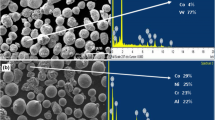
Abstract
Monel K-500 is a nickel-based alloy broadly used in several industries such as power generation, aerospace, marine and chemical processing for manufacturing several critical components. During hydraulic applications, the alloy is subjected to different degradation phenomena such as cavitation erosion, slurry erosion and corrosion. The current study assesses the potential of using two HVOF-sprayed nickel-based cermet coatings: WC-10Ni-5Cr and WC-18Hastelloy C to control the slurry erosion of Monel K-500. The coatings were subjected to slurry erosion tests for 90 min at normal (90°) and oblique (30°) impingement angles. It was observed that these coatings significantly reduced the erosive wear in Monel alloy. WC-10Ni-5Cr coating, having relatively better microhardness and fracture toughness has shown minimum erosion losses. At normal impact, WC-10Ni-5Cr coating and WC-18Hastelloy C coating reduced the erosion rate of Monel by 2.3 and 1.6 times, respectively. At oblique impact, WC-10Ni-5Cr coating and WC-18Hastelloy C coating reduced the erosion rate of Monel by 4.75 and 2.4 times, respectively. In-depth study of the erosion mechanism for the investigated materials was conducted using scanning electron microscopy. Ploughing and micro-cutting were the primary erosion mechanisms in Monel alloy, whereas coating spallation and crater formation were the primary erosion mechanisms in the coatings.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.A. Al-bukhaiti, S.M. Ahmed, F.M.F. Badran and K.M. Emara, Effect of Impingement Angle on Slurry Erosion Behaviour and Mechanisms of 1017 Steel and high-Chromium White Cast Iron, Wear, 2007, 262, p 1187–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.11.018
Y. Li, G.T. Burstein and I.M. Hutchings, The Influence of Corrosion on the Erosion of Aluminium by Aqueous Silica Slurries, Wear, 1995, 186–187, p 515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(95)07181-4
S.S. Rajahram, T.J. Harvey and R.J.K. Wood, Evaluation of a Semi-Empirical Model in Predicting Erosion-Corrosion, Wear, 2009, 267, p 1883–1893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.03.002
V. Javaheri, D. Porter and V.T. Kuokkala, Slurry Erosion of Steel: Review of Tests, Mechanisms and Materials, Wear, 2018, 408–409, p 248–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2018.05.010
P.P. Shitole, S.H. Gawande, G.R. Desale and B.D. Nandre, Effect of Impacting Particle Kinetic Energy on Slurry Erosion, J. Bio- Tribo-Corros., 2015, 1, p 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-015-0028-6
S. Khurana and K.A. Varun, Effect of Silt Particles on Erosion of Turgo Impulse Turbine Blades, Int. J. Ambient Energy., 2014, 35, p 155–162. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2013.789985
B.D. Nandre and G.R. Desale, Study the Effect of Impact Angle on Slurry Erosion Wear of Four Different Ductile Materials, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5, p 7561–7570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.428
I. Finnie, G.R. Stevick and J.R. Ridgely, The Influence of Impingement Angle on the Erosion of Ductile Metals by Angular Abrasive Particles, Wear, 1992, 152, p 91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(92)90206-N
I. Finne, Erosion of Surfaces by Solid Particles, Wear, 1960, 3, p 87–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(60)90055-7
J.G.A. Bitter, A Study of Erosion Phenomena, Part II. Wear., 1963, 6, p 169–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(63)90073-5
H.J. Amarendra, P. Kalhan, G.P. Chaudhari, S.K. Nath and S. Kumar, Slurry Erosion Response of Heat Treated 13cr-4ni Martensitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Forum., 2012, 710, p 500–505. https://www.scientific.net/MSF.710.500
B. Kishor, G.P. Chaudhari and S.K. Nath, Slurry Erosion of Thermo-Mechanically Processed 13Cr4Ni Stainless Steel, Tribol. Int., 2016, 93, p 50–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.08.048
K.H. Lo, F.T. Cheng and H.C. Man, Laser Transformation Hardening of AISI 440C Martensitic Stainless Steel for Higher Cavitation Erosion Resistance, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2003, 173, p 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00347-5
H.S. Grewal, H.S. Arora, A. Agrawal, H. Singh and S. Mukherjee, Slurry Erosion of Thermal Spray Coatings: Effect of Sand Concentration, Procedia Eng., 2013, 68, p 484–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2013.12.210
P.S. Babu, B. Basu and G. Sundararajan, The Influence of Erodent Hardness on the Erosion Behavior of Detonation Sprayed WC-12Co Coatings, Wear, 2011, 270, p 903–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2011.02.019
R.J.K. Wood, B.G. Mellor and M.L. Binfield, Sand Erosion Performance of Detonation Gun Applied Tungsten Carbide/Cobalt-Chromium Coatings, Wear, 1997, 211, p 70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00071-9
