Abstract
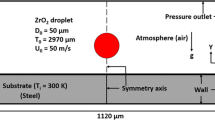
In this paper, impact, spreading, and solidification of molten droplet on a dissimilar substrate along with substrate melting and its re-solidification are investigated numerically. Volume of fluid surface tracking method coupled with the solidification model within a one-domain continuum formulation is used to model the transient flow during the droplet impact, its subsequent spreading, and solidification. Evolution of melting front in the substrate is modeled by solving the governing equations for solidification in the substrate, too. Simulations are performed for the impact of a heated droplet on a substrate. The model predicts substrate melting, which can give better insight of bonding between the coating material and substrate, where droplet and substrate are of different materials. It is observed that melting in the substrate in the present case starts soon after the impact of the heated droplet. The depth and the width of the melting front in the substrate increase with the time and after reaching a maximum they start to decrease because of start of re-solidification from the melted edge. In the central part of the splat droplet solidifies, while the substrate remains melted which can enhance the coating strength and its bonding with the substrate.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
Specific heat capacity (J/kg/K)
- C :
-
Constant related to Darcy source term (kg/m3/s)
- D 0 :
-
Initial droplet diameter (m)
- f l :
-
Weight fraction of liquid
- f s :
-
Weight fraction of solid
- F :
-
Volume of fluid function
- F vol :
-
Continuum surface tension force (N/m3)
- \(\vec{g}\) :
-
Acceleration due to gravity vector (m/s2)
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/m/K)
- L :
-
Latent heat of fusion (J/kg)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- U 0 :
-
Droplet’s initial impact velocity (m/s)
- \(\vec{u}\) :
-
Continuum velocity vector (m/s)
- μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg/m/s)
- ρ:
-
Density (kg/m3)
- σ:
-
Surface tension (N/m)
- d:
-
Droplet
- sub:
-
Substrate
- air:
-
Air
- 0:
-
Initial
- s:
-
Solid
- solidus:
-
Solidus temperature
- l:
-
Liquid
- liquidus:
-
Liquidus temperature
- l,d:
-
Liquid droplet
- s,d:
-
Solid droplet
- l,sub:
-
Liquid phase in substrate
- s,sub:
-
Solid substrate
References
S. Kitahara and A. Hasui, A Study of the Bonding Mechanism of Sprayed Coatings, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 1974, 11, p 747-752
R. McPherson, The Relationship Between the Mechanism of Formation, Microstructure and Properties of Plasma Sprayed Coatings, Thin Solid Films, 1981, 83, p 297-310
S. Dallaire, Influence of Temperature on the Bonding Mechanism of Plasma-Sprayed Coatings, Thin Solid Films, 1982, 95, p 237-244
H.D. Steffens, B. Wielage, and J. Drozak, Interface Phenomena and Bonding Mechanism of Thermally-Sprayed Metal and Ceramic Composites, Surf. Coat. Technol., 1991, 45, p 299-308
C.H. Amon, K.S. Schmaltz, R. Merz, and F.B. Prinz, Numerical and Experimental Investigation of Interface Bonding Via Substrate Remelting of an Impinging Molten Metal Droplet, J. Heat Transf., 1996, 118, p 164-172
L.J. Zarzalejo, K.S. Schmaltz, and C.H. Amon, Molten Droplet Solidification and Substrate Remelting in Microcasting—Part I: Numerical Modeling and Experimental Verification, Heat Mass Transf., 1999, 34, p 477-485
K.S. Schmaltz, L.J. Zarzalejo, and C.H. Amon, Molten Droplet Solidification and Substrate Remelting in Microcasting—Part II: Parametric Study and Effect of Dissimilar Materials, Heat Mass Transf., 1999, 35, p 17-23
S.-P. Wang, G.-X. Wang, and E.F. Matthys, Melting and Resolidification of a Substrate in Contact with a Molten Metal: Operational Maps, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 1998, 41, p 1177-1188
D. Attinger and D. Poulikakos, Melting and Resolidification of a Substrate Caused by Molten Microdroplet Impact, J. Heat Transf., 2001, 123, p 1110-1122
H. Zhang, X.X. Wang, L.L. Zheng, and X.X. Jiang, Studies of Splat Morphology and Rapid Solidification During Thermal Spraying, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2001, 44, p 4579-4592
L. Li, X.Y. Wang, G. Wei, A. Vaida, H. Zhang, and S. Sampath, Substrate Melting During Thermal Spray Splat Quenching, Thin Solid Films, 2004, 468, p 113-119
F.J. Hong and H.-H. Qiu, Modeling of Substrate Remelting, Flow, and Resolidification in Microcasting, Numer. Heat Transf. A, 2005, 48, p 987-1008
W. Wang, R.A. Lambert, and R.H. Rangel, Parametric Study of Multi-splat Solidification/Remelting Including Contact Resistance Effects, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2008, 51, p 4811-4819
C.J. Li, C.X. Li, G.J. Yang, and Y.Y. Wang, Examination of Substrate Surface Melting-Induced Splashing During Splat Formation in Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2006, 15(4), p 717-724
S. Kamnis and S. Gu, Numerical Modelling of Droplet Impingement, J. Phys. D, 2005, 38, p 3664-3673
A. Kumar, S. Gu, H. Tabbara, and S. Kamnis, Study of Impingement of Hollow ZrO2 Droplets onto a Substrate, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 220, p 164-169
A. Kumar, S. Gu, and S. Kamnis, Simulation of Impact of a Hollow Droplet on a Flat Surface, Appl. Phys. A, 2012, 109, p 101-109
A.D. Brent, V.R. Voller, and K.J. Reid, The Enthalpy-Porosity Technique for Modelling Convection Diffusion Phase Change: Application to the Melting of a Pure Metal, Numer. Heat Transf., 1988, 13, p 297-318
J.U. Brackbill, D.B. Kothe, and C. Zemach, A Continuum Method for Modeling Surface Tension, J. Comput. Phys., 1992, 100, p 335-354
N. Pathak, A. Kumar, A. Yadav, and P. Dutta, Effects of Mould Filling on Evolution of the Solid-Liquid Interface During Solidification, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2009, 29, p 3669-3678
N.Z. Mehdizadeh, M. Lamontagne, C. Moreau, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Photographing Impact of Molten Molybdenum Particles in a Plasma Spray, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2005, 14(3), p 354-361
M. Pasandideh-Fard, V. Pershin, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Splat shapes in a Thermal Spray Coating Process: Simulations and Experiments, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2001, 11, p 206-217
J. Mostaghimi, Modelling Droplet Impact in Plasma Spray Processes, Pure Appl. Chem., 1998, 70(6), p 1209-1215
M. Pasandideh-Fard, M. Qiao, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Capillary Effects During Droplet Impact on a Solid Surface, Phys. Fluids, 1996, 8(3), p 650-659
M. Xue, Y. Heichal, and S. Chandra, Modeling the Impact of a Molten Metal Droplet on a Solid Surface Using Variable Interfacial Thermal Contact Resistance, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 9-18
V. Mehdi-Nejad, J. Mostaghimi, and S. Chandra, Air Bubble Entrapment Under an Impacting Droplet, Phys. Fluids, 2003, 15, p 173-183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the 6th Asian Thermal Spray Conference (ATSC 2014) and has been expanded from the original presentation. ATSC 2014 was held in Hyderabad, India, November 24-26, 2014, and was organized by the International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials (ARCI) and the Asian Thermal Spray Society.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, R.K., Kumar, A. Substrate Melting and Re-solidification During Impact of High-Melting Point Droplet Material. J Therm Spray Tech 24, 1368–1376 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0326-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0326-z