Abstract
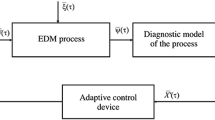
One approach for controlling the twin wire arc spray process is to use optical properties of the particle beam as input parameters for a process control. The idea is that changes in the process like eroded contact nozzles or variations of current, voltage, and/or atomizing gas pressure may be detected through observation of the particle beam. It can be assumed that if these properties deviate significantly from those obtained from a beam recorded for an optimal coating process, the spray particle and thus the coating properties change significantly. The goal is to detect these deviations and compensate the occurring errors by adjusting appropriate process parameters for the wire arc spray unit. One method for monitoring optical properties is to apply the diagnostic system particle flux imaging (PFI): PFI fits an ellipse to an image of a particle beam thereby defining easy to analyze characteristical parameters by relating optical beam properties to ellipse parameters. Using artificial neural networks (ANN), mathematical relations between ellipse and process parameters can be defined. It will be shown that in the case of a process disturbance through the use of an ANN-based control new process parameters can be computed to compensate particle beam deviations.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Pawlowski, The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, Wiley, Chichester, UK, 1995
F.-W. Bach, A. Laarmann, and T. Wenz, Ed., Modern Surface Technology, Wiley, Weinheim, Germany, 2006
E. Lugscheider, F. Ernst, K. Seemann, T. Pfeifer, J. Dören, and J. Zierhut, Quality Control of Thermal Spray Processes Through Cost Effective Diagnostic Methods, Thermal Spray 2005: Thermal Spray Connects: Explore its Surfacing Potential Basel, E. Lugscheider, Ed., Switzerland, DVS-ASM, 2005, p 1534-1539
A. Jakimov, M. Hertter, and H. Abdullahi, Plasma Spray Process Control with Neural Network, Thermal Spray 2005: Thermal Spray Connects: Explore its Surfacing Potential, E. Lugscheider, Ed., DVS-ASM, Basel, Switzerland, 2005, p 673-678
A.-F. Kanta, G. Montavon, M.-P. Planche, and C. Coddet, Artificial Intelligence Computation to Establish Relationships Between APS Process Parameters and Alumina-Titania Coating Properties, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 2008, 28(2), p 249-262
T.A. Choudhury, N. Hosseinzadeh, and C.C. Berndt, Artificial Neural Network Application for Predicting In-Flight Particle Characteristics of an Atmospheric Plasma Spray Process, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2011, 205(21-22), p 4886-4895
R.B. Heimann, Better Quality Control: Stochastic Approaches to Optimize Properties and Performance of Plasma-Sprayed Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(4), p 765-778
K. Hartz-Behrend, J. Schein, D.P. Jonke, M. Englhart, and J. Zierhut, Control of Wire Arc Spraying Using Artificial Neural Networks for the Production of Thin-Walled Moulds for Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics, Thermal Spray 2012: Air, Land, Water and the Human Body: Thermal Spray Science and Applications, R.S. Lima, A. Agarwal, M.M. Hyland, Y.-C. Lau, C.-J. Li, A. McDonald, and F.-L. Toma, Ed., ASM International, Houston, Texas, 2012, p 436-441
A. Khudhair, N.A. Talib, Neural Network Analysis for Sliding Wear of 13% Cr Steel Coatings by Electric Arc Spraying, First Engineering Scientific Conference, College of Engineering—University of Diyala, Diyala Journal of Engineering Sciences, 22-23 December, 2010, p 157-169
Y. Korobov, S. Nevezhin, V. Verkhorubov, G. Rimer, A. Zhilin, Optimization of Alloying of Heat Resistant Core Wires for Arc Spraying by Neural Network Modeling. Thermal Process Modeling: Proceedings from the 5th International Conference on Thermal Process Modeling and Computer Simulation, B.L. Ferguson, R. Goldstein, R. Papp, Ed., June 16-18, (Orlando, Florida), ASM International, 2014, p 323-328
K.D. Landes, T.V. Streibl, J. Zierhut, Particle Flux Imaging (PFI) and Particle Shape Imaging (PSI)—Two Innovative Diagnostics for Thermal Coating. International Thermal Spray Conference, E. Lugscheider and C.C. Berndt, Ed., March 4-6, (Essen, Germany), DVS Deutscher Verband für Schweißen, 2002, p 47-51
J. Zierhut, W. Pellkofer, A. Sagel, T. Haug, and K.D. Landes, Verification of Particle Flux Imaging (PFI) an In-Situ Diagnostic Method, Thermal Spray 2001 New Surfaces for a New Millennium, 28-30, C.C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, Singapore, 2001, p 787-790
J. Zierhut, K.D. Landes, W. Krömmer, and P. Heinrich, Particle Flux Imaging (PFI) In-Situ Diagnostics for Thermal Coating Process, Thermal Spray: Surface Engineering via Applied Research, May 8-11, 2000, C.C. Berndt, Ed., ASM International, Montréal, Québec, 2000, p 63-66
M. McCord Nelson and W.T. Illingworth, A Practical Guide to Neural Nets, Addison Wesley, New York, 1991
Acknowledgments
Parts of this research and development project were funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) within the Framework Concept “Research for Tomorrow’s Production” (funding Number 02PO2394) and managed by the Project Management Agency Karlsruhe (PTKA). The authors are responsible for the contents of this publication. For our investigations, we were also supported with a spray gun from the company T-Spray and with a power source from the company EWM. We thank the BMBF, the PTKA, T-Spray, and EWM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartz-Behrend, K., Schaup, J., Zierhut, J. et al. Controlling the Twin Wire Arc Spray Process Using Artificial Neural Networks (ANN). J Therm Spray Tech 25, 21–27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0341-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0341-0