Abstract
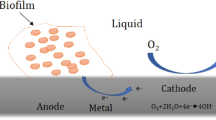
The corrosion behavior of X80 pipeline steel induced by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) was investigated. More corrosion pits were found in the SRB-inoculated medium than in the sterile medium. Carbon starvation tests were carried out in the SRB-inoculated culture media with 0, 10, and 100% organic carbon. Electrochemical results indicate that coupons immersed in the 0% and 10% carbon source media exhibited far more aggressive corrosion. FIB images show a loose outer corrosion layer of the coupons immersed in the 0% carbon source medium. Both metabolite and extracellular electron transfer worked as the corrosion mechanism in this study, while the predominant mechanism in the carbon source reduced media was extracellular electron transfer.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Enning and J. Garrelfs, Corrosion of Iron by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria: New Views of an Old Problem, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2014, 80, p 1226–1236.
A.M. Olszewski, Avoidable MIC-Related Failure, J. Fail. Anal. Prev., 2017, 7, p 239–246.
A. Vigneron, I.M. Head and N. Tsesmetzis, Damage to Offshore Production Facilities by Corrosive Microbial Biofilms, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2018, 102, p 2525–2533.
P.J. Antony, R.S. Raman, R. Raman and P. Kumar, Role of Microstructure on Corrosion of Duplex Stainless Steel in Presence of Bacterial Activity, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 1404–1412.
B. Liu, Z. Li, X. Yang, C. Du and X. Li, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of X80 Pipeline Steel by Nitrate Reducing Bacteria in Artificial Beijing soil, Bioelectrochemistry, 2020, 135, p 107551.
R. Javaherdashti, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC), 2nd ed. Springer, Cham, 2017, p 29–79
Y. Wang, W. Zhao, H. Ai, X. Zhou and T. Zhang, Effects of Strain on the Corrosion Behaviour of X80 Steel, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, p 2761–2766.
D. Xu and T. Gu, Carbon Source Starvation Triggered more Aggressive Corrosion Against Carbon Steel by the Desulfovibrio vulgaris Biofilm, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2014, 91, p 74–81.
G. Muyzer and A.J. Stams, The Ecology and Biotechnology of Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2008, 6, p 441–454.
J. Wu, D. Zhang, P. Wang, Y. Cheng, S. Sun, Y. Sun and S. Chen, The Influence of Desulfovibrio sp. and Pseudoalteromonas sp. on the Corrosion of Q235 Carbon Steel in Natural Seawater, Corros. Sci., 2016, 112, p 552–562.
W. Dou, J. Liu, W. Cai, D. Wang, R. Jia, S. Chen and T. Gu, Electrochemical Investigation of Increased Carbon Steel Corrosion via Extracellular Electron Transfer by a Sulfate Reducing Bacterium Under Carbon Source Starvation, Corros. Sci., 2019, 150, p 258–267.
Y. Li, D. Xu, C. Chen, X. Li, R. Jia, D. Zhang, W. Sand, F. Wang and T. Gu, Anaerobic Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Mechanisms Interpreted Using Bioenergetics and Bioelectrochemistry: A Review, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34, p 1713–1718.
T. Gu, R. Jia, T. Unsal and D. Xu, Toward a Better Understanding of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Caused by Sulfate Reducing Bacteria, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2019, 35, p 631–636.
R. Jia, J.L. Tan, P. Jin, D.J. Blackwood, D. Xu and T. Gu, Effects of Biogenic H2S on the Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of C1018 Carbon Steel by Sulfate Reducing Desulfovibrio vulgaris Biofilm, Corros. Sci., 2018, 130, p 1–11.
H.T. Dinh, J. Kuever, M. Mußmann, A.W. Hassel, M. Stratmann and F. Widdel, Iron Corrosion by Novel Anaerobic Microorganisms, Nature, 2014, 427, p 829–832.
