Abstract
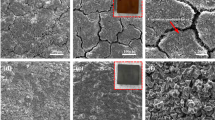
Steel is an indispensable material in the modern construction industry. The economic loss and safety threats caused by steel corrosion are very serious each year. Some traditional measures, such as surface coating and corrosion inhibitors, have been implemented to mitigate steel degradation. These methods are typically environmentally unfriendly and uneconomical. Therefore, a novel, promising and “green” approach was investigated in this study for the protection of steel corrosion through the formation of organic-inorganic hybrid biofilms composed of calcite minerals and microbial extracellular polymeric substances in the presence of the biomineralized bacterium Paenibacillus. The surface morphologies and electrochemical tests revealed that the hybrid biofilm was dense and compact, providing a strong protective barrier for the steel. In addition, the mechanism by which bacteria inhibited steel corrosion was discussed carefully in this study. Hence, this study introduces a new perspective and an alternative for inhibiting steel corrosion.
Graphical Abstract




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
A. López, R. Bayón and F. Pagano, Tribocorrosion Behavior of Mooring High Strength Low Alloy Steels in Synthetic Seawater, Wear, 2015, 338–339, p 1–10.
X.G. Li, D.W. Zhang, Z.Y. Liu, Z. Li, C.W. Du and C.F. Dong, Materials Science: Share Corrosion Data, Nature, 2015, 527, p 441–442.
D.V. Andreeva, D. Fix, H. Mohwald and D.G. Shchukin, Self-healing Anticorrosion Coatings Based on pH-Sensitive Polyelectrolyte/Inhibitor Sandwich like Nanostructures, Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, p 2789–2794.
D.G. Shchukin, M. Zheludkevich, K. Yasakau, S. Lamaka, M.G.S. Ferreira and H. Mohwald, Layer-by-Layer Assembled Nanocontainers for Self-healing Corrosion Protection, Adv. Mater., 2006, 18, p 1672–1678.
A.S. Yaro, H. Al-Jendeel and A.A. Khadom, Cathodic Protection System of Copper-Zinc-Saline Water in Presence of Bacteria, Desalination, 2011, 270, p 193–198.
I.M. Mousaa, Gamma Irradiation Processed (Epoxidized Soybean Fatty Acids/Rho-substituted Aromatic Amines) Adducts as Corrosion Inhibitors for UV Curable Steel Coatings, Prog. Org. Coat., 2017, 111, p 220–230.
R. Jia, T. Unsal, D.K. Xu, Y. Lekbach and T.Y. Gu, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion and Current Mitigation Strategies: A State of the Art Review, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2018, 125, p 116–124.
F. Mansfeld, The interaction of bacteria and metal surfaces, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, p 7670–7680.
F. Mansfeld, H. Hsu, D. Örnek, T.K. Wood and B.C. Syrettc, Corrosion Control Using Regenerative Biofilms on Aluminum 2024 and Brass in Different Media, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2002, 149, p B130–B138.
T. Unsal, E. Ilhan-Sungur, S. Arkan and N. Cansever, Effects of Ag and Cu Ions on the Microbial Corrosion of 316L Stainless Steel in the Presence of Desulfovibrio sp, Bioelectrochemistry, 2016, 110, p 91–99.
V.L. Finkenstadt, G.L. Cote and J.L. Willett, Corrosion Protection of lowcarbosteel Using Exopolysaccharide Coatings from Leuconostoc Mesenteroides, Biotechnol. Lett., 2011, 33, p 1093–1100.
H.Y. Tang, C. Yang, T. Ueki et al., Stainless Steel Corrosion via Direct Iron-to-Microbe Electron Transfer by Geobacter Species, ISME J., 2021, 15, p 3084–3093.
A. Tg, W.A. Di, B. Yl et al., Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbial Biocorrosion, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2021, 29, p 100763.
A. Ez, A. Yl, B. Tg et al., Bioenergetics and Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbial Fuel Cells and Microbial Corrosion, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2021, 31, p 100830.
A. Nagiub and F. Mansfeld, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Inhibition (MICI) Due to Bacterial Contamination, Mater. Corros., 2001, 52(11), p 817–826.
Y. Gao, D. Feng, M. Moradi et al., Inhibiting Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy 5083 Through Vibrio Species Biofilm, Corros. Sci., 2021, 180, 109188.
Z. Li, J. Zhou, X. Yuan, Xu. Yan, Xu. Dake, D. Zhang, D. Feng and F. Wang, Marine Biofilms with Significant Corrosion Inhibition Performance by Secreting Extracellular Polymeric Substances, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2021, 13(39), p 47272–47282.
T. Liu, Z. Guo, Z. Zeng, N. Guo, Y. Lei, T. Liu, S. Sun, X. Chang, Y. Yin and X. Wang, Marine Bacteria Provide Lasting Anticorrosion Activity for Steel via Biofilm-Induced Mineralization, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, p 40317–40327.
N. Guo, Y. Wanga, X. Huia, Q. Zhaoa, Z. Zeng, S. Pana, Z. Guoa, Y. Yina and T. Liua, Marine Bacteria Inhibit Corrosion of Steel via Synergistic Biomineralization, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2021, 66, p 82–90.
A. Pedersen, Bacterial Corrosion of Iron in Seawater In situ, and in Aerobic and Anaerobic Model Systems, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2002, 86, p 139–147.
S.K. Karn, G. Fang and J. Duan, Bacillus sp. Acting as Dual Role for Corrosion Induction and Corrosion Inhibition with Carbon Steel (CS), Front. Microbiol., 2017, 8, p 2038.
