Abstract
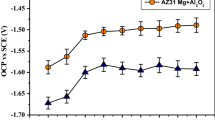
Corrosion and corrosion-related mechanical behaviors of Ti-microalloyed AZ31 Mg alloy (AZ31Ti) in simulated body fluid (SBF) under a dynamic environment were investigated. AZ31 Mg alloy was used as a control alloy. Microstructure analysis of the samples was performed by using a scanning electron microscope and an x-ray diffractometer. Mass loss measurements and corrosion-related tensile tests were carried out by immersing the samples in the SBF solution at \(37.5 \pm 0.5\) °C for 24, 72, and 336 h under dynamic conditions. Potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were also employed in the SBF solution at \(37.5 \pm 0.5\) °C. Microstructural studies showed that the β (\({\text{Mg}}_{17} {\text{Al}}_{12}\)) intermetallic phases in the AZ31 alloy are dispersed in the microstructure and formed as relatively angular particles, and that the dimensions of the β phases transformed to a smaller size and globular form with Ti microalloying. While the tensile strength and hardness values of AZ31 and AZ31Ti alloys were similar to each other, Ti microalloying showed a considerable increase in the yield strength and elongation. This study suggests that microalloying of AZ31 alloy with Ti is beneficial in terms of their corrosion resistance and corrosion-related mechanical properties in an SBF environment under dynamic conditions.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Chen, L. Tan, X. Yu, I.P. Etim, M. Ibrahim and K. Yang, Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Alloys for Medical Application: A review, J Mech Behav Biomed., 2018, 87, p 68–79.
S. Amani and G. Faraji, Processing and Properties of Biodegradable Magnesium Microtubes for Using as Vascular Stents: A Brief Review, Met Mater Int., 2019, 25, p 1341–1359.
N. Sezer, Z. Evis, S.M. Kayhan, A. Tahmasebifar and M. Koç, Review of Magnesium-Based Biomaterials and Their Applications, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2018, 6, p 23–43.
S. Agarwal, J. Curtin, B. Duffy and S. Jaiswal, Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys for Orthopaedic Applications: A review on Corrosion Biocompatibility and Surface Modifications, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, 68, p 948–963.
F. Witte, V. Kaese, H. Haferkamp, E. Switzer, A. Meyer-Lindenberg, C.J. Wirth and H. Windhagen, In vivo Corrosion of Four Magnesium Alloys and the Associated Bone Response, Biomaterials, 2005, 26, p 3557–3565.
G. Yuan and J. Niu, Research Progress of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys for Orthopedic Applications, Acta Metall. Sin., 2017, 53, p 1168–1180.
K. Pichler, S. Fischerauer, P. Ferlic, E. Martinelli, H.P. Brezinsek, P.J. Uggowitzer, J.F. Loffler and A.M. Weinberg, Immunological Response to Biodegradable Magnesium Implants, JOM, 2014, 66, p 573–579.
Y. Chen, J. Dou, H. Yu and C. Chen, Degradable Magnesium-Based Alloys for Biomedical Applications: The Role of Critical Alloying Elements, J. Biomater. Appl., 2019, 33, p 1348–1372.
X. Zhang, J. Dai, Q. Dong, Z. Ba and Y. Wu, Corrosion behavior and Mechanical Degradation of as-Extruded Mg-Gd-Zn-Zr Alloys for Orthopedic Application, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B, 2020, 1088, p 698–708.
Y. Sasikumar, A.M. Kumar, R. Suresh-Babu, P. Dhaiveegan, N. Al-Aqeeli and A.L.F. de Barros, Fabrication of Brushite Coating on AZ91D and AZ31 Alloys by Two-Step Chemical Treatment and Its Surface Protection in Simulated Body Fluid, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28, p 3803–3815.
X.J. Wang, D.K. Xu, R.Z. Wu, X.B. Chen, Q.M. Peng, L. Jin, Y.C. Xin, Z.Q. Zhang, Y. Liu, X.H. Chen, G. Chen, K.K. Deng and H.Y. Wang, What is Going on in Magnesium Alloys?, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34, p 245–247.
M.B. Kannan, Influence of Microstructure on the in-vitro Degradation Behaviour of Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2010, 64, p 739–742.
X. Gong, J. Chen, H. Yan, W. Xia, B. Su, Z. Yu and H. Yin, Effects of Minor Sr Addition on Biocorrosion and Stress Corrosion Cracking of As-Cast Mg-4Zn Alloys, Corrosion, 2020, 76, p 71–81.
