Abstract
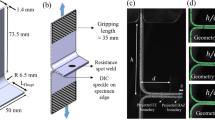
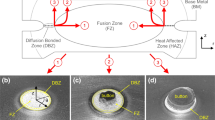
Conducting tensile shear test for the spot-welded specimens is a common practice in resistance spot welding as it helps to understand the loading behavior and its corresponding effect. Two categories of weld failures are conventionally regarded, as to distinguish the sound weld over a poor one. This approach has severe drawback from early days and therefore the postcrack propagation (PCP) method is carried out as an alternative in this experimental study. With the PCP experimental results in hand, the tensile shear test is simulated using ANSYS to observe the corresponding strain distribution. Based on the visual inspection of simulation and practical results, three classifications (IF, PF, and TF) are consequently categorized; so that the weld failures of tensile shearing test can now be accurately distinguished by means of cracking patterns. Moreover, some degrees of fractures have regularly been noticed by other fellow researchers within these three categories and thereby the fractures have been named after the degrees of cracking severity. Carbon steel welds, partially corroded carbon steel welds, stainless steel welds, and mixed steel welds have been parallelly analyzed for the PCP modes and the results obeyed the categorization very well.



(©Nachimani)












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Marya, X.Q. Gayden, Development of requirements for resistance spot welding dual-phase (DP600) Steels Part 1—the causes of interfacial fracture. Weld. J. 11, 172–182 (2009)
J.H. Song, H. Huh, Failure characterization of spot welds under combined axial-shear loading conditions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 53, 513–525 (2011)
D. Radaj, Stress singularity, notch stress and structural stress at spot-welded joints. Eng. Fract. Mech. 34(2), 495–506 (1989)
M. Pouranvari, S.P.H. Marashi, Failure mode transition in AHSS resistance spot welds. Part I. Controlling factors. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 8337–8343 (2011)
M. Pouranvari, S.P.H. Marashi, D.S. Safanama, Failure mode transition in AHSS resistance spot welds, Part II: experimental investigation and model validation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 8344–8352 (2011)
S. Dancette, D. Fabrègue, V. Massardier, J. Merlin, T. Dupuy, M. Bouzekri, Investigation of the tensile shear fracture of advanced high strength steel spot welds. Eng. Fail. Anal. 25, 112–122 (2012)
P. Marashi, M. Pouranvari, S. Amirabdollahian, A. Abedi, M. Goodarzi, Microstructure and failure behavior of dissimilar resistance spot welds between low carbon galvanized and austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 480, 175–180 (2008)
S.M. Darwish, A.M. Al-Samhan, Peel and shear strength of spot-welded and weld-bonded dissimilar thickness joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 147, 51–59 (2004)
C. Maa, D.L. Chena, S.D. Bhole, G. Boudreau, A. Lee, E. Biro, Microstructure and fracture characteristics of spot-welded DP600 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 485, 334–346 (2008)
F. Hayat, The effects of the welding current on heat input, nugget geometry, and the mechanical and fractural properties of resistance spot welding on Mg/Al dissimilar materials. Mater. Des. 32, 2476–2484 (2011)
S. Hassanifard, M.A. Mohtadi Bonab, Gh Jabbari, Investigation of fatigue crack propagation in spot-welded joints based on fracture mechanics approach. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22, 245–250 (2013)
H. Hatsuhiko, M. Gen, S. Tatsuya, T. Yasuoand, I. Tadashi, Resistance spot weldability of high strength steel sheets for automobiles, Nippon Steel Technical Report No 95, pp. 39–45 (2007)
S. Ibrahim, Effect of hardness to fracture toughness for spot welded steel sheets. Mater. Des. 27, 21–30 (2006)
A. Aravinthan, N. Charde, Analysis of spot welds growth on carbon and stainless steel. Weld. J. 90, 143–147 (2011)
A. Aravinthan, N. Charde, 4, A metallurgical study of spot welds growth on carbon steel with 1 mm and 2 mm thicknesses. J. Inst. Eng. Malays. 72, 32–36 (2011)
Florent Krajcarz, Anne Françoise, Gourgues Lorenzon, Emmanuel Lucas, Andre Pineau, Fracture toughness of the molten zone of resistance spot welds. Int. J. Fract. 181, 209–226 (2013)
D.J. Radakovic, M. Tumuluru, An evaluation of the cross-tension test of resistance spot welds in high-strength dual-phase steels. Weld. J. 91, 8–15 (2012)
X. Sun, E.V. Stephens, M.A. Khaleel, Effects of fusion zone size and failure mode on peak load and energy absorption of advanced high strength steel spot welds under lap shear loading conditions. Eng. Fail. Anal. 15, 356–367 (2008)
R. Qiu, C. Iwamoto, S. Satonaka, Interfacial microstructure and strength of steel/aluminum alloy joints welded by resistance spot welding with cover plate. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 4186–4193 (2009)
M. Marya, X.Q. Gayden, Development of requirements for resistance spot welding dual-phase (DP600) steels, part 1—the causes of interfacial fracture. Weld. J. 84, 172–182 (2005)
P. Prasad, M.L Kulkarni, Monte carlo simulation of single spot and multi-spot welded lap shear specimen by using finite element method. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2, 715–718 (2012)
J. Triyono, M.N. Ilman, R. Soekrisno, Comparative study of fatigue assessment methods with and without considering residual stress on resistance spot–welded unequal sheet thickness stainless steel. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 11(3), 118–122 (2012)
H. Nordberg, Fatigue properties of stainless steel lap joints. SAE Int. J. 1, 1–16 (2005)
F. Xu, G. Sun, G. Li, Q. Li, Failure analysis for resistance spot welding in lap–shear specimens. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 78, 154–166 (2014)
C. Zhang, S.V.D. Vyver, X. Hua, P. Lu, Fatigue crack growth behavior in weld–repaired high–strength low–alloy steel. Eng. Fract. Mech. 78, 1862–1875 (2011)
N. Charde, F. Yusof, R. Rajkumar, Material characterizations of mild steels, stainless steels, and both steel mixed joints under resistance spot welding (2-mm sheets). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 75(1–4), 373–384 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charde, N. Postcrack Propagation of Tensile Shear Test: Analyzing the Carbon Steel Welds, Stainless Steel Welds, and Both Steels Mixed Welds in Resistance Spot Welding. J Fail. Anal. and Preven. 16, 803–810 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0153-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11668-016-0153-7