Abstract
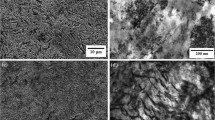
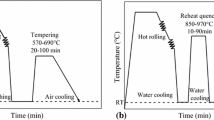
Nitrogen is an alloying element that can significantly improve the yield strength of steel by means of interstitial solid solution strengthening. The effects of quenching temperature on the evolution of second phase and grain size were investigated, as well as tensile properties, impact energy and hardness of a new nitrogen-alloyed Fe-Cr-Mo-V-N steel. The results show that with the increase of quenching temperature, the number and size of the second phase decrease as the high temperature promotes the dissolution and refinement of the second phase. For instance, the number of second phase M23C6 particles decreases gradually with temperature increasing. When the quenching temperature reaches 1050 °C, the grain is refined. Under the same tempering treatment, with the increase of quenching temperature, the tensile properties, impact energy and hardness increase first and then decrease. When the quenching temperature is 1050 °C and the tempering temperature is 180 °C, the obtained mechanical properties are the best. Under this condition, the tensile strength at room temperature is 2110 MPa, the yield strength is 1620 MPa, and the impact energy is 29.1 J, respectively.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.J. Lee, S.L. Chong, and Y.W. Chang, Role of Nitrogen in the Cyclic Deformation Behavior of Duplex Stainless Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36(4), p 967.
D. Canadinc, I. Karaman, H. Sehitoglu, Y.I. Chumlyakov, and H.J. Maier, The Role of Nitrogen on the Deformation Response of Hadfield Steel Single Crystals, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34(9), p 1821.
S. Hertzman and M. Jarl, A Thermodynamic Analysis of the Fe-Cr-N System, Metall. Trans. A, 1987, 67(7), p 1745.
C. Uebing, H. Viefhaus, and H.J. Grabke, Formation of CrN Surface Compounds and Surface Precipitates on Fe-15%Cr-N Single Crystals, Appl. Surf. Sci., 1998, 32(4), p 363.
H. Naima, D.M. Lamine, and B. Laurent, Precipitation During the Nitriding in Fe-Cr-C Steels, Mater. Today, 2018, 5(9), p 17501.
V.A. Shabashov, A.V. Makarov, K.A. Kozlov, V.V. Sagaradze, A.E. Zamatovskii, E.G. Volkova, and S.N. Luchko, Deformation-Induced Dissolution and Precipitation of Nitrides in Austenite and Ferrite of a High-Nitrogen Stainless Steel, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2018, 119(2), p 180.
H.P. Qu, H.T. Chen, C.X. Cao, Y.P. Lang, S.X. Zhang, and Y. Cui, Mechanism Research on Accelerated Embrittlement Phenomenon of a Warm Deformed Cr-Mn-Ni-Mo-N Austenitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 680, p 1.
M. Mendez, H. Mancha, G. Mendoza, J.I. Escalante, M.M. Cisneros, and H.F. Lopez, Structure of a Fe-Cr-Mn-Mo-N Alloy Processed by Mechanical Alloying, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33(10), p 3273.
T. Steiner, S.R. Meka, H. Göhring, and E.J. Mittemeijer, Alloying Element Nitride Stability in Iron-Based Alloys: Denitriding of Nitrided Fe-V Alloys, Mater. Sci. Tech., 2017, 33(1), p 23.
M.H. Ras and P.C. Pistorius, Possible Mechanisms for the Improvement by Vanadium of the Pitting Corrosion Resistance of 18% Chromium Ferritic Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2002, 44, p 2479.
I.I. Gorbachev, V.V. Popov, and A.Y. Pasynkov, Calculations of the Influence of Alloying Elements (Al, Cr, Mn, Ni, Si) on the Solubility of Carbonitrides in Low-Carbon Low-Alloy Steels, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2016, 117(12), p 1226.
Y. Kobayashi, H. Todoroki, and N. Shiga, Behaviour of Nitrogen Dissolution in Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo System Stainless Steels, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2014, 41(6), p 459.
X. Ma, L. Wang, B. Qin, C. Liu, and S.V. Subramanian, Effect of N on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 16Cr5Ni1Mo Martensitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Des., 2012, 34(11), p 74.
M. Kulka, D. Panfil, J. Michalski, and P. Wach, The effects of Laser Surface Modification on the Microstructure and Properties of Gas-Nitrided 42CrMo4 Steel, Opt. Laser Tech., 2016, 82, p 203.
R. Amini, M.J. Hadianfard, E. Salahinejad, M. Marasi, and T. Sritharan, Microstructural Phase Evaluation of High-Nitrogen Fe-Cr-Mn Alloy Powders Synthesized by the Mechanical Alloying Process, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44(1), p 136.
A. Makaya and H. Fredriksson, Study on the Production of Fe-Cr-Mn-C-Si Foam by Nitrogen Solubility Difference Between the Liquid and Solid Phases, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 413–414, p 533.
L. Luo, W. Li, Y. Gong, L. Wang, and X.J. Jin, Tensile Behavior and Deformation Mechanism of Quenching and Partitioning Treated Steels at Different Deforming Temperatures, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2017, 24(11), p 1104.
