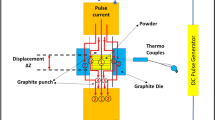
Abstract
In the present study, a uniform distribution of nanosized TiB2 particles in the metal matrix was achieved by powder metallurgy using the composite powders with pre-embedded particles. The composite powders were consolidated into compacts via spark plasma sintering without additional treatment such as mechanical milling or mixing. The concentrated shear stress around the uniformly distributed TiB2 particles with size similar to the width of the elongated grains during hot extrusion leads into grain fragmentation and refinement. The T4-treated TiB2/2024 composites had a better combination of yield strength of 385 MPa, ultimate tensile strength of 568 MPa and uniform elongation of 14.6% compared to the Al-Cu-Mg alloys and Al-Cu-Mg based composites in the published work. The longer uniform elongation of the composites in the present work was analyzed in respects of dislocation accumulation rate k1 and dislocation recovery rate k2.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Yi, N. Ma, Y. Zhang, X. Li, and H. Wang, Effective Elastic Moduli of Al–Si Composites Reinforced In Situ with TiB2 Particles, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54(6), p 1093–1097.
M. Wang, D. Chen, Z. Chen, Y. Wu, F. Wang, N. Ma, and H. Wang, Mechanical Properties of In-Situ TiB2/A356 Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 590, p 246–254.
I. Dinaharan and N. Murugan, Effect of Friction Stir Welding on Microstructure, Mechanical and Wear Properties of AA6061/ZrB2 In Situ Cast Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 543, p 257–266.
Y. Zhang, N. Ma, H. Wang, Y. Le, and S. Li, Effect of Ti on the Damping Behavior of Aluminum Composite Reinforced with In Situ TiB2 Particulate, Scr. Mater., 2005, 53(10), p 1171–1174.
Y. Ma, Z. Chen, M. Wang, D. Chen, N. Ma, and H. Wang, High Cycle Fatigue Behavior of the In-Situ TiB2/7050 Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 640, p 350–356.
G. Chen, X. Song, N. Hu, H. Wang, and Y. Tian, Effect of Initial Ti Powders Size on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Al3Ti/2024 Al Composites Prepared by Ultrasonic Assisted In-Situ Casting, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 694, p 539–548.
L. Ceschini, G. Minak, A. Morri, and F. Tarterini, Forging of the AA6061/23vol.%Al2O3p Composite: Effects on Microstructure and Tensile Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 513, p 176–184.
W.L. Zhang, M.Y. Gu, D.Z. Wang, and Z.K. Yao, Rolling and Annealing Textures of a SiCw/Al Composite, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58(27), p 3414–3418.
L. Ceschini, I. Boromei, G. Minak, A. Morri, and F. Tarterini, Microstructure, Tensile and Fatigue Properties of AA6061/20vol%Al2O3p Friction Stir Welded Joints, Compos. A, 2007, 38(4), p 1200–1210.
T. Kobayashi, Metal matrix composites, Strength and Toughness of Materials. T. Kobayashi Ed., Springer Japan, Tokyo, 2004, p 163–187
L. Babout, E. Maire, and R. Fougères, Damage Initiation in Model Metallic Materials: X-Ray Tomography and Modelling, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(8), p 2475–2487.
G. Liu, G.J. Zhang, F. Jiang, X.D. Ding, Y.J. Sun, J. Sun, and E. Ma, Nanostructured High-Strength Molybdenum Alloys with Unprecedented Tensile Ductility, Nat. Mater., 2013, 12(4), p 344–350.
J. Liu, Z. Chen, F.G. Zhang, G. Ji, M.L. Wang, Y. Ma, V. Ji, S.Y. Zhong, Y. Wu, and H.W. Wang, Simultaneously Increasing Strength and Ductility of Nanoparticles Reinforced Al Composites via Accumulative Orthogonal Extrusion Process, Mater. Res. Lett., 2018, 6(8), p 406–412.
C.F. Feng and L. Froyen, Microstructures of In Situ Al/TiB2 MMCs Prepared by a Casting Route, J. Mater. Sci., 2000, 35(4), p 837–850.
L.Y. Chen, J.Q. Xu, H. Choi, M. Pozuelo, X. Ma, S. Bhowmick, J.M. Yang, S. Mathaudhu, and X.-C. Li, Processing and Properties of Magnesium Containing a Dense Uniform Dispersion of Nanoparticles, Nature, 2015, 528(7583), p 539–543.
Z. Chen, J. Li, A. Borbely, G. Ji, S.Y. Zhong, Y. Wu, M.L. Wang, and H.W. Wang, The Effects of Nanosized Particles on Microstructural Evolution of an In-Situ TiB2/6063Al Composite Produced by Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Des., 2015, 88, p 999–1007.
S.M. Ma, P. Zhang, G. Ji, Z. Chen, G.A. Sun, S.Y. Zhong, V. Ji, and H.W. Wang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Processed Al–Mg–Si Alloys Dispersion-Strengthened by Nanosized TiB2 Particles, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 616, p 128–136.