S. Dodds, A.H. Jones and S. Cater, Tribological Enhancement of AISI 420 Martensitic Stainless Steel Through Friction-Stir Processing, Wear, 2013, 302, p 863–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2013.01.007
R. Knight, The HVOF Process: The Hottest Topic in the Thermal Spray Industry. Weldi. J., 1993; p 25-30
T.S. Sidhu, S. Prakash and R.D. Agrawal, State of the Art of HVOF Coating Investigations: - A Review, Mar. Technol. Soc. J., 2005, 39, p 53–64. https://doi.org/10.4031/002533205787443908
J.A. Picas, M. Punset, M.T. Baile, E. Martín and A. Forn, Tribological Evaluation of HVOF Thermal-Spray Coatings as a Hard Chrome Replacement, Surf. Interface Anal., 2011, 43, p 1346–1353. https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.3721
G. Santacruz, A.S. Takimi, FVDe Camargo, CP Bergmann and C Fragassa, Comparative Study of Jet Slurry Erosion of Martensitic Stainless Steel with Tungsten Carbide HVOF Coating, Metals., 2019, 9, p 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9050600
L. Thakur, N. Arora, R. Jayaganthan and R. Sood, An Investigation on Erosion Behavior of HVOF Sprayed WC-CoCr Coatings, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 258, p 1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.09.079
S. Hong, Y. Wu, J. Zhang, Y. Zheng, Y. Zheng and J. Lin, Synergistic Effect of Ultrasonic Cavitation Erosion and Corrosion of WC-CoCr and FeCrSiBMn Coatings Prepared by HVOF Spraying, Ultrason. Sonochem., 2016, 31, p 563–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.02.011
K. Kumari, K. Anand, M. Bellacci and M. Giannozzi. Effect of microstructure on abrasive wear behavior of thermally sprayed WC–10Co–4Cr coatings. Wear. 2010, 268, p 1309–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.02.001.
V.A.D. Souza and A. Neville, Corrosion and Erosion Damage Mechanisms During Erosion-Corrosion of WC-Co-Cr Cermet Coatings, Wear, 2003, 255, p 146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00210-2
R. Piola, A.S.M. Ang, M. Leigh and S.A. Wade, A Comparison of the Antifouling Performance of Air Plasma Spray (APS) Ceramic And High Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Coatings for Use in Marine Hydraulic Applications, Biofouling, 2018, 34, p 479–491. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2018.1465052
R. Jasionowski, W. Depczyński and D. Zasada, Analysis of the Initial Cavitation Erosion Period of Selected Nickel Alloys, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2019, 461, p 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/461/1/012032
T.M. Pollock and S. Tin, Nickel-Based Alloys for Advanced Turbine Engines Chemistry, Microstructure, and Properties, J. Propul. Power, 2006, 22, p 361–374. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.18239
J. Cárach, S. Hloch, P. Hlaváček, M. Gombár, D. Klichová, F. Botko, D. Mital and D. Lehocká, Hydro-Abrasive Disintegration of Alloy Monel K-500-the Influence of Technological and Abrasive Factors on the Surface Quality, Procedia Eng., 2016, 149, p 17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.633
O. Marenych and A. Kostryzhev, Strengthening Mechanisms in NIckel-Copper Alloys: A Review, Metals (Basel), 2020 https://doi.org/10.3390/met10101358
V.A.D. Souza and A. Neville, Linking Electrochemical Corrosion Behaviour and Corrosion Mechanisms of Thermal Spray Cermet Coatings (WC-CrNi and WC/CrC-CoCr). Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003;A 352, p 202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093%2802%2900888-2.
A.S.M. Ang, H. Howse, S.A. Wade and C.C. Berndt, Manufacturing of Nickel Based Cermet Coatings by the HVOF Process, Surf. Eng., 2016, 32, p 713–724. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743294415Y.0000000031
H. Howse, A.S.M. Ang, S.A. Wade and C.C Berndt. Investigation into the Suitability of HVOF Nickel Based Cermets in Marine Hydraulic Service Subject to Biofouling. ITSC, 2018, p 759–765
H.J. Amarendra, G.P. Chaudhari and S.K. Nath, Synergy of Cavitation and Slurry Erosion in the Slurry Pot Tester, Wear, 2012, 290–291, p 25–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.05.025
S.A. Romo, J.F. Santa, J.E. Giraldo and A. Toro, Cavitation and High-Velocity Slurry Erosion Resistance of Welded Stellite 6 Alloy, Tribol. Int., 2012, 47(16), p 24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.10.003
C.H. Zhang, C.L. Wu, S. Zhang, Y.F. Jia, M. Guan, J.Z. Tan and B. Lin, Laser Cladding of NiCrSiB on Monel 400 to Enhance Cavitation Erosion and Corrosion Resistance, Rare Met, 2016 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-016-0814-4
Z. Song, W. Shiqi, C. Wendong, H. Siwen, Z. Chunhua and G. Meng, Cavitation Erosion Properties of Ni-Based Re Alloy Coating on Monel Alloy by Laser Cladding, Rare Met Mater Eng, 2018, 47, p 1517–1522.
