Abstract
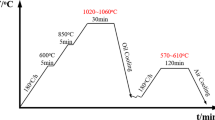
In this paper, the conventional hot forming and hybrid quenching hot forming processes of Al-Si-coated 22MnB5 steel sheet were investigated and compared at 0.5 s-15 s holding times in the press tool related to the mechanical properties, microstructure, and dimensional accuracy. The conventional hot forming method is classified as a direct method and an indirect method. Both methods have limitations due to processing time and cooling of the press tool. To speed up the process, an alternative cooling method based on spray or jet cooling was used outside of the die tool. The hybrid quenching method involves hot forming and spray cooling process. This method, using spray parameters, provides more effective control in mechanical properties and microstructure compared to the conventional method by using spray parameters. Vickers hardness tests and tensile tests were carried out to compare mechanical properties. Changes in the microstructure of the materials were investigated using an optical microscope. The results show that spray cooling can be used as part of quenching in the hot forming process by reducing the holding time in the press tool by 97%. However, the microstructure, mechanical properties, and geometry deviations of the stamped parts are still below tolerances after the hybrid quenching hot forming process. The use of the hybrid quenching method with multi-point nozzles in the hot forming process resulted in sheet hardness up to 470 HV1 and 8% elongation with tensile strength of 1500 MPa.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Taylor and A. Clough, Critical Review of Automotive Hot-Stamped Sheet Steel from an Industrial Perspective, Mater. Sci Technol., 2018, 34(7), p 809–861.
H. Karbasian and A.E. Tekkaya, A Review on Hot Stamping, J Mater. Proc. Technol., 2010, 210(15), p 2103–2118.
P. Hu, L. Ying and B. He, Hot stamping advanced manufacturing technology of lightweight car body, Springer, Singapore, 2017, p 45–91
R. Neugebauer, T. Altan, M. Geiger and A. Sterzing, Sheet Metal Forming at Elevated Temperatures, CIRP Ann., 2006, 55(2), p 793–816.
M. Tisza,2020 Development of Lightweight Steels for Automotive Applications, Engineering Steels and High Entropy-Alloys, A. Sharma, S. Kumar, and Z. Duriagina, Eds., IntechOpen Publisher, UK, , p 101–122
A. Mayyas, A. Qattawi, M. Omar and D. Shan, Design for Sustainability in Automotive Industry: A Comprehensive Review, Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2012, 16, p 1845–1862.
S. Li, L. Zhou, X. Wu, Y. Zhang and J. Li, The Influence of Thermal Conductivity of Die Material on the Efficiency of Hot-Stamping Process, J Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 4848–4867.
C. Löbe, O. Hering, L. Hiegemann and E. Tekkaya, Setting Mechanical Properties of High Strength Steels for Rapid Hot Forming Processes, Materials, 2016, 9, p 229.
H.-H. Bok, M.-G. Lee, E.J. Pavlina, F. Barlat and H.-D. Kim, Comparative Study of the Prediction of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties for a Hot-Stamped B-Pillar Reinforcing Part, Int. J Mech. Sci, 2011, 53, p 744–752.
M. Muro, G. Artola, A. Gorriño and C. Angulo, Effect of the Martensitic Transformation on the Stamping Force and Cycle Time of Hot Stamping Parts, Metals, 2018, 8(6), p 385.
Y. Chang, X. Tang, K. Zhao, P. Hu and Y. Wu, Investigation of the Factors Influencing the Interfacial Heat Transfer Coefficient in Hot Stamping, J Mater. Proc. Technol., 2016, 228, p 25–33.
K. Mori, B.F. Bariani, B.-A. Behrens, A. Brosius, M. Merklein and J. Yanagimoto, Hot Stamping of Ultra-High Strength Steel Parts, CIRP Ann., 2017, 66(2), p 755–777.
J. Aspacher, D. Haller, P. Thom, (2015) From first draft to serial production: hot stamping part design and feasibility study with respect to functionality and optimization of production costs. In: Proceeding CHS2,Toronto, Canada, p 197-207
B.-A. Behrens, A. Bouguecha,C. M. Gaebel, J. Moritz, J. Schrödter, (2014) Hot Stamping of Load Adjusted Structural Parts.In: 11th International conference on technology of plasticity, 19-24 October 2014, Nagoya Congress Center, Nagoya, Japan
G. Sevilgen, R. Ertan, E. Bulut, F. Ozturk, F. Esiyok, T.T. Abi and İ Alyay, The investigation of the Effects of Spray Parameters on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of 22MnB5 Steel During Hybrid Quenching Process, Heat Transf. Res., 2021, 52(14), p 63–77.