K. Gusieva, C.H.J. Davies, J.R. Scully and N. Birbilis, Corrosion of Magnesium Alloys: The Role of Alloying, Int. Mater. Rev., 2015, 60, p 169–194.
Y. Ding, C. Wen, P. Hodgson and Y. Li, Effects of Alloying Elements on the Corrosion Behavior and Biocompatibility of Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys: A Review, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2014, 2, p 1912–1933.
M.B. Kannan and R.K.S. Raman, In Vitro Degradation and Mechanical Integrity of Calcium-Containing Magnesium Alloys in Modified-Simulated Body Fluid, Biomaterials, 2008, 29, p 2306–2314.
G. Wu, Y. Fan, H. Gao, C. Zhai and Y.P. Zhu, The Effect of Ca and Rare Earth Elements on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behaviour of AZ91D, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 408, p 255–263.
Z. Li, X. Gu, S. Lou and Y. Zheng, The Development of Binary Mg-Ca Alloys for use as Biodegradable Materials Within Bone, Biomaterials, 2008, 29, p 1329–1344.
Y. Liu, Q. Wang, Y. Song, D. Zhang, S. Yu and X. Zhu, A study on the Corrosion Behavior of Ce-Modified Cast AZ91 Magnesium Alloy in the Presence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 473, p 550–556.
N. Hort, Y. Huang, D. Fechner, M. Stormer, C. Blawert, F. Witte, C. Vogt, H. Drucker, R. Willumeit, K.U. Kainer and F. Feyerabend, Magnesium Alloys as Implant Materials-Principles of Property Design for Mg–RE Alloys, Acta Biomater., 2010, 6, p 1714–1725.
P.C. Ferreira, K.A. de Piai, A.M. Takayanagui and S.I. Segura-Muñoz, Aluminum as a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease, Lat. Am. Enfermagem, 2008, 16, p 151–157.
H.R. Bakhsheshi-Rad, M.H. Idris, M.R. Abdul-Kadir, A. Ourdjini, M. Medraj, M. Daroonparvar and E. Hamzah, Mechanical and Bio-Corrosion Properties of Quaternary Mg-Ca-Mn-Zn Alloys Compared with Binary Mg-Ca Alloys, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 283–292.
J. Gonzalez, R.Q. Hou, E.P.S. Nidadavolu, R. Willumeit-Römer and F. Feyerabend, Magnesium Degradation under Physiological Conditions-Best Practice, Bioact, Mater., 2018, 3, p 174–185.
J. Wang, Y. Jang, G. Wan, V. Giridharan, G.L. Song, Z. Xu, Y. Koo, P. Qi, J. Sankar, N. Huang and Y. Yun, Flow-Induced Corrosion of Absorbable Magnesium Alloy: In-situ and Real-Time Electrochemical Study, Corros. Sci., 2016, 104, p 277–289.
A.P. Md Saad, R.A. Abdul Rahim, M.N. Harun, H. Basri, J. Abdullah, M.R. Abdul Kadir and A. Syahrom, The influence of Flow Rates on the Dynamic Degradation Behaviour of Porous Magnesium Under a Simulated Environment of Human Cancellous Bone, Mater. Des., 2017, 122, p 268–279.
T. Wang, D. Kevorkov, A. Mostafa and M. Medraj, Experimental Investigation of the Phase Equilibria in the Al-Mn-Zn System at 400 °C, J. Mater., 2014, 2014, p 1–13.
Y. Koo, T. Tiasha, V.N. Shavov and Y. Yun, Expandable Mg-based Helical Stent Assessment using Static, Dynamic, and Porcine Ex Vivo Models, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7–1173, p 1–10.
L. Han, X. Lib, J. Baia, F. Xuea, Y. Zhengc and C. Chu, Effects of Flow Velocity and Different Corrosion Media on the in Vitro Biocorrosion Behaviors of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, Mater Chem Phys., 2018, 217, p 300–307.
S. Candan, M. Unal, E. Koc, Y. Turen and E. Candan, Effects of Titanium Addition on Mechanical and Corrosion Behaviours of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509, p 1958–1963.
S. Candan, M. Celik and E. Candan, Effectiveness of Ti-Micro Alloying in Relation to Cooling Rate on Corrosion of AZ91 Mg Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 672, p 197–203.