M.S. Khan, C. Yang, Y. Zhao, H. Pan, J. Zhao, M.B. Shahzad, S.K. Kolawole, I. Ullah and K. Yang, An Induced Corrosion Inhibition of X80 Steel by Using Marine Bacterium Marinobacter Salsuginis, Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2020, 189, p 110858.
C. Qian and Q. Zhan, Bioremediation of Heavy Metal Ions by Phosphateâ mineralization Bacteria and Its Mechanism, J. Chin. Chem. Soc., 2016, 63(7), p 1.
Q. Zhan, C. Qian and H. Yi, Microbial-Induced Mineralization and Cementation of Fugitive Dust and Engineering Application, Constr. Build. Mater., 2016, 121, p 1.
Y. Chen, C. Qian, H. Zhou and S. Das, Characterization Methods for the Effect of Microbial Mineralization on the Microstructure of Hardened C3S Paste, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2020, 2020, p 1.
Y. Su, J. Feng, P. Jin and C. Qian, Influence of Bacterial Self-healing Agent on Early Age Performance of Cement-Based Materials, Constr. Build. Mater., 2019, 218, p 1.
B.N. Grgur, V. Lazić, D. Stojić and R. Rudolf, Electrochemical Testing of Noble Metal Dental Alloys: The Influence of Their Chemical Composition on the Corrosion Resistance, Corros. Sci., 2021, 184, p 109412.
B.A. Abdulhessein and A.M. Ali, Green Corrosion Inhibitor of Low Carbon Steel in Acidic Media by Pectin Nanoparticles Using Potentiostatic and Weight Losses Method, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2021, 6198, p 1.
Y. Shen, Study of Pitting Corrosion Inhibition Effect on Aluminum Alloy in Seawater by Biomineralized Film, Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, 132, 107408.
T. Zheng and C. Qian, Influencing Factors and Formation Mechanism of CaCO3 Precipitation Induced by Microbial Carbonic Anhydrase, Process Biochem., 2020, 91, p 271–281.
ASTM, G. Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. American Society for Testing and Materials, 2003.
S. Fonna, I.B.M. Ibrahim, S. Huzni, M. Ikhsan and S. Thalib, Investigation of Corrosion Products Formed on the Surface of Carbon Steel Exposed in Banda Aceh’s Atmosphere, Heliyon, 2021, 7(4), p e06608.
K. Xiao et al., Corrosion Products and Formation Mechanism During Initial Stage of Atmospheric Corrosion of Carbon Steel, J. Iron Steel Res. (Int.), 2008, 15(5), p 42–48.
Y. Oppenheimer-Shaanan, O. Sibony-Nevo, Z. Bloom-Ackermann, R. Suissa, N. Steinberg, E. Kartvelishvily, V. Brumfeld and I. Kolodkin-Gal, Spatio-Temporal Assembly of Functional Mineral Scaffolds within Microbial Biofilms, NPJ Biofilms Microbiol., 2016, 2, p 15031–15041.
B. Pokroy, J.P. Quintana, E.N. Caspi, A. Berner and E. Zolotoyabko, Anisotropic Lattice Distortions in Biogenic Aragonite, Nat. Mater., 2004, 3, p 900–902.
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, Transportation Research Board, National Cooperative Highway Research Program. Electrochemical Test Methods to Evaluate the Corrosion Potential of Earthen Materials. National Academies Press, 2021–02–11.
H. Ma, Y. Gu, H. Gao et al., Microstructure, Chemical Composition and Local Corrosion Behavior of a Friction Stud Welding Joint, J. Mater. Eng. Perform, 2018, 27, p 666–676.
J. Wu, D. Zhang, P. Wang et al., The Influence of Desulfovibrio sp and Pseudoalteromonas sp on the Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel in Natural Seawater, Corros. Sci. J. Environ. Degrad. Mater. Control, 2016, 112, p 552–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2016.04.047
R. Jia, J.L. Tan, P. Jin, D.J. Blackwood, D.K. Xu and T.Y. Gu, Effects of Biogenic H2S on the Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of C1018 Carbon Steel by Sulfate Reducing Desulfovibrio Vulgaris Biofilm, Corros. Sci., 2018, 130, p 1–11.
M. Dubiel, C.H. Hsu, C.C. Chien, F. Mansfeld and D.K. Newman, Microbial Iron Respiration can Protect Steel from Corrosion, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2002, 68, p 1440–1445.
L. Hall-Stoodley, J.W. Costerton and P. Stoodley, Bacterial Biofilms: From the Natural Environment to Infectious Diseases, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2004, 2, p 95–108.
A. Jayaraman, F.B. Mansfeld and T.K. Wood, Inhibiting Sulfate reducing Bacteria in Biofilms by Expressing the Antimicrobial Peptides Indolicid in and Bactenecin, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1999, 22, p 167–175.
M. Moradi, T. Xiao and Z.L. Song, Investigation of Corrosion Inhibitory Process of Marine Vibrio neocaledonicus sp Bacterium for Carbon Steel, Corrosion. Sci., 2015, 100, p 186–193.
T. Zheng, Y. Su, C. Qian and H. Zhou, Low Alkali Sulpho-Aluminate Cement Encapsulated Microbial Spores for Self-healing Cement-Based Materials, Biochem. Eng. J., 2020, 163, p 1.
Z. Tianwen, S. Yilin, Z. Xuan, Z. Hengyi and Q. Chunxiang, Effect and Mechanism of Encapsulation-Based Spores on Self-Healing Concrete at Different Curing Ages, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(47), p 1.
Acknowledgments
The financial support provided by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51738003) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper; this article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, W., Qian, C. & Rui, Y. A Strong Inhibitory Effect of Microbe-Induced Mineralization on Corrosion on Steel Surfaces. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 6957–6973 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07586-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07586-7