X. Ju, F. Zhang, Z. Chen, G. Ji, M. Wang, V. Wu, S. Zhong, and H.W. Wang, Microstructure of Multi-Pass Friction-Stir-Processed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys Reinforced by Nano-Sized TiB2 Particles and the Effect of T6 Heat Treatment, Metals, 2017, 7(12), p 530.
J. Liu, Z. Chen, F.G. Zhang, J. Gang, M. Yu, M.L. Wang, S.Y. Zhong, J. Li, H. Wang, and H.W. Wang, Improved Structural Homogeneity and Mechanical Properties of Nanoparticles Reinforced Al Composites After Orthogonal Thermomechanical Processes, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 767, p 293–301.
F.M. Heim, Y. Zhang, and X. Li, Uniting Strength and Toughness of Al Matrix Composites with Coordinated Al3Ni and Al3Ti Reinforcements, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, 20, p 1700605.
S.C. Tjong, Novel Nanoparticle-Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites with Enhanced Mechanical Properties, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2007, 9(8), p 639–652.
C. Suryanarayana and N. Al-Aqeeli, Mechanically Alloyed Nanocomposites, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2013, 58(4), p 383–502.
H.M. John, D.Y. Brennan, M.H. Jacob, A.M. Justin, A.S. Tobias, and M.P. Tresa, 3D Printing of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys, Nature, 2017, 549, p 365–369.
C.D. Wu, K.K. Ma, J.L. Wu, P. Fang, G.Q. Luo, F. Chen, Q. Shen, L.M. Zhang, J.M. Schoenung, and E.J. Lavernia, Influence of Particle Size and Spatial Distribution of B4C Reinforcement on the Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Precipitation Strengthened Al Alloy Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 675, p 421–430.
D.B. Witkin and E.J. Lavernia, Synthesis and Mechanical Behavior of Nanostructured Materials via Cryomilling, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2006, 51(1), p 1–60.
H. Yang, E.J. Lavernia, and J.M. Schoenung, Novel Fabrication of Bulk Al with Gradient Grain Size Distributions via Powder Metallurgy, Philos. Mag. Lett., 2015, 95, p 177–186.
M. Chen, X. Li, G. Ji, Y. Wu, Z. Chen, W. Baekelant, K. Vanmeensel, H. Wang, and J.-P. Kruth, Novel Composite Powders with Uniform TiB2 Nano-Particle Distribution for 3D Printing, Appl. Sci. 7(3) (2017)
X.P. Li, G. Ji, Z. Chen, A. Addad, Y. Wu, H.W. Wang, J. Vleugels, J. Van Humbeeck, and J.P. Kruth, Selective Laser Melting of Nano-TiB2 Decorated AlSi10Mg Alloy with High Fracture Strength and Ductility, Acta Mater., 2017, 129, p 183–193.
Q. Yang, Y. Ma, Z. Chen, G. Ji, M.L. Wang, S.Y. Zhong, Y. Wu, V. Ji, and H.W. Wang, A New Powder Metallurgy Routine to Fabricate TiB2/Al–Zn–Mg–Cu Nanocomposites based on Composite Powders with Pre-Embedded Nanoparticles, Materialia, 2019, 8, p 100458.
Y. Tang, Z. Chen, A. Borbely, G. Ji, S.Y. Zhong, D. Schryvers, V. Ji, and H.W. Wang, Quantitative study of particle size distribution in an in-situ grown Al–TiB2 composite by synchrotron X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy Mater, Charact, 2015, 102, p 131–136.
Q. Yang, Y.T. Liu, J. Liu, L. Wang, Z. Chen, M.L. Wang, S.Y. Zhong, Y. Wu, and H.W. Wang, Microstructure Evolution of the Rapidly Solidified Alloy Powders and Composite Powders, Mater. Des., 2019, 182, p 108045.
B. Derby, The Dependece of Grain Size on Stress During Dynamic Recrystallisation, Acta Metall. Mater., 1990, 39, p 955–962.
R.E.D. Mann, R.L. Hexemer, I.W. Donaldson, and D.P. Bishop, Hot Deformation of an Al–Cu–Mg Powder Metallurgy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(16), p 5476–5483.
L. Hu, Z. Liu, and E. Wang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 2024 Aluminum Alloy Consolidated from Rapidly Solidified Alloy Powders, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 323(1), p 213–217.
Y. Lian, Z. Yang, J. Yang, and C. Mao, Processing and Mechanical Properties of 2024 Aluminum Matrix Composites Containing Tungsten and Tantalum Prepared by PM, Rare Met., 2006, 25(6), p 136–140.
S.E. Shin, H.J. Choi, J.H. Shin, and D.H. Bae, Strengthening Behavior of Few-Layered Graphene/Aluminum Composites, Carbon, 2015, 82, p 143–151.
Y.S. Su, Q.B. Ouyang, W.L. Zhang, Z.Q. Li, Q. Guo, G.L. Fan, and D. Zhang, Composite Structure Modeling and Mechanical Behavior of Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 597, p 359–369.
