Abstract
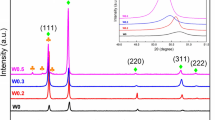
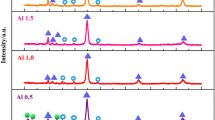
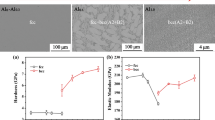
Two AlxCoCrFeNi (x = 0.75, 1.25) high entropy alloys (HEAs) were prepared and annealed with different temperatures (800, 1000 and 1200 °C) and holding times (2 h, 4 h and 8 h) using furnace cooling. Effects of annealing treatment details on the microstructure and hardness of the HEAs were investigated. It was found that the σ-phase did not form in the Al0.75CoCrFeNi alloy for whatever annealing temperatures or holding times. The σ-phase was produced at 610 °C and dissolved at 930 °C in the Al1.25CoCrFeNi alloy. After dissolution, the σ-phase could reappear when this alloy furnace cooled from higher annealed temperature (1200 °C for 4 h) or longer duration time (1000 °C for 8 h). The reason is that the redistribution of Cr element in the post-holding stage or furnace cooling stage was sufficient to precipitate σ-phase. The formation and dissolution of σ-phase and their influences on the hardness in the HEAs were analyzed and discussed thoroughly.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Cantor, Multicomponent and High Entropy Alloys, Entropy, 2014, 16, p 4749–4768.
O.N. Senkov, J.D. Miller, D.B. Miracle and C. Woodward, Accelerated Exploration of Multi-principal Element Alloys with Solid Solution Phases, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, p 1–10.
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw and Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and Properties of High-Entropy Alloys, Prog. Mater Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93.
A. Munitz, S. Salhov, S. Hayun, S. Hayun and N. Frage, Heat Treatment Impacts the Micro-structure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 683, p 221–230.
I. Basu and J.T.M. De Hosson, Strengthening Mechanisms in High Entropy Alloys: Fundamental Issues, Scripta Mater., 2020, 187, p 148–156.
J.M. Zhu, H.F. Zhang, H.M. Fu, A.M. Wang, H. Li and Z.Q. Hu, Microstructures and Compressive Properties of Multicomponent AlCoCrCuFeNiMox Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 497, p 52–56.
E. Ma and X. Wu, Tailoring Heterogeneities in High-Entropy Alloys to Promote Strength–Ductility Synergy, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, p 1–10.
S.T. Chen, W.Y. Tang, Y.F. Kuo, S.Y. Chen, C.H. Tsau, T.T. Shun and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and Properties of Age-Hardenable AlxCrFe1.5MnNi0.5 Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 2010, 527, p 5818–5825.
J.J. Wang, S.S. Wu, S. Fu, S.N. Liu, M.Y. Yan, Q.Q. Lai, S. Liu, H. Hahn and T. Feng, Ultrahigh Hardness with Exceptional Thermal Stability of a Nanocrystalline CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Prepared by Inert Gas Condensation, Scripta Mater., 2020, 187, p 335–339.
M.H. Tsai, H. Yuan, G. Cheng, W. Xu, W.W. Jian, M.H. Chuang and Y. Zhu, Significant Hardening Due to the Formation of a Sigma Phase Matrix in a High Entropy Alloy, Intermetallics, 2013, 33, p 81–86.
M.R. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh and S.K. Chen, Effect of Vanadium Addition on the Microstructure, Hardness, and Wear Resistance of Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy, Metal. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, 37A, p 1363–1369.
M.H. Chuang, M.H. Tsai, W.R. Wang, S.J. Lin and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AlXCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 6308–6317.
C.Y. Hsu, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen and T.T. Shun, Wear Resistance and High-Temperature Compression Strength of FCC CuCoNiCrAl0.5Fe Alloy with Boron Addition, Metal. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35A, p 1465–1469.
Y.L. Chou, J.W. Yeh and H.C. Shih, The Effect of Molybdenum on the Corrosion Behavior of the High-Entropy Alloys Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5MoX in Aqueous Environments, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 2571–2581.
K. Biswas, J.W. Yeh, P.P. Bhattacharjee and J.T.M. DeHosson, High Entropy Alloys: Key Issues Under Passionate Debate, Scripta Mater., 2020, 188, p 54–58.
V. Shivam, J. Basu, Y. Shadangi, M.K. Singh and N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Mechano-Chemical Synthesis, Thermal Stability and Phase Evolution in AlCoCrFeNiMn High Entropy Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2018, 757, p 87–97.