D.T. Hang, Microbiological Study of the Anaerobic Corrosion of Iron, in Trabajo de Grado para el titulo de Doctor en Ciencias Naturales, Universidad de Bremen, Alemania, 2003, p 56–71.
T. Gu, K. Zhao, S. Nesic, A New Mechanistic Model for MIC Based on a Biocatalytic Cathodic Sulfate Reduction Theory, in Corrosion Conference and Expo, NACE, Atlanta, 2009, p 1–12.
R. Jia, D. Yang, J. Xu, D. Xu and T. Gu, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of C1018 Carbon Steel by Nitrate Reducing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Under Organic Carbon Starvation, Corros. Sci., 2017, 127, p 1–9.
L.Y. Cui, Z.Y. Liu, D.K. Xu, P. Hu, J.M. Shao, C.W. Du and X.G. Li, The Study of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Based on High-Resolution Characterization, Corros. Sci., 2020, 30, p 108842.
X. Yang, J. Shao, Z. Liu, D. Zhang, L. Cui, C. Du and X. Li, Stress-Assisted Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Mechanism of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Caused by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Corros. Sci., 2020, 20, p 108746.
Y. Chen, Q. Tang, J.M. Senko, G. Cheng, B.M.Z. Newby, H. Castaneda and L.K. Ju, Long-Term Survival of Desulfovibrio vulgaris on Carbon Steel and Associated Pitting Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2015, 90, p 89–100.
P. Zhang, D. Xu, Y. Li, K. Yang and T. Gu, Electron Mediators Accelerate the Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel by the Desulfovibrio vulgaris Biofilm, Bioelectrochemistry, 2015, 101, p 14–21.
H. Liu, T. Gu, G. Zhang, H. Liu and Y.F. Cheng, Corrosion of X80 Pipeline Steel Under Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Biofilms in Simulated CO2-Saturated Oilfield Produced Water with Carbon Source Starvation, Corros. Sci., 2018, 136, p 47–59.
C.B. Walker, Z. He, Z.K. Yang, J.A. Ringbauer, Q. He, J. Zhou, G. Voordouw, J.D. Wall, A.P. Arkin, T.C. Hazen and S. Stolyar, The Electron Transfer System of Syntrophically Grown Desulfovibrio vulgaris, J. Bacteriol., 2019, 191, p 5793–5801.
G. Reguera, K.D. McCarthy, T. Mehta, J.S. Nicoll, M.T. Tuominen and D.R. Lovley, Extracellular Electron Transfer via Microbial Nanowires, Nature, 2005, 435, p 1098–1101.
D. Xu, Y. Li, F. Song and T. Gu, Laboratory Investigation of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of C1018 Carbon Steel by Nitrate Reducing Bacterium Bacillus Licheniformis, Corros. Sci., 2013, 77, p 385–390.
L. Huang, Y. Huang, Y. Lou, H. Qian, D. Xu, L. Ma, C. Jiang and D. Zhang, Pyocyanin-Modifying Genes phzM and phzS Regulated the Extracellular Electron Transfer in Microbiologically-Influenced Corrosion of X80 Carbon Steel by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Corros. Sci., 2020, 164, p 108355.
P. Marcus and J.M. Grimal, The Anodic Dissolution and Passivation of NiCrFe Alloys Studied by ESCA, Corros. Sci., 1992, 33, p 805–814.
M. Oku and K. Hirokawa, X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Co3O4, Fe3O4, Mn3O4, and Related Compounds, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 1976, 8, p 475–481.
T. Wu, J. Xu, M. Yan, C. Sun, C. Yu and W. Ke, Synergistic Effect of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Elastic Stress on Corrosion of X80 Steel in Soil Solution, Corros. Sci., 2014, 83, p 38–47.
J. Wang, B. Hou, J. Xiang, X. Chen, T. Gu and H. Liu, The Performance and Mechanism of Bifunctional Biocide Sodium Pyrithione Against Sulfate Reducing Bacteria in X80 Carbon Steel Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2019, 150, p 296–308.