F. Nürnberger, M. Diekamp, J. Moritz, L. Wolf, S. Hübner and B.A. Behrens, Spray Cooling of Early Extracted Hot Stamped Parts, TMS 2014: 143rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition. Springer, Cham, 2014, p 983–990
L. Ying, T. Gao, M. Dai, Y. Yang and P. Hu, Experimental Investigation of Temperature-Dependent Interfacial Heat Transfer Mechanism with Spray Quenching for 22MnB5 Steel, App. Therm. Eng., 2017, 121, p 48–66.
M. Diekamp, S. Hübner, F. Nürnberger, M. Schaper, B.-A. Behrens and W.F. Bach, Optimised Press-Hardening Process Using Spray Cooling–Process Integrated Heat Treatment of 22MnB5 Sheet Metal, J. Heat. Treat. Mater, 2011, 66(6), p 316–322.
A.B. Barenji, A.R. Eivani, H.R. Jafarian and N. Park, Effects of Hot Forming Cold Die Quenching and Solution Treatment on Formability and Pressing Load During Equal Channel Angular Deformation of AA2024 Aluminum Alloy, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9(3), p 5599–5609.
M. Naderi, M. Ketabchi, M. Abbasi and W. Bleak, Semi-Hot Stamping as an Improved Process of Hot Stamping, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2011, 27(4), p 369–376.
X. Han, Y. Li, S. Chen, S. Tan, Y. Ding and J. Chen, Research on Q&P Hot Stamping Process Integrated with Fractional Cooling Strategy, Proc. Eng., 2017, 207, p 705–710.
K. Kim, Y. Song, W. Yang, H. Choi, S.H. Park and J. Yoon, Partial Strengthening Method for Cold Stamped B-Pillar with Minimal Shape Change, Int. J. Advan. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 102(9–12), p 4241–4255.
L. Ying, T. Gao, M. Dai, P. Hu and H. Teng, Experimental and Numerical Investigation on Temperature Field and Tailored Mechanical Properties Distribution of 22MnB5 Steel in Spray Quenching Process, J. Manuf. Process, 2020, 57, p 930–956.
O. Golovko, M.H. Stolte, K. Wölki, S. Hübner, B.-A. Behrens, H.J. Maier and F. Nürnberger, Tailoring Soft Local Zones in Quenched Blanks of the Steel 22MnB5 by Partial Pre-Cooling with Compressed Air, J Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29, p 4379–4389.
L. Wolf, M. Diekamp, T. Gretzki, F. Nürnberger, F.-W. Bach, D. Rodman, J. Moritz, J. Schrödter, S. Hübner, B.-A. Behrens, (2014) Hot stamping and subsequent spray cooling: a new manufacturing approach. Plastic Deformation of Metals, p 36–55
M. Merklein, M. Wieland, M. Lechner, S. Bruschi and A. Ghiotti, Hot Stamping of Boron Steel Sheets with Tailored Properties: A Review, J. Mater. Proces. Technol., 2016, 228, p 11–24.
Z.-X. Gui, K. Wang, Y.-S. Zhang and B. Zhu, Cracking and Interfacial Debonding of the Al-Si Coating in Hot Stamping of Pre-Coated Boron Steel, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 316, p 595–603.
K. Wang, Z. Gui, P. Liu, Y. Wang and Y. Zhang, Cracking Behavior of Al-Si Coating on Hot Stamping Boron Steel Sheet, Proc. Eng., 2014, 81, p 1713–1718.
T. Gao, L. Ying, M. Dai, G. Shen, P. Hu and L. Shen, A comparative Study of Temperature-Dependent Interfacial Heat Transfer Coefficient Prediction Methods for 22MnB5 Steel in Spray Quenching Process, Int. J Therm. Sci., 2019, 139, p 36–60.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK) for supporting this research under project number 3180620-TÜBİTAK 1501 regarding “Adaptation of hybrid cooling technique to the hot forming process and optimization of part characteristics” and also thank Beyçelik Gestamp for the financial support of the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Eşiyok, F., Ertan, R., Sevilgen, G. et al. A Comparative Study on Conventional and Hybrid Quenching Hot Forming Methods of 22MnB5 Steel for Mechanical Properties and Microstructure. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 1347–1356 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07167-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07167-8