Abstract
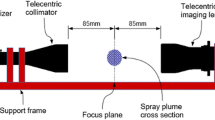
Wire arc spraying is one of the most common and elementary thermal spray processes. Due to its easy handling, high deposition rate, and relative low process costs, it is a frequently used coating technology for the production of wear and corrosion resistant coatings. In order to produce reliable and reproducible coatings, it is necessary to be able to control the coating process. This can be achieved by analyzing the parameters of the particles deposited. Essential for the coating quality are, for example, the velocity, the size, and the temperature of the particles. In this work, an innovative diagnostic for particle velocity and location determination is presented. By the use of several synchronized CMOS-Cameras positioned around the particle jet, a series of images from different directions is simultaneously taken. The images contain the information that is necessary to calculate the 3D-location-vector of the particles and finally with the help of the exposure time the trajectory can be determined. In this work, the experimental setup of the tomographic diagnostic is presented, the mathematical method of the reconstruction is explained, and first measured velocity distributions are shown.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- v x , v y , and v z :
-
Velocity components
- \(\vec{\upsilon}\) :
-
Particle trajectory
- F P :
-
Particle trace surface
- E C :
-
E-Coordinate of the center of area
- z C :
-
z-Coordinate of the center of area
- a :
-
Major axis of an ellipse
- b :
-
Minor axis of an ellipse
- ε:
-
Angle between the E-axis and the major axis of the ellipse
- i :
-
Number of camera
- φ i :
-
Angle of camera i
- D :
-
Particle diameter
- L :
-
Covered distance in the Ez-plane
- dz :
-
Covered distance in z-direction
- P S :
-
Start point of a particle trace
- P E :
-
End point of a particle trace
- E S :
-
E-Coordinate of the start point
- E E :
-
E-Coordinate of the end point
- z S :
-
z-Coordinate of the start point
- z E :
-
z-Coordinate of the end point
- N :
-
Number of measurement points
- A :
-
Amplitude of the sinus wave
- P :
-
Phase of the sinus wave
- K 1, K 2 :
-
Parameters of the lineraized function
- R :
-
Square error
- x S , y S , z S :
-
Coordinates of the start point
- x E , y E , z E :
-
Coordinates of the end point
- M :
-
Scale
- t B :
-
Exposure time
- T :
-
Temperature of the particle surface
- λ1, λ2 :
-
Wavelengths of the interference filters
- C 2 :
-
Second Planck constant
- Q :
-
Ratio of the two corresponding pictures taken at different wavelengths
References
P.L. Fauchais, J. Heberlein, and M.I. Boulos, Wire Arc Spraying, Thermal Spray Fundamentals, Springer, New York, 2014, p 577-629
H.-D. Steffens, Z. Babiak, and M. Wewel, Recent Developments in Arc Spraying, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 1990, 18(6), p 974-979
B. Budig, Mündersbach, EWM-forceArc® ein kraftvolles Werkzeug zum MIG-/MAG-Schweißen, 2008.
M.H. Malek, N.H. Saad, S.K. Abas, and N.M. Shah, Thermal Arc Spray Overview, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2013, 46, p 1-10
F. Bach, K. Möhwald, A. Laarmann, and T. Wenz, Modern Surface Technology, Wiley, Weinheim, 2006
K. Hartz-Behrend, S. Kirner, J. Schein, D. Jonke, M. Englhart, and J. Zierhut, Control of Wire Arc Spraying Using Artificial Neural Networks for the Production of Thin-Walled Moulds for Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics, Thermal Spray 2012: Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference (ASM International), Vol 6, 2012, p 436-441
E. Pfender, Thermal Plasma Technology: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Going?, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process., 1999, 19(1), p 1-31
I. Gedzevicius and A.V. Valiulis, Analysis of Wire Arc Spraying Process Variables on Coatings Properties, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 175(1), p 206-211
A.P. Newbery, P.S. Grant, and R.A. Neiser, The Velocity and Temperature of Steel Droplets During Electric Arc Spraying, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2005, 195(1), p 91-101
A. Pourmousa, J. Mostaghimi, A. Abedini, and S. Chandra, Particle Size Distribution in a Wire-Arc Spraying System, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2005, 14(4), p 502-510
X. Wang, J. Heberlein, E. Pfender, and W. Gerberich, Effect of Nozzle Configuration, Gas Pressure, and Gas Type on Coating Properties in Wire Arc Spray, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 1999, 8(4), p 565-575
H.-E. Albrecht, M. Borys, N. Damaschke, and C. Tropea, Laser Doppler and Phase Doppler Measurement Techniques, Springer, Berlin, 2003
S. Zimmermann, E. Vogli, M. Kauffeldt, M. Abdulgader, B. Krebs, B. Rüther, K. Landes, J. Schein, and W. Tillmann, Supervision and Measuring of Particle Parameters During the Wire-Arc Spraying Process with the Diagnostic Systems Accuraspray-g3 and LDA (Laser-Doppler-Anemometry), J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(4), p 745-755
G. Mauer, R. Vaßen, S. Zimmermann, T. Biermordt, M. Heinrich, J.-L. Marques, K. Landes, and J. Schein, Investigation and Comparison of In-Flight Particle Velocity During the Plasma-Spray Process as Measured by Laser Doppler Anemometry and DPV-2000, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2013, 20, p 1-9
J. Zierhut, “Entwicklung von Diagnostikverfahren zur Optimierung von Plasmaspritzsystemen”, Dissertation, Universität der Bundeswehr München, 2000
A.P. Newbery, T. Rayment, and P.S. Grant, A Particle Image Velocimetry Investigation of In-Flight and Deposition Behaviour of Steel Droplets During Electric Arc Sprayforming, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 383(1), p 137-145
T. Streibl, “Entwicklung eines bildgebenden Partikeldiagnostikverfahrens zur Untersuchung Thermischer Spritzprozesse,” Dissertation, Universität der Bundeswehr München, 2002.
S. Zimmermann, K. Landes, and J. Schein, Innovative Methode zur Partikelklassifizierung beim thermischen Spritzen, Materialwiss. Werkstofftech., 2008, 39(1), p 18-23
J. Thevenet, M. Siroux, and B. Desmet, Measurements of Brake Disc Surface Temperature and Emissivity by Two-Color Pyrometry, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2010, 30(6), p 753-759
E. Siewert, J. Schein, and G. Forster, Determination of Enthalpy, Temperature, Surface Tension and Geometry of the Material Transfer in PGMAW for the System Argon-Iron, J. Phys. D, 2013, 46(22), p 224008
B. Liptak, Temperature Measurement, Chilton Book Company, West Chester, 1993
T. McGee, Principles and Methods of Temperature Measurement, Wiley, Inc., New York, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the 2014 International Thermal Spray Conference, held May 21-23, 2014, in Barcelona, Spain, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirner, S., Forster, G. & Schein, J. Tomographic Particle Localization and Velocity Measurement. J Therm Spray Tech 24, 38–45 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-014-0157-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-014-0157-3