H. Konno, K. Sasaki, M. Tsunekawa, T. Takamori and R. Furuichi, X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic Analysis of Surface Products on Pyrite Formed by Bacterial Leaching, Bunseki Kagaku, 1991, 40, p 609–616.
V.I. Nefedov, Y.V. Salyn, G. Leonhardt and R. Scheibe, A Comparison of Different Spectrometers and Charge Corrections Used in X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 1977, 10, p 121–124.
B.J. Tan, K.J. Klabunde and P.M. Sherwood, X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Studies of Solvated Metal Atom Dispersed Catalysts. Monometallic Iron and Bimetallic Iron-Cobalt Particles on Alumina, Chem. Mater., 1990, 2, p 186–191.
B.R. Strohmeier and D.M. Hercules, Surface Spectroscopic Characterization of Manganese/Aluminum Oxide Catalysts, J. Phys. Chem., 1984, 88, p 4922–4929.
S. Karthe, R. Szargan and E. Suoninen, Oxidation of Pyrite Surfaces: A Photoelectron Spectroscopic Study, Appl. Surf. Sci., 1993, 72, p 157–170.
J.M. Thomas, I. Adams, R.H. Williams and M. Barber, Valence Band Structures and Core-Electron Energy Levels in the Monochalcogenides of Gallium. Photoelectron SPECTROSCOPIC study, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans., 1972, 2(68), p 755–764.
T. Wu, J. Xu, C. Sun, M. Yan, C. Yu and W. Ke, Microbiological Corrosion of Pipeline Steel Under Yield Stress in Soil Environment, Corros. Sci., 2014, 88, p 291–305.
M. Stern and A.L. Geary, Electrochemical Polarization: I. A Theoretical Analysis of the Shape of Polarization Curves, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1957, 104, p 56–63.
T. Wu, W.C. Ding, D.C. Zeng, C.F. Xu, M.C. Yan, J. Xu, C.K. Yu and C. Sun, Microbiologically Induced Corrosion of X80 Pipeline Steel in an Acid Soil Solution: (I) Electrochemical Analysis, J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot., 2014, 34, p 346–352.
V. Margaria, T. Tommasi, S. Pentassuglia, V. Agostino, A. Sacco, C. Armato, A. Chiodoni, T. Schilirò and M. Quaglio, Effects of pH Variations on Anodic Marine Consortia in a Dual Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2017, 42, p 1820–1829.
D. Enning, H. Venzlaff, J. Garrelfs, H.T. Dinh, V. Meyer, K. Mayrhofer, A.W. Hassel, M. Stratmann and F. Widdel, Marine Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Cause Serious Corrosion of Iron Under Electroconductive Biogenic Mineral Crust, Environ. Microbiol., 2012, 14, p 1772–1787.
K. Xiao, Z. Li, J. Song, Z. Bai, W. Xue, J. Wu, C. Dong, Effect of Concentrations of Fe2+ and Fe3+ on the Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in Cl− and SO42− Aqueous Environments. Met. Mater. Int., 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00590-y.
L. Yu, M. Yan, J. Ma, M. Wu, Y. Shu, C. Sun, J. Xu and C. Yu, Sulfate Reducing Bacteria Corrosion of Pipeline Steel in Fe-Rich Red Soil, Acta Metall. Sin., 2017, 53, p 1568–1578.
T. Gu, Theoretical Modeling of the Possibility of Acid Producing Bacteria Causing Fast Pitting Biocorrosion, J. Microb. Biochem. Technol., 2014, 6, p 68–74.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFB0304701), Open Fund of Shandong Key Laboratory of Corrosion Science (No. KLCS201909) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. FRF-NP-20-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, L., Liu, Z., Hu, P. et al. Laboratory Investigation of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of X80 Pipeline Steel by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 7584–7596 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05974-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05974-z