Abstract
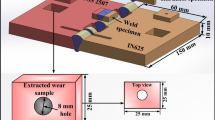
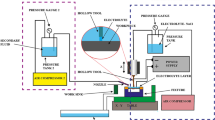
The role of the electrode in electric discharge machining (EDM) performance is crucial because it has an impact on the geometrical accuracy, machining efficiency and surface finish of the machined components. In the present work, a new technical approach combining equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) and deep cryogenic treatment (DCT) was put forward to manufacture copper electrodes for enhancing the machining characteristics of electric discharge machining (EDM). Effects of the ECAP, the ECAP + DCT on the EDM performances including the electrode wear rate (EWR), the workpiece corner sharpness (WCS), the surface roughness (Ra) and the surface characteristics of EDM workpieces have been investigated. The EWR after the ECAP and the ECAP + DCT was reduced to the minimum after two passes of ECAP. The EWR and WCS after the ECAP + DCT were less than that after the ECAP due to the higher hardness and electrical conductivity. The Ra of EDM workpieces using electrodes processed by the ECAP + DCT was slightly less than that after ECAP. An analogous Hall–Petch relation between the Ra of EDM workpieces and the grain size of electrodes was observed, indicating that ultrafine-grained electrodes processed by ECAP and the additional DCT would enhance the surface finish. The surface finish of EDM workpieces was discussed based on the features of the surface morphology.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Lee and X.P. Li, Study of the Effect of Machining Parameters on the Machining Characteristics in Electrical Discharge Machining of Tungsten Carbide, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, 115, p 344–358
L. Li, Y.S. Wong, J.Y.H. Fuh, and L. Lu, Effect of TiC in Copper–Tungsten Electrodes on EDM Performance, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, 113, p 563–567
H.C. Tsai, B.H. Yan, and F.Y. Huang, EDM Performance of Cr/Cu-Based Composite Electrodes, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf, 2003, 43, p 245–252
P.K. Patowari, U.K. Mishra, P. Saha, and P.K. Mishra, Surface Integrity of C-40 Steel Processed with WC-Cu Powder Metallurgy Green Compact Tools in EDM, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2011, 26, p 668–676
S.S. Gill, J. Singh, R. Singh, and H. Singh, Metallurgical Principles of Cryogenically Treated Tool Steels: A Review on the Current State of Science, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2011, 54, p 59–82
A.K. Singla, J. Singh, and V.S. Sharma, Processing of Materials at Cryogenic Temperature and its Implications in Manufacturing: A Review, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2018, 33, p 1603–1640
V. Srivastava and P.M. Pandey, Performance Evaluation of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) Process using Cryogenically Cooled Electrode, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2012, 27, p 683–688
J.M. Jafferson and P. Hariharan, Machining Performance of Cryogenically Treated Electrodes in Microelectric Discharge Machining: A Comparative Experimental Study, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2013, 28, p 397–402
K. Edalati, K. Imamura, T. Kiss, and Z. Horita, Equal-Channel Angular Pressing and High-Pressure Torsion of Pure Copper: Evolution of Electrical Conductivity and Hardness with Strain, Mater. Trans., 2012, 53, p 123–127
K.X. Wei, Z.Q. Chu, W. Wei, Q.B. Du, I.V. Alexandrov, and J. Hu, Effect of Deep Cryogenic Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of Pure Copper Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2019, 21, p 1801372
H. Marashi, D.M. Jafarlou, A.A.D. Sarahan, and N.A. Mardi, Employing Severe Plastic Deformation to the Processing of Electrical Discharge Machining Electrodes, Precis. Eng., 2016, 46, p 309–322
O.F. Higuera and J.M. Cabrera, Microstructure Influencing Physical and Mechanical Properties of Electrolytic Tough Pitch Copper Produced by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Mech. Mater., 2013, 67, p 9–14
A.L. Woodcraft, Recommended Values for the Thermal Conductivity of Aluminium of Different Purities in the Cryogenic to Room Temperature Range, and a Comparison with Copper, Cryogenics, 2005, 45, p 626–636
C. Isaak and W. Reitz, The Effects of Cryogenic Treatment on the Thermal Conductivity of GRCop-84, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2007, 23, p 82–91
H.H. Fu, D.J. Benson, and M.A. Meyers, Analytical and Computational Description of Effect of Grain Size on Yield Stress of Metals, Acta Mater., 2001, 49, p 2567–2582
S. Singh, S. Maheshwari, and P.C. Pandey, Some Investigations into the Electric Discharge Machining of Hardened Tool Steel using Different Electrode Materials, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, 149, p 272–277
R. Kumar and I. Singh, A Modified Electrode Design for Improving Process Performance of Electric Discharge Drilling, J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2019, 264, p 211–219
M. Kiyak and O. Cakır, Examination of Machining Parameters on Surface Roughness in EDM of Tool Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 191, p 141–144
Y.H. Guu, AFM Surface Imaging of AISI D2 Tool Steel Machined by the EDM Process, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2005, 242, p 245–250
S.H. Lee and X.S. Li, Study of the Surface Integrity of the Machined Workpiece in the EDM of Tungsten Carbide, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 139, p 315–321
K.H. Ho and S.T. Newman, State of the Art Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf, 2003, 43, p 1287–1300
H.T. Lee and T.Y. Tai, Relationship Between EDM Parameters and Surface Crack Formation, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 142, p 676–683
D.K. Panda and R.K. Bhoi, Electro-Discharge Machining–A Qualitative Approach, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2006, 21, p 853–862
L.C. Lee, L.C. Lim, Y.S. Wong, and H.H. Lu, Towards a Better Understanding of the Surface Features of Electro-Discharge Machined Tool Steels, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1990, 24, p 513–523
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51561001), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), the Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (TAPP), and the Science and Technology Project of Changzhou, P. R. China (Nos. CZ20180016 and CE20170028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, K.X., Chu, Z.Q., Yang, L.C. et al. Performance Evaluation of Electrical Discharge Machining using Ultrafine-Grained Cu Electrodes Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing and Deep Cryogenic Treatment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 281–289 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05351-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05351-2