E. Candan, S. Candan, M. Unal, Y. Turen and E. Koc, High Strength and Corrosion Resistant Mg alloys Microalloyed with Ti or/and Pb, Turkish Patent Office, Patent No TR 2008 09986 B, 2008.
H.Y. Choi and W.J. Kim, Development of the Highly Corrosion Resistant AZ31 Magnesium Alloy by the Addition of a Trace Amount of Ti, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 664, p 25–37.
H.Y. Choi and W.J. Kim, The Improvement of Corrosion Resistance of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy Through Development of Dense and Tight Network Structure of Al-Rich a Phase by Addition of a Trace Amount of Ti, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 696, p 736–745.
T. Kokubo and H. Takadama, How Useful is SBF in Predicting in Vivo Bone Bioactivity?, Biomaterials, 2006, 27, p 2907–2915.
H. Zhao, P. Li and L. He, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of an Asymmetric Twin-Roll Cast AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Strip, J. Mater. Process Technol., 2012, 212, p 1670–1675.
L. Wu, F. Pan, M. Yang and R. Cheng, An Investigation of Second Phases in as-Cast AZ31 Magnesium Alloys with Different Sr Contents, J. Mater. Sci., 2013, 48, p 5456–5469.
H. Baker, Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM Handbook, 1998, 3, p 280.
I. Polmear, D.S. John, J.F. Nie, M. Qian, Light Alloys, 5th Edn., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2017.
S. Candan and E. Candan, Comparative Study on Corrosion Behaviors of Mg-Al-Zn Alloys, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2018, 28, p 642–650.
P. Zhao, Q. Wang, C. Zhai and Y. Zhu, Effects of Strontium and Titanium on the Microstructure, Tensile Properties and Creep Behavior of AM50 Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 444, p 318–326.
J.Y. Choi and W.J. Kim, Significant Effects of Adding Trace Amounts of Ti on the Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of Mg-6A-1Zn Magnesium Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 614, p 49–55.
X. Ai and G. Quan, Effect of Ti on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion of Cast AZ91 Magnesium Alloy, Open Mater. Sci. J., 2012, 6, p 6–13.
E. Mena-Morcillo and L. Veleva, Degradation of AZ31 and AZ91 Magnesium Alloys in different Physiological Media: Effect of Surface Layer Stability on Electrochemical Behaviour, J. Magnes. Alloys, 2020, 8, p 667–675.
A.D. Sudholz, N. Birbilis, C.J. Bettles and M.A. Gibson, Corrosion Behaviour of Mg-alloy AZ91E with Atypical Alloying Additions, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 471, p 109–115.
R. Bertolini, S. Bruschia, A. Ghiottia, L. Pezzatoa and M. Dabalàa, The Effect of Cooling Strategies and Machining Feed Rate on the Corrosion Behavior and Wettability of AZ31 Alloy for Biomedical Applications, Procedia CIRP, 2017, 65, p 7–12.
S. Candan, S. Cim and E. Candan, Effectiveness of Ti Micro-Alloying for the Suppression of Fe Impurities in AZ91 Mg Alloys and Associated Corrosion Properties, Mater. Test., 2019, 61, p 1165–1170.
M. Liu, S. Zanna, H. Ardelean, I. Frateur, P. Schmutz, G. Song, A. Atrens and P. Marcus, A first Quantitative XPS Study of the Surface Films Formed, by Exposure to Water, on Mg and on the Mg–Al Intermetallics: Al3Mg2 and Mg17Al12, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, 68, p 948–963.
G.L. Song and A. Atrens, Corrosion Mechanisms of Magnesium Alloys, Adv. Eng. Mater., 1999, 1, p 11–33.
M. Esmaily, D.B. Blücher, J.E. Svensson, M. Halvarsson and L.G. Johansson, New Insights into the Corrosion of Magnesium Alloys-The Role of Aluminum, Scr. Mater., 2016, 115, p 91–95.
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by Bilecik Seyh Edebali University, Grant No: 2018-01.BŞEU.03-02. The authors would like to thank Fethi Candan for construction of the real-time dynamic corrosion test apparatus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Candan, S., Emir, S. & Candan, E. In Vitro Degradation Behavior of Ti-Microalloyed AZ31 Magnesium Alloy in Simulated Body Fluid. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 1–10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06142-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06142-z