N.K. Singh, A.S.M. Ang, D.K. Mahajan and H. Singh. Cavitation erosion resistant nickel-based cermet coatings for Monel K-500. Tribol. Int. 2021;159, p 106954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2021.106954
Y.Y. Wang, C.J. Li and A. Ohmori, Influence of Substrate Roughness on the Bonding Mechanisms of High Velocity Oxy-Fuel Sprayed Coatings, Thin Solid Films, 2005, 485, p 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2005.03.024
H.S. Grewal, S. Bhandari and H. Singh, Parametric Study of Slurry-Erosion of Hydroturbine Steels With and Without Detonation Gun Spray Coatings Using Taguchi Technique, Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 2012, 43, p 3387–3401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1148-y
"Standard test method for vickers indentation hardness of advanced ceramics." C13217-08. ASTM Int. 2003; p 1–9.
X. Ding, Y. Huang, C. Yuan and Z. Ding, Deposition and Cavitation Erosion Behavior of Multimodal WC-10Co4Cr Coatings Sprayed by HVOF, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2020, 392, 125757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125757
A. Vackel, G. Dwivedi and S. Sampath, Structurally Integrated, Damage-Tolerant, Thermal Spray Coatings, JOM, 2015, 67, p 1540–1553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1400-1
S. Usmani, S. Sampath, D.L. Houck and D. Lee, Effect of Carbide Grain Size on the Sliding and Abrasive Wear Behavior Of Thermally Sprayed WC-Co Coatings, Tribol. Trans., 1997, 40, p 470–478. https://doi.org/10.1080/10402009708983682
H.S. Grewal, A. Agrawal and H. Singh, Slurry Erosion Mechanism of Hydroturbine Steel: Effect of Operating Parameters, Tribol. Lett., 2013, 52, p 287–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-013-0213-z
H.S. Grewal, A. Agrawal and H. Singh, Design and Development of High-Velocity Slurry Erosion Test Rig Using CFD, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 152–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0219-y
"Standard Test Method for Liquid Impingement Erosion Using Rotating Apparatus" G-73-10. ASTM Stand. 2017, p 1–19
W.A. González-Hermosilla, D. Chicot, J. Lesage, J.G.L Barbera-Sosa, I.C. Gruescu, M.H. Statia and E.S. Puchi-Cabrera, Effect of Substrate Roughness on the Fatigue Behavior of a SAE 1045 Steel Coated with a WC-10Co-4Cr Cermet, Deposited by HVOF Thermal Spray. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2010;A 527, p 6551–6561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.07.014.
"Standard test methods of determining area percentage porosity in thermal sprayed coatings." E2109-01. ASTM Stand, 2014, pp 1–8.
S.Y. Cui, Q. Miao, W.P. Liang, B.Z. Huang, Z. Ding and B.W. Chen, Slurry Erosion Behavior of F6NM Stainless Steel and High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel-Sprayed WC-10Co-4Cr Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2017, 26, p 473–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-016-0515-4
C.W. Lee, J.H. Han, J. Yoon, M.C. Shin and S.I. Kwun, A Study on Powder Mixing for High Fracture Toughness and Wear Resistance of WC-Co-Cr Coatings Sprayed by HVOF, Surf. Coat.ings Technol., 2010, 204, p 2223–2229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.12.014
M.Á. Reyes-Mojena, M. Sánchez-Orozco, H. Carvajal-Fals, R. Sagaró-Zamora and C.R. Camello-Lima. A Comparative Study on Slurry Erosion Behavior of HVOF Sprayed Coatings. DYNA, 2017, 84, p 239–246. https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v84n202.56542.
A.K. Chauhan, D.B. Goel and S. Prakash, Erosive Wear of a Surface Coated Hydroturbine Steel, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2010, 33, p 483–489.
I.M. Hutchings, A Model for the Erosion of Metals by Spherical Particles at Normal Incidence, Wear, 1981, 70, p 269–281.
A.K. Maiti, N. Mukhopadhyay and R. Raman, Improving the wear behavior of WC-CoCr-based HVOF coating by surface grinding, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2009, 18, p 1060–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-009-9354-5
Acknowledgment
The authors thankfully acknowledge the support provided by the Indian Institute of Technology Ropar, India, and Swinburne University of Technology Melbourne, Australia. The authors would also like to thank the Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India for providing the research equipment and facility under DST FIST project No. SR/FST/ETI-379/2014 (c) for the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N.K., Kumar, A., Ang, A.S.M. et al. Characterization and Slurry Erosion Mechanisms of Nickel-Based Cermet Coatings on Monel K-500. J Therm Spray Tech 30, 2138–2154 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-021-01267-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-021-01267-y