Abstract
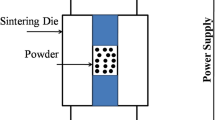
Al-4.5 wt.% Cu alloy powder was produced by inert gas spray atomization process. The size of the powder in the range of 10 to 500 µm produced by spray atomization process was analyzed using laser particle analyzer. The smaller powder particles of size less than 25 µm are of spherical shape, whereas larger-sized powders are elongated and irregular-shaped. The smaller powder particles exhibit cellular morphology and are of equiaxed grains. The longer and irregular-shaped powder reveals coarse grains, whereas elongated grains exhibit dendritic morphology. The powder of different sizes was compacted by spark plasma sintering by applying temperature and pressure simultaneously. The density of the compact was determined using water displacement method, and the average density of the compact was 2.65 g/cc. After compacting and sintering the powder, 95 percent relative density of the compact is achieved. The porosity present in the compact was captured by optical metallurgical microscope. The microstructural characterization of powder and sintered compact was carried out by using optical metallurgical microscope and scanning electron microscope. The micro-hardness of the compact was tested using micro-Vickers hardness testing machine, and the hardness was found to be varied from 67.1 to 69.6 HV. The yield strength, ultimate strength and ductility of the sintered compact were determined by conducting the compression test.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Fogagnolo, D. Amador, E. M. Ruiz-Navas, and J. M. Torralba, Solid Solution in Al-4.5wt.% Cu Produced by Mechanical Alloying, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2006, 433,p 45-49
C.L. De Castro and B.S. Mitchell, Crystal Growth Kinetics of Nanocrystalline Aluminum Prepared by Mechanical Attrition in Nylon Media, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 396, p 124–128.
P. Keblinski, S.R. Phillpot, D. Wolf and H. Gleiter, Amorphous Structure of Grain Boundaries and Grain Junctions in Nanocrystalline Silicon by Molecular dynamics Simulation, Acta Mater., 1997, 45, p 987–998.
R.K. Guduru, K.L. Murty, K.M. Youssef, R.O. Scattergood and C.C. Koch, Mechanical Behavior of Nanocrystalline Copper, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 463, p 14–21.
S. Cheng a, Y.H. Zhao, Y.T. Zhu, and E. Ma, Optimizing the Strength and Ductility of Fine Structured, Al Alloy by Nano-precipitation, Acta Mater., 2024, 2007(55), p 5822–5832.
C. Badani, F. Marino and E. Verne, Calorimetric Study on Precipitation Path in 2024 Alloy and its SiC Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, 191, p 185–191.
J.M. Papazian and P.N. Adler, Tensile Properties of Short Fiber-Reinforced SiC/Ai Composites, Metall. Trans. A, 1990, 21, p 401–410.
S.C. Wang and M.J. Starink, International Material Reviews, Precip. Intermet. Phases Precip., 2005, 50, p 193–215.
E. Fleury , J.H. Lee , S.H. Kim , G.S. Song , J.S. Kim , W.T. Kim and D.H. Kim, Synthesis of Bulk Quasicrystals by Spark Plasma Sintering,Mater. Res. Soc., 2001, 643, K2.1.1-K2.1.6
Jatin Kumar Rana, D. Sivaprahasamb, K. Seetharama Rajua, and V. Subramanya Sarma, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline High Strength Al–Mg–Si (AA6061) Alloy by High Energy Ball Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 527, p 292–296
Th. Schubert, J. Schmidt, T. Weissgärber, and B. Kieback, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of an Al-Si Alloy Consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering, PM2010 World Congress – Spark Plasma Sintering, p 1-8
E. Fleury, J.H. Lee, S.H. Kim, W.T. Kim, J.S. Kim and D.H. Kim, Spark Plasma Sintering of Al-Si-Cu-Fe Quasi-Crystalline Powder, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34A, p 841–849.
S.W. Wanga, L.D. Chena, Y.S. Kang, M. Niino and T. Hirai, Effect of Plasma Activated Sintering (PAS) Parameters on Densification of Copper Powder, Mater. Res. Bull., 2000, 35, p 619–628.
M. Sato, M. Nanko, K. Matsumaru and K. Ishizaki, Homogeneity in Sintering of Fine Ni-20Cr Powder by Pulsed Electric Current Sintering (PECS) Process, J. Mater. online, 2006, 2, p 1–11.
D. Tiwari, B. Basu and K. Biswas, Simulation of Thermal and Electric Field Evolution During Spark Plasma Sintering, Ceram. Int., 2009, 35, p 699–708.
H. Kaftelena, M. Lutfi Ovecoglu, H. Henein, and H. Cimenoglu, ZrC Particle Reinforced Al–4 wt.% Cu Alloy Composites Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Vacuum Hot Pressing: Microstructural Evaluation and Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Eng. A.,2010, 527, p 5930–5938
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra Mohan, H.K., Devaraj, S. & Narayana Swamy, K.S. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Spark-Plasma-Sintered Compact of Al-4.5 wt.% Cu Alloy Powder. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 2433–2438 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05503-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05503-y