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang, S.C. Wang, Y.C. Tsai, C.H. Lai and J.W. Yeh, Effects of Al Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Property of AlxCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2012, 26, p 44–51.
S. Varalakshmi, M. Kamaraj and B.S. Murty, Synthesis and Characterization of Nanocrystalline AlFeTiCrZnCu High Entropy Solid Solution by Mechanical Alloying, J. Alloy. Compd., 2008, 460, p 253–257.
C. Li, J.C. Li, M. Zhao and Q. Jiang, Effect of Aluminum Contents on Microstructure and Properties of AlxCoCrFeNi Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 504, p 515–518.
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang and J.W. Yeh, Phases, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlXCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys at Elevated Temperatures, J. Alloy. Compd., 2014, 589, p 143–152.
M.H. Tsai and J.W. Yeh, High-Entropy Alloys: a Critical Review, Mater. Res. Lett., 2014, 2, p 107–123.
V. Shivam, J. Basu, R. Manna and N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Local Composition Migration Induced Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Non-Equiatomic Fe40Cr25Ni15Al15Co5 Medium-Entropy Alloy, Metall. and Mater. Trans. A., 2021, 52, p 1777–1789.
C. Zhang, F. Zhang, S.L. Chen and W.S. Cao, Computational Thermodynamics Aided High-Entropy Alloy Design, J. Minerals, 2012, 64, p 839–845.
K. Zhang and Z. Fu, Effects of Annealing Treatment on Phase Composition and Microstructure of CoCrFeNiTiAlx High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2012, 22, p 24–32.
L. Duprez, B.C. De Cooman and N. Akdut, Redistribution of the Substitutional Elements During σ and χ Phase Formation in a Duplex Stainless Steel, Steel Res., 2001, 72, p 311–316.
V. Shivam, J. Basu, V.K. Pandey, Y. Shadangi and N.K. Mukhopadhyay, Alloying Behaviour, Thermal Stability and Phase Evolution in Quinary AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy, Adv. Powder Technol., 2018, 29, p 2221–2230.
G. Laplanche, S. Berglund, C. Reinhart, A. Kostka, F. Fox and E.P. George, Phase Stability and Kinetics of σ-phase Precipitation in CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloys, Acta Mater., 2018, 161, p 338–351.
Y.F. Kao, T.J. Chen, S.K. Chen and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of As-Cast, -Homogenized, and -Deformed AlxCoCrFeNi (0≤ x≤ 2) High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 488, p 57–64.
J.Y. He, W.H. Liu, H. Wang, Y. Wu, X.J. Liu, T.G. Nieh and Z.P. Lu, Effects of Al Addition on Structural Evolution and Tensile Properties of the FeCoNiCrMn High-Entropy Alloy System, Acta Mater., 2014, 62, p 105–113.
J.M. Park, J. Moon, J.W. Bae, J. Jung, S. Lee and H.S. Kim, Effect of Annealing Heat Treatment on Microstructural Evolution and Tensile Behavior of Al0.5CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 2018, 728, p 251–258.
T. Bhattacharjee, I.S. Wani, S. Sheikh, I.T. Clark, T. Okawa, S. Guo, P.P. Bhattacharjee and N. Tsuji, Simultaneous Strength-Ductility Enhancement of a Nano-Lamellar AlCoCrFeNi21 Eutectic High Entropy Alloy by Cryo-Rolling and Annealing, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, p 1–8.
J. Michalska and M. Sozańska, Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of σ and χ phases in 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel, Mater. Charact., 2006, 56, p 355–362.
I.S. Wani, T. Bhattacharjee, S. Sheikh, Y.P. Lu, S. Chatterjee, P.P. Bhattacharjee and N. Tsuji, Ultrafine-Grained AlCoCrFeNi21 Eutectic High-Entropy Alloy, Mater. Res. Lett., 2016, 4, p 174–179.
Acknowledgments
This work is financially sponsored by Shanghai Sailing Program (19YF1446600 and 20YF1415800). We also thank Mr. Pan from Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the SEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that the authors have no conflicts of interest publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zhang, S., Li, F. et al. Effect of Annealing Treatment on the Microstructure and Hardness of AlxCoCrFeNi (x = 0.75, 1.25) High Entropy Alloys . J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 1444–1455 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06240-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06240-y