L. Wang, F. Qiu, J.Y. Liu, H.Y. Wang, J.G. Wang, L. Zhu, and Q.C. Jiang, Microstructure and Tensile Properties of In Situ Synthesized Nano-Sized TiCx/2009Al Composites, Mater. Des., 2015, 79, p 68–72.
M. Alizadeh, Comparison of Nanostructured Al/B4C Composite Produced by ARB and Al/B4C Composite Produced by RRB Process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 528, p 578–582.
H. Wei, Z.Q. Li, D.B. Xiong, Z.Q. Tan, G.L. Fan, Z. Qin, and D. Zhang, Towards Strong and Stiff Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced High-Strength Aluminum Alloy Composites Through a Microlaminated Architecture Design, Scr. Mater., 2014, 75, p 30–33.
J. Lin, Y. Hanry, K.Y. Joshua, M. Xuan, T. Troy, E.J. Lavernia, and J.M. Schoenung, Toughening of Aluminum Matrix Nanocomposites via Spatial Arrays of Boron Carbide Spherical Nanoparticles, Acta Mater., 2016, 103, p 128–140.
O.N. Senkov, M.R. Shagiev, S.V. Senkova, and D.B. Miracle, Precipitation of Al3(Sc, Zr) particles in an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr Alloy During Conventional Solution Heat Treatment and its Effect on Tensile Properties, Acta Mater., 2008, 56, p 3723–3738.
X.Z. Kai, Z.Q. Li, G.L. Fan, Q. Guo, Z.Q. Tan, W.L. Zhang, Y.S. Su, W.J. Lu, W.J. Moon, and D. Zhang, Strong and Ductile Particulate Reinforced Ultrafine-Grained Metallic Composites Fabricated by Flake Powder Metallurgy, Scr. Mater., 2013, 68, p 555–558.
H.N. Dong, I.C. Seung, K.L. Byung, M.P. Hoon, S.H. Do, and H. Hong, Soon Synergistic Strengthening by Load Transfer Mechanism and Grain Refinement of CNT/Al–Cu Composites, Carbon, 2012, 50, p 2417–2423.
M. Li, K.K. Ma, L. Jiang, H. Yang, E.J. Lavernia, L.M. Zhang, and J.M. Schoenung, Synthesis and Mechanical Behavior of Nanostructured Al 5083/n-TiB2 Metal Matrix Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 656, p 241–248.
T. Gladman, Precipitation Hardening in Metals, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2013, 15(1), p 30–36.
J.C. Fisher, E.W. Hart, and R.H. Pry, The Hardening of Metal Crystals by Precipitate Particles, Acta Metall., 1953, 1, p 336–339.
Y. Zhang, D. Juul Jensen, Y. Zhang, F. Lin, Z. Zhang, and Q. Liu, Three-Dimensional Investigation of Recrystallization Nucleation in a Particle-Containing Al Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2012, 67(4), p 320–323.
T.A. Bennett, R.H. Petrov, L.A.I. Kestens, L.Z. Zhuang, and P. de Smet, The Effect of Particle-Stimulated Nucleation on Texture Banding in an Aluminium Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2010, 63(5), p 461–464.
K. Huang, K. Marthinsen, Q. Zhao, and R.E. Logé, The Double-Edge Effect of Second-Phase Particles on the Recrystallization Behaviour and Associated Mechanical Properties of Metallic Materials, Prog. Mater Sci., 2018, 92, p 284–359.
J.D. Robson, D.T. Henry, and B. Davis, Particle Effects on Recrystallization in Magnesium–Manganese Alloys: Particle-Stimulated Nucleation, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(9), p 2739–2747.
T. Mayama, M. Noda, R. Chiba, and M. Kuroda, Crystal Plasticity Analysis of Texture Development in Magnesium Alloy During Extrusion, Int. J. Plast, 2011, 27(12), p 1916–1935.
W. Wu, Y. Wang, J. Wang, and S. Wei, Effect of Electrical Pulse on the Precipitates and Material Strength of 2024 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 608, p 190–198.
D.R. Ni, D.L. Chen, D. Wang, B.L. Xiao, and Z.Y. Ma, Tensile properties and Strain-Hardening Behaviour of Friction Stir Welded SiCp/AA2009 Composite Joints, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 608, p 1–10.
H. Mecking and U.F. Kocks, Kinetics of Flow and Strain Hardening, Acta Metall., 1981, 29, p 1865–1875.
I.S. Yasnikov, Y. Estrin, and A. Vinogradov, What Governs Ductility of Ultrafine-Grained Metals? A Microstructure Based Approach to Necking Instability, Acta Mater., 2017, 141, p 18–28.
C. Mondal, A.K. Singh, A.K. Mukhopadhyay, and K. Chattopadhyay, Tensile Flow and Work Hardening Behavior of Hot Cross-Rolled AA7010 Aluminum Alloy Sheets, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 577, p 87–100.
M.F. Ashby, The Deformation of Plastically Non-Homogeneous Materials, Phil. Mag., 1970, 21(170), p 399–424.
Acknowledgment
This work is financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China [Nos. 51971137, 11875192, U1930101].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Zhang, F., Yang, Q. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of In Situ TiB2/2024 Composites Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 8775–8783 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06900-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06900-7