indicate the surface hardness deficiencies in many locations specifically at center of the driven gear, area of severe pitting. The developed hardness profile for all locations is lower than that specified by the manufacturer. Fractographic analysis revealed that failure occurred by pitting followed by crack propagation. A number of cracks are seen to branch in different directions indicating the presence of high contact stresses combined with weak surface strength. Bending fatigue and pitting fatigue stress calculations revealed that the safety factor under contact is well below the desired value.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Asi, Fatigue failure of a helical gear in a gearbox. Eng. Fail. Anal. 13, 1116–1125 (2006)
L. Alban, Number 1 gear failure—tooth bending fatigue. SAE technical paper 841088 (1984)
G.W. Powell, Failure analysis and prevention, in ASM Handbook (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1986), p. 11
P.J.L. Fernandes, Tooth bending fatigue failures in gears. Eng. Fail. Anal. 3, 219–225 (1996)
S. Netpu, P. Srichandr, Failure analysis of a herringbone gear. Key Eng. Mater. 462–463, 366–371 (2011)
Y. Ding, N.F. Rieger, Spalling formation mechanism for gears. Wear 254, 1307–1317 (2003)
Y. Ding, R. Jones, B.T. Kuhnell, Elastic–plastic finite element analysis of spall formation in gears. Wear 197(1), 197–205 (1996)
B.-R. Michaeli, K. Höhn, Influence of oil temperature on gear failures. Tribol. Int. 37, 103–109 (2004)
P.J.L. Fernandes, A. James, Failure analysis report, metallurgical and corrosion services, CSIR 1994
P.J.L. Fernandes, C. McDuling, Surface contact fatigue failures in gears. Eng. Fail. Anal. 4(2), 99–107 (1997)
A.D. Deutschman, W.J. Michels, C.E. Wilson, Machine Design, Theory and Practice (Macmillan, London, 1975)
C.R. Das, S.K. Albert, A.K. Bhaduri, S.K. Ray, Failure analysis of a pinion. Eng. Fail. Anal. 12, 287–298 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support provided by King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Safety Factors Under Bending and Contact Stresses
Appendix: Safety Factors Under Bending and Contact Stresses

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merah, N., Al-Qutub, A. Premature Failure of an Industrial Mixer Timing Gears. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 17, 871–881 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-017-0300-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-017-0300-9