A. Zafra, L.B. Peral, J. Belzunce, and C. Rodríguez, Effect of Hydrogen on the Tensile Properties of 42CrMo4 Steel Quenched and Tempered at Different Temperatures, Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2018, 43(18), p 9068.
B. Jiang, M. Wu, M. Zhang, F. Zhao, Z. Zhao, and Y. Liu, Microstructural Characterization, Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms of a Quenched and Tempered Steel: Effect of Heat Treatment Parameters, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 707, p 306.
C. Li, B. Ma, Y. Song, J. Zheng, and J. Wang, Grain refinement of non-magnetic austenitic steels during asymmetrical hot rolling process, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(12), p 1572.
Q. Grong, L. Kolbeinsen, C. Eijk, and G. Tranell, Microstructure Control of Steels Through Dispersoid Metallurgy Using Novel Grain Refining Alloys, ISIJ Int., 2006, 46(6), p 824.
J. Kang, C.N. Li, G. Yuan, and G.D. Wang, Improvement of strength and toughness for hot rolled low-carbon bainitic steel via grain refinement and crystallographic texture, Mater. Lett., 2016, 175, p 157.
A.L. Greer, Overview: Application of Heterogeneous Nucleation in Grain-Refining of Metals, J. Chem. Phys., 2016, 145(21), p 211704.
W. Xu, Z. Li, H. Yuan, and G. Zhang, Effect of Second Phase on Grain Growth of Spray Formed Superalloy GH742y, Rare Met., 2011, 30, p 392.
M.C. Zhao, X. Huang, and A. Atrens, Role of Second Phase Cementite and Martensite Particles on Strength and Strain Hardening in a Plain C-Mn Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 549, p 222.
X. Qi, M. Chen, and J.H. Chen, Effect of Second Phase Particles on Microstructure and Toughness of CGHAZ in Ti-Nb Microalloyed Steel, Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2005, 41, p 86.
C. Zang, T. Zhou, H. Zhou, Y. Yuan, P. Zhang, and C. Meng, Effects of Substrate Microstructure on Biomimetic Unit Properties and Wear Resistance of h13 Steel Processed by Laser Remelting, Opt. Laser Tech., 2018, 106, p 299.
M. Eroğlu and M. Aksoy, Effect of Initial Grain Size on Microstructure and Toughness of Intercritical Heat-Affected Zone of a Low Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 286(2), p 289.
D. Zeng, L. Lu, Y. Gong, Y. Zhang, and J. Zhang, Influence of Solid Solution Strengthening on Spalling Behavior of Railway Wheel Steel, Wear, 2017, 372, p 158.
M. Walbrühl, D. Linder, J. Ågren, and A. Borgenstam, Modelling of Solid Solution Strengthening in Multicomponent Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 700, p 301.
I.J. Moore, J.I. Taylor, M.W. Tracy, M.G. Burke, and E.J. Palmiere, Grain Coarsening Behaviour of Solution Annealed Alloy 625 Between 600–800 °C, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 682, p 402.
D. Ma, M. Friák, J. Pezold, D. Raabe, and J. Neugebauer, Computationally Efficient and Quantitatively Accurate Multiscale Simulation of Solid-Solution Strengthening by Ab initio Calculation, Acta Mater., 2015, 85, p 53.
R. Song, F. Ye, C. Yang, and S. Wu, Effect of Alloying Elements on Microstructure, Mechanical and Damping Properties of Cr-Mn-Fe-V-Cu High-Entropy Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34(11), p 2014.
N.C. Ritter, R. Sowa, J.C. Schauer, D. Gruber, T. Goehler, R. Rettig, and R.F. Singer, Effects of Solid Solution Strengthening Elements Mo, Re, Ru, and W on Transition Temperatures in Nickel-Based Superalloys with High γ′-Volume Fraction: Comparison of Experiment and CALPHAD Calculations, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, 49(8), p 3206.
C.L. Zhang, Y.Z. Liu, L.Y. Zhou, and C. Jiang, Secondary Hardening, Austenite Grain Coarsening and Surface Decarburization Phenomenon in Nb-Bearing Spring Steel, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2012, 19(3), p 47.
W. Wang, X. Mao, S. Liu, G. Xu, and B. Wang, Microstructure Evolution and Toughness Degeneration of 9Cr Martensitic Steel After Aging at 550 °C for 20000 h, J. Mater. Sci., 2018, 53(6), p 4574.
S. Berbenni, V. Favier, and M. Berveiller, Micro-Macro Modelling of the Effects of the Grain Size Distribution on the Plastic Flow Stress of Heterogeneous Materials, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2007, 39(1), p 96.
P. Lehto, H. Remes, T. Saukkonen, H. Hänninen, and J. Romanoff, Influence of Grain Size Distribution on the Hall-Petch Relationship of Welded Structural Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 592(13), p 28.
T.Y. Kwak and W.J. Kim, Mechanical Properties and Hall-Petch Relationship of the Extruded Mg-Zn-Y Alloys with Different Volume Fractions of Icosahedral Phase, J Alloy Compd., 2019, 770, p 589.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (202101AU070152); Natural Science Research Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology (KKZ3202051043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, S., Yuan, X. & Yang, M. Improved Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Mo-V-N Steel by Controlling the Quenching Temperature. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 4195–4203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06470-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06470-0