Abstract
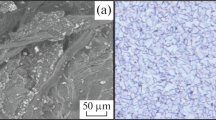
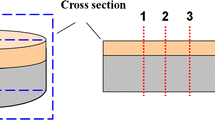
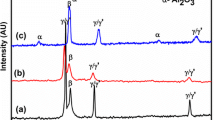
The behavior of NiCrBSi coatings deposited by three different spraying techniques was studied: flame spray with a subsequent flame treatment (FS + Flame), flame spray with post-laser treatment (FS + Laser) and laser cladding (LC). The coating responses under wear and oxidation conditions were analyzed. Although the microstructure of the coatings deposited by the three different techniques showed similar phases and precipitates, some changes in the size and distribution of these constituents were observed. The pin on disk configuration was used to determine the friction coefficients and wear rates. LC coatings showed the highest wear resistance, with plastic deformation being the main wear mechanism identified for all of the coatings analyzed. Tests under aggressive environments were also performed to determine the oxidation kinetics.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Glaeser, Materials for Tribology, Elsevier Science Publishers B.V, The Netherlands, 1992
J.R. Davis, International Handbook Committee, A.S.M. Nickel, Cobalt, and Their Alloys, ASM Handbook series, ASM International, Ohio, 2001
U. Heubner, Nickel Alloys, Marcell Dekker Inc, New York, 1998
M. Roy, Surface Engineering for Enhanced Performance against Wear, Springer, Heidelberg, 2013
J. Burnell-Gray and P.K. Datta, Surface Engineering Casebook: Solutions to Corrosion and Wear, Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, 1996
L. Pawlowski, The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, Wiley, England, 2008
S. Houdková, E. Smazalová, M. Vostřák, and J. Schubert, Properties of NiCrBSi Coating, as Sprayed and Remelted by Different Technologies, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 253, p 14-26
C. Navas, R. Colaço, J. de Damborenea, and R. Vilar, Abrasive Wear Behaviour of Laser Clad and Flame Sprayed-Melted NiCrBSi Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200, p 6854-6862
R. González, M. Cadenas, R. Fernández, J.L. Cortizo, and E. Rodríguez, Wear Behaviour of Flame Sprayed NiCrBSi Coating Remelted by Flame or by Laser, Wear, 2007, 262, p 301-307
R. González, M.A. García, I. Penuelas, M. Cadenas, M. del Rocío Fernández, A. Hernández Battez, and D. Felgueroso, Microstructural Study of NiCrBSi Coatings Obtained by Different Processes, Wear, 2007, 263, p 619-624
J.M. Miguel, J.M. Guilemany, and S. Vizcaino, Tribological Study of NiCrBSi Coating Obtained by Different Processes, Tribol. Int., 2003, 36, p 181-187
Z. Bergant and J. Grum, Quality Improvement of Flame Sprayed, Heat Treated, and Remelted NiCrBSi Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2009, 18, p 380-390
J. Suutala, J. Tuominen, and P. Vuoristo, Laser-Assisted Spraying and Laser Treatment of Thermally Sprayed Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 201, p 1981-1987
M.R. Karimi, H.R. Salimijazi, and M.A. Golozar, Effects of Remelting Processes on Porosity of NiCrBSi Flame Sprayed Coatings, Surf. Eng., 2016, 32, p 238-243
J.R. Davis, Handbook of Thermal Spray Technology, ASM International, Ohio, 2004
R.J.K. Wood, Tribo-Corrosion Of Coatings: A Review, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2007, 40, p 5502-5521
A.A. Boudi, M.S.J. Hashmi, and B.S. Yilbas, HVOF Coating of NI, 625 onto Stainless and Carbon Steel Surfaces: Corrosion and Bonding Testing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, 155-156, p 2051-2055
J.R. Davis, Surface Engineering for Corrosion and Wear Resistance, ASM International, Ohio, 2001
E. Fernández, M. Cadenas, R. González, C. Navas, R. Fernández, and J. de Damborenea, Wear Behaviour of Laser Clad NiCrBSi Coating, Wear, 2005, 259, p 870-875
T. Gómez del Río, M.A. Garrido, J.E. Fernández, M. Cadenas, and J. Rodríguez, Influence of the Deposition Techniques on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of NiCrBSi Coatings, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 204, p 304-312
Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile method—Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. ISO 4287:1997, International Organization for Standardization, 1997, p 1-25
Geometrical Product Specification (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile Method—Motif Parameters. ISO 12085:1998-05, International Organization for Standardization, 1998, p 1-17
Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin on Disk Apparatus. ASTM G99-95, ASTM International, 1995, p 1-6
J.F. Archard, Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces, J. Appl. Phys., 1953, 24, p 981-988
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7(4), p 1564-1583
Standard Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys. ASTM E407-99, ASTM International, 1999, p 1-21
Standard guide for Metallographic Preparation of Thermal Sprayed Coatings. ASTM E1920-03, ASTM International, 2003, p 1-5
J. Rodriguez, A. Martin, R. Fernandez, and J.E. Fernandez, An Experimental Study of the Wear Performance of NiCrBSi Thermal Spray Coatings, Wear, 2003, 255, p 950-955
Q. Li, D. Zhang, T. Lei, C. Chen, and W. Chen, Comparison of Laser-Clad and Furnace-Melted Ni-Based Alloy Microstructures, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2001, 137, p 122-135
D.W. Zhang, T.C. Lei, J.G. Zhang, and J.H. Ouyang, The Effects of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Erosion Properties of Laser Surface-Clad Ni-Base Alloy, Surf. Coat. Technol., 1999, 115, p 176-183
A.K. Nusair, J. Lu, and H. Liao, Effect of Residual Stresses on Air Plasma Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 168, p 291-299
Y.Y. Santana, J.G. La Barbera-Sosa, M.H. Staia, J. Lesage, E.S. Puchi-Cabrera, D. Chicot, and E. Bemporad, Measurement of Residual Stress in Thermal Spray Coatings by the Incremental Hole Drilling Method, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 201, p 2092-2098
N. Serres, F. Hlawka, S. Costil, C. Langlade, F. Machi, and A. Cornet, Dry Coatings and Ecodesign. Part 2. Tribological Performances, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 204, p 197-204
N. Serres, F. Hlawka, S. Costil, C. Langlade, and F. Machi, Microstructures of Metallic NiCrBSi Coatings Manufactured via Hybrid Plasma Spray and In Situ Laser Remelting Process, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2011, 20, p 336-343
G. Qian, T. Nakamura, and C.C. Berndt, Effects of Thermal Gradient and Residual Stresses on Thermal Barrier Coating Fracture, Mech. Mater., 1998, 27, p 91-110
J.A. Greenwood and J.B.P. Willamson, Contact of Nominally Flat Surfaces, Proc. R. Soc. Lond., 1966, 295(1442), p 300-319
A. Rico, M.A. Garrido Maneiro, T. Gómez del Rio, A. Salazar, and J. Rodríguez, On the Determination of Elastic Modulus in Very Stiff Materials by Depth Sensing Indentation, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44(21), p 5795-5799
H. Hertz, On the Contact of Elastic Solids, J. Reine. Angew. Math., 1881, 92, p 156-171 (in German)
I.M. Hutchings and E. Arnold, Friction and Wear of Engineering Materials, Hodder & Stoughton, London, 1992
A.G. Evans, J.W. Hutchinson, and M.Y. He, Micromechanics Model for the Detachment of Residually Brittle Films and Coatings, Acta Mater., 1999, 47, p 1513-1522
C.H. Hsueh and E.R. Fuller, Analytical Modelling of Oxide Thickness Effects on Residual Stress in Thermal Barrier Coatings, Scr. Mater., 2000, 42(8), p 781-787
M.Y. Ali, S.Q. Nusier, and G.M. Newaz, Mechanism of Damage Initiation and Growth in a TBC/Superalloy System, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2001, 38, p 3329-3340
A. Rabiei and A.G. Evans, Failure Mechanisms Associated with the Thermally Grown Oxide in Plasma-Sprayed Thermal Barrier Coatings, Acta Mater., 2000, 48, p 3963-3976
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Spanish government CICYT through Grants MAT2001-3528-C03-03 and MAT2013-41784-R for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrido, M.A., Rico, A., Gómez, M.T. et al. Tribological and Oxidative Behavior of Thermally Sprayed NiCrBSi Coatings. J Therm Spray Tech 26, 517–529 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-016-0521-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-016-0521-6