Abstract
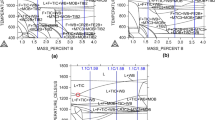
In this paper, the effect of wire drawing on the microstructures, mechanical properties, and shape memory effect of compositions Cu87.85-Al11.70-Be0.45 (CAB) and Cu87.73-Al11.70-Be0.45-Zr0.12 (CABZ) has been experimentally investigated. The wires with a diameter of 1.33 mm are manufactured from the casted round bars through the rolling and drawing (secondary) process. Investigations are performed on microstructure and phase for both as-cast and wire-drawn SMAs. Further, wire-drawn SMAs are investigated for phase transformation temperatures, hardness, ductility, and shape memory effect. The results show that the average grain size decreased with 73.06% by adding Zr to the CAB alloy. Further, the grain size of CABZ alloy wire decreased with 67.38% in the longitudinal direction and 67.07% in the transverse direction as compared to CAB alloy wire after the secondary process. Improvement of the grain structure in CABZ alloy wire resulted in an enhancement in the hardness of 13.86% in longitudinal and 12.43% in the transverse direction, and tensile strength of 134.58% and ductility of 177.06%. The phase transformation temperatures reduced by the addition of Zr, and better shape recovery is observed in CABZ alloy wire.
Graphic Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.A. Schroeder and C.M. Wayman, The Formation of Martensite and the Mechanism of the Shape Memory Effect in Single Crystals of Cu-Zn Alloys, Acta Metall., 1977, 25(12), p 1375–1391
K. Otsuka and X. Ren, Recent Developments in the Research of Shape Memory Alloys, Intermetallics, 1999, 7(5), p 511–528
A.L. Roitburd and G.V. Kurdjumov, The Nature of Martensitic Transformations, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1979, 39(2), p 141–167
M. Muruganant, A. Chirazi, and B. Raj, Frontiers in Materials Processing, Applications, Research and Technology, Springer Singapore, Singapore, 2018
W.J. Buehler, J.V. Gilfrich, and R.C. Wiley, Effect of Low-Temperature Phase Changes on the Mechanical Properties of Alloys Near Composition TiNi, J. Appl. Phys., 1963, 34(5), p 1475–1477
D. Stoeckel, The Shape Memory Effect—Phenomenon, Alloys, and Applications, Shape Mem. Eff. Alloy, 1995, 1, p 1–13
K. Otsuka and T. Kakeshita, Science and Technology of Shape-Memory Alloys: New Developments, MRS Bull., 2002, 27(2), p 91–100
J. Mohd Jani, M. Leary, A. Subic, and M.A. Gibson, A Review of Shape Memory Alloy Research, Applications and Opportunities, Mater. Des., 2014, 56, p 1078–1113
Y. Liu and J. van Humbeeck, On the Damping Behaviour of Niti Shape Memory Alloy, Le J. Phys. IV, 1997, 07(5), p C5-519-C5-524
R. DesRoches, J. McCormick, and M. Delemont, Cyclic Properties of Superelastic Shape Memory Alloy Wires and Bars, J. Struct. Eng., 2004, 130(1), p 38–46
V. Recarte, R. Pérez-Sáez, E. Bocanegra, M. Nó, and J. San Juan, Dependence of the Martensitic Transformation Characteristics on Concentration in Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1999, 273–275, p 380–384
M. Franz and E. Hornbogen, Martensitic Transformation of a CuZnAl-Shape Memory Alloy Strengthened by Hot-Rolling, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1998, 252(2), p 157–165
V. Recarte, R.B. Pérez-Sáez, J. San Juan, E.H. Bocanegra, and M.L. Nó, Influence of Al and Ni Concentration on the Martensitic Transformation in Cu-Al-Ni Shape-Memory Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33(8), p 2581–2591
N.J. Park, Texture in CuZnAl Shape Memory Alloys, Met. Mater. Int., 1996, 2(3), p 159–168
S. Belkahla, H.F. Flores Zuñiga, and G. Guenin, Elaboration and Characterization of New Low Temperature Shape Memory Cu-Al-Be Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1993, 169(1–2), p 119–124
S. Najah Saud Al-Humairi, Cu-based shape memory alloys: modified structures and their related properties, in Recent Advancements in the Metallurgical Engineering and Electrodeposition (IntechOpen, 2020)
S.H. Chang, Influence of Chemical Composition on the Damping Characteristics of Cu–Al–Ni Shape Memory Alloys, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 125(3), p 358–363
Ş.N. Balo and M. Ceylan, Effect of Be Content on Some Characteristics of Cu–Al–Be Shape Memory Alloys, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2002, 124(1–2), p 200–208
A.R. Pelton, S.M. Russell, and J. DiCello, The Physical Metallurgy of Nitinol for Medical Applications, JOM, 2003, 55(5), p 33–37
G.B. Cho, Y.H. Kim, S.G. Hur, C.A. Yu, and T.H. Nam, Transformation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of a Nanostructured Ti-50.0Ni(at.%) Alloy, Met. Mater. Int., 2006, 12(2), p 181–187
S. Montecinos, A. Cuniberti, R. Romero, and M. Stipcich, Grain Size Evolution in Cu-Based Shape Memory Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 2015, 50(11), p 3994–4002
