Abstract
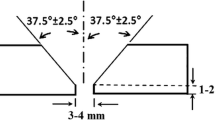
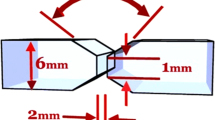
Dissimilar metal weld joints of austenitic stainless steel (SS) 316Ti and 15-5PH stainless steel were produced through gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) using two different grades of filler wire, viz., ER316L (austenitic grade) and ER630 (PH grade). Microstructure evaluation and mechanical properties of weldments were carried out to derive the best filler wire combination. The results showed that the joints prepared with ER316L filler wire possess austenite-ferrite dendritic weld structure and has lower strength than the 316Ti base metal. The weld joint ER630 filler wire displayed superior mechanical properties compared to the weld with ER316L filler wire. The use of ER630 filler wire led to the formation of martensitic structure in the weld, making the weld stronger than the austenitic 316Ti base metal. Thus, failure occurred in the base metal 316Ti during testing instead of weld. However, the fractographic examination of tensile tested specimens revealed presence of dimples in both cases, indicating that the failure mode was ductile. Based on this study, it is recommended to use ER630 filler wire to weld 316Ti–15-5PH for obtaining stronger weld joints.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Dak and C. Pandey, A Critical Review on Dissimilar Welds Joint between Martensitic and Austenitic Steel for Power Plant Application, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 58(July), p 377–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.08.019
D. Kumar Singh, G. Sahoo, R. Basu, V. Sharma and M.A. Mohtadi-Bonab, Investigation on the Microstructure—Mechanical Property Correlation in Dissimilar Steel Welds of Stainless Steel SS 304 and Medium Carbon Steel EN 8, J. Manuf. Process., 2018, 36(August), p 281–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.10.018
J.V. Thomas, K. Thomas Tharian, C.R. Anoop and P. Chakravarthy, Influence of Filler Wire Material on Dissimilar Welding of 15–5PH to KC20WN (Haynes 25), Mater. Sci. Forum, 2015, 830–831, p 298–301.
M.F. McGuire, Stainless Steels for Design Engineers, 1st ed. ASM International, 2008. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.tb.ssde.9781627082860
S. Mohan Kumar, S. Sankarapandian and N. Siva Shanmugam, Investigations on Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Examination of Activated TIG-Welded Nuclear Grade Stainless Steel, J. Braz Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng., 2020, 42(6), p 292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02393-4
W. Xie and C. Yang, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Austenitic Stainless Steel Sheet Joints Welded by Gas Tungsten Arc (GTA) and Ultrasonic-Wave-Assisted Gas Tungsten Pulsed Arc (U–GTPA), Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng., 2020, 20(2), p 43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00044-y
H. Naffakh, M. Shamanian and F. Ashrafizadeh, Dissimilar Welding of AISI 310 Austenitic Stainless Steel to Nickel-Based Alloy Inconel 657, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2009, 209(7), p 3628–3639.
G. Krishna Kumar, C. Velmurugan, R.S. Jayaram and M. Manikandan, Effect of Laser Welding Process Parameters on Dissimilar Joints of AISI 316 and Nickel 201, Mater. Today Proc., 2019, 22, p 2964–2973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.431
A. Pardo, M.C. Merino, A.E. Coy, F. Viejo, M. Carboneras and R. Arrabal, Influence of Ti, C and N Concentration on the Intergranular Corrosion Behaviour of AISI 316Ti and 321 Stainless Steels, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(7), p 2239–2251.
J. Brnic, G. Turkalj, M. Canadija and D. Lanc, AISI 316Ti (1.4571) Steel-Mechanical, Creep and Fracture Properties Versus Temperature, J. Constr. Steel Res., 2011, 67(12), p 1948–1952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2011.06.011
H.R. Habibi Bajguirani, The Effect of Ageing Upon the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Type 15-5 PH Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, 338(1–2), p 142–159.
V.A. Kumar, M.K. Karthikeyan, R.K. Gupta, F.G. Prakash and P.R. Kumar, Aging Behavior in 15-5(PH) Precipitation Hardening Martensitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2012, 710, p 483–488.
H.R. Habibi Bajguirani, Mechanism of Austenitic Transformation in the Martensitic Stainless Steel of Type PH 15-5, J. Phys. IV JP, 1994, 4(3), p 123–132.
M. Sadeghian, M. Shamanian and A. Shafyei, Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Joints Between Super Duplex Stainless Steel and High Strength Low Alloy Steel, Mater. Des., 2014, 60, p 678–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.03.057
I. Hajiannia, M. Shamanian and M. Kasiri, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AISI 347 Stainless Steel/A335 Low Alloy Steel Dissimilar Joint Produced by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, Mater. Des., 2013, 50, p 566–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.029
M. Sireesha, V. Shankar, S.K. Albert and S. Sundaresan, Microstructural Features of Dissimilar Welds between 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel and Alloy 800, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 292(1), p 74–82.
J.C. Lippold, Welding Metallurgy and Weldability, Wiley, Hoboken, 2014.
M. Sireesha, S.K. Albert, V. Shankar and S. Sundaresan, A Comparative Evaluation of Welding Consumables for Dissimilar Welds between 316LN Austenitic Stainless Steel and Alloy 800, J. Nucl. Mater., 2000, 279(1), p 65–76.
H. Shah Hosseini, M. Shamanian and A. Kermanpur, Characterization of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Inconel 617/310 Stainless Steel Dissimilar Welds, Mater. Charact., 2011, 62(4), p 425–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2011.02.003
J.A. Brooks and W.M. Garrison, Weld Microstructure Development and Properties of Precipitation-Strengthened Martensitic Stainless Steels, Weld. J. (Miami, Fla), 1999, 78(8), p 280–291.
Steel, Corrosion-Resistant, Sheet, Strip and Plate 15Cr-4.5Ni-0.03Cb(Nb)-3.5Cu Consumable Electrode Remelted, Solution Heat Treated Precipitation Hardenable, AMS5862M, (Warrendale, PA), 2017.
Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size, E112, ASTM Internationals, West Conshohocken, PA, 2013.
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials, E8, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2021.
15-5 PH (UNS S15500) Stainless Steel Product Data Bulletin, AK Steel Corporation, West Chester, OH 45069, 2017.
SS316Ti(UNS S31635) Technical Data Sheet, Allegheny Technologies Incorporation, Pittsburgh, 2012.
C. Pandey, Mechanical and Metallurgical Characterization of Dissimilar P92/SS304 L Welded Joints Under Varying Heat Treatment Regimes, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 2020, 51(5), p 2126–2142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-05660-0
M. Jula, R. Dehmolaei and S.R. Alavi Zaree, The Comparative Evaluation of AISI 316/A387-Gr.91 Steels Dissimilar Weld Metal Produced by CCGTAW and PCGTAW Processes, J. Manuf. Process., 2018, 36, p 272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.10.032
A. Ozsoy, E.B. Tureyen, M. Baskan and E. Yasa, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Additive Manufactured Dissimilar 17–4 PH and 316L Stainless Steels, Mater. Today Commun., 2021, 28(9), p 102561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102561
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank their AML/MME colleagues for timely support rendered during fabrication, characterization and mechanical testing. Authors express their sincere thanks to Director, Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre, ISRO, for granting permission to publish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R.R., Singh, R.K., Anoop, C.R. et al. Influence of Filler Metal on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 316Ti–15-5 PH Stainless Steel Weld Joints. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 10099–10107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07000-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07000-2