P. Zhang, A. Ma, J. Jiang, S. Lu, P. Lin, D. Yang, and G. Liu, Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Response of Cu–Al–Be–B Shape Memory Alloy Processed by Repetitive Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 497(1–2), p 210–214
V. Sampath, Studies on the Effect of Grain Refinement and Thermal Processing on Shape Memory Characteristics of Cu–Al–Ni Alloys, Smart Mater. Struct., 2005, 14(5), p S253–S260
S. Yang, F. Zhang, J. Wu, J. Zhang, C. Wang, and X. Liu, Microstructure Characterization, Stress-Strain Behavior, Superelasticity and Shape Memory Effect of Cu–Al–Mn–Cr Shape Memory Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(10), p 5917–5927
X. Zhang, M. Zhang, T. Cui, J. Li, Q. Liu, and H. Wang, The Enhancement of the Mechanical Properties and the Shape Memory Effect for the Cu-13.0Al-4.0Ni Alloy by Boron Addition, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 776, p 326–333
V.H.C. de Albuquerque, T.A.A. de Melo, R.M. Gomes, S.J.G. de Lima, and J.M.R.S. Tavares, Grain Size and Temperature Influence on the Toughness of a CuAlBe Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, 528(1), p 459–466
B.N. Guniputi and S.M. Murigendrappa, Influence of Gd on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Shape Memory Properties of Cu-Al-Be Polycrystalline Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2018, 737(June), p 245–252
G.-S. Yang, J.-K. Lee, and W.-Y. Jang, Effect of Grain Refinement on Phase Transformation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Based Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2009, 19(4), p 979–983
G. Bala Narasimha and S.M. Murigendrappa, Effect of Zirconium on the Properties of Polycrystalline Cu-Al-Be Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2019, 755(November 2018), p 211–219
J. Yang, Q.Z. Wang, F.X. Yin, C.X. Cui, P.G. Ji, and B. Li, Effects of Grain Refinement on the Structure and Properties of a CuAlMn Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, 664, p 215–220
V. Sampath, Improvement of Shape-Memory Characteristics and Mechanical Properties of Copper–Zinc–Aluminum Shape-Memory Alloy with Low Aluminum Content by Grain Refinement, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2006, 21(8), p 789–795
J.S. Lee and C.M. Wayman, Grain Refinement of Cu-Zn-Al Shape Memory Alloys, Metallography, 1986, 19(4), p 401–419
J.S. Lee and C.M. Wayman, Grain Refinement of a Cu-Al-Ni Shape Memory Alloy by Ti and Zr Additions, Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1986, 27(8), p 584–591
G. Mussot-Hoinard, E. Patoor, and A. Eberhardt, Influence of Wire-Drawing on the Properties of a Cu–Al–Be Polycrystalline Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, 481–482(1–2 C), p 538–541
K. Mehta and K. Gupta, Fabrication and Processing of Shape Memory Alloys, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2019
E. Hornbogen, Ausforming of NiTi, J. Mater. Sci., 1999, 34(3), p 599–606
M.E. Mitwally and M. Farag, Effect of Cold Work and Annealing on the Structure and Characteristics of NiTi Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2009, 519(1–2), p 155–166
J.R. Davis, ASM Speciality Handbook, Copper and Copper Alloys, ASM International, Cleveland, 2001
F. Fang, L. Zhou, X. Hu, X. Zhou, Y. Tu, Z. Xie, and J. Jiang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Cold-Drawn Pearlitic Wires Affect by Inherited Texture, Mater. Des., 2015, 79, p 60–67
C.S. Çetinarslan, A Study on Influences of Some Process Parameters on Cold Drawing of Ferrous Wires, Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci., 2012, 19(4), p 221–228
G. Choi and K. Lee, Effect of Cold Rolling on the Microstructural Evolution of New β-Typed Ti–6Mo–6 V–5Cr–3Sn–2.5Zr Alloys, Mater. Charact., 2017, 123, p 67–74
F.C. Campbell, Deformation processing, in Elements of Metallurgy and Engineering Alloys (ASM International, 2008), p. 279–302
S. Ergen, O. Uzun, F. Yilmaz, and M.F. Kiliçaslan, Shape Memory Properties and Microstructural Evolution of Rapidly Solidified CuAlBe Alloys, Mater. Charact., 2013, 80, p 92–97
P. Zhang, A. Ma, S. Lu, P. Lin, J. Jiang, H. Ma, and C. Chu, Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing and Heat Treatment on the Microstructure of Cu–Al–Be–B Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Lett., 2009, 63(30), p 2676–2679
C.-C. Hsu and W.-H. Wang, Superplastic Forming Characteristics of a Cu-Zn-Al-Zr Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1996, 205(1–2), p 247–253
Acknowledgment
This study financially supported by the SERB, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, under Project No: EMR/2016/001247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.K., Murigendrappa, S.M. & Kattimani, S. Investigation on Properties of Shape Memory Alloy Wire of Cu-Al-Be Doped with Zirconium. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 7260–7269 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05233-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05233-7