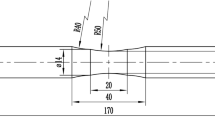
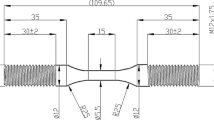
Abstract
Ceramic micro-shot peening (CMSP) and steel micro-shot peening (SMSP) were utilized to investigate the effect of micro-shot peening (MSP) on the high-cycle fatigue properties of Al-7Si-0.3Mg casting aluminum alloy in a previous study. However, the improvement effects of CMSP and SMSP on the fatigue strength (at 5 × 107 cycles) were only 33% because the depth of harden layers was only 20 and 55 μm while the depth of compressive residual stress affected layers was only 37 and 68 μm. In this study, conventional shot peening (CSP) was utilized, and the results were compared with those of MSP, with the expectation that CSP would provide a greater improvement in the fatigue strength. The affected surface layers of the shot-peened specimens were characterized using surface morphology, microhardness, and residual stress analyses. In addition, the effect of CSP on the fatigue strength at 5 × 107 cycles was investigated using a rotating bending fatigue test (R = − 1). An investigation of the extensive surface compressive residual stress relaxation process for the three different shot-peened specimens during cyclic loading was conducted using x-ray diffraction. In addition, the initiation sites for fatigue cracks on the fracture surface were observed using scanning electron microscopy. Furthermore, the fatigue life of the samples with the internal casting defect failure mode was predicted using linear elastic fracture mechanics, while that for samples with the surface crack initiation failure mode was predicted using the modified Morrow model considering the residual stress.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.H. Fan, S.H. Liu, and Y. Wang, Application of EN AC-AlSi7Mg0.6 Aluminum Alloy for Railway Contact Network, Hot Work. Technol., 2015, 7, p 108–109
M. Benedetti, V. Fontanari, P. Scardi, C.A. Ricardo, and M. Bandini, Reverse Bending Fatigue of Shot Peened 7075-T651 Aluminium Alloy: The Role of Residual Stress Relaxation, Int. J. Fatigue, 2009, 31(8–9), p 1225–1236
J. González, S. Bagherifard, M. Guagliano, and I.F. Pariente, Influence of Different Shot Peening Treatments on Surface State and Fatigue Behaviour of Al 6063 Alloy, Eng. Fract. Mech., 2017, 185, p 72–81
X. Li, J. Zhang, B. Yang, J. Zhang, M. Wu, and L. Lu, Effect of Micro-shot Peening, Conventional Shot Peening and Their Combination on Fatigue Property of EA4T Axle Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, 275, p 116320
S. Kikuchi, Y. Nakamura, K. Nambu, and M. Ando, Effect of Shot Peening Using Ultra-Fine Particles on Fatigue Properties of 5056 Aluminum Alloy under Rotating Bending, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 652, p 279–286
K. Oguri, Fatigue Life Enhancement of Aluminum Alloy for Aircraft by Fine Particle Shot Peening (FPSP), J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, 211(8), p 1395–1399
K. Oguri, T. Sekigawa, and A. Inoue, Fatigue Property Enhancement of Aircraft Metallic Materials by Fine Particle Shot Peening, Bull. Jpn. Inst. Met., 2008, 47, p 553–559
D.J. Chadwick, S. Ghanbari, D.F. Bahr, and M.D. Sangid, Crack Incubation in Shot Peened AA7050 and Mechanism for Fatigue Enhancement, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2018, 41(1), p 71–83
H. Luong and M.R. Hill, The Effects of Laser Peening on High-Cycle Fatigue in 7085-T7651 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 477(1–2), p 208–216
E. Maleki, O. Unal, and K.R. Kashyzadeh, Efficiency Analysis of Shot Peening Parameters on Variations of Hardness, Grain Size and Residual Stress via Taguchi Approach, Met. Mater. Int., 2019, 25, p 1–12
J.H. Zhang, X.Q. Cheng, Q.X. Xia, and J.Y. Li, Influence of Laser Shot Peening Parameters on the Surface Hardness and Roughness of 7075 Aluminum Alloy. In Materials Science Forum (Vol. 920, pp. 83–88). Trans Tech Publications (2018)
R. Ramos, N. Ferreira, J.A.M. Ferreira, C. Capela, and A.C. Batista, Improvement in Fatigue Life of Al 7475-T7351 Alloy Specimens by Applying Ultrasonic and Microshot Peening, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 92, p 87–95
A. Turnbull, E.R. De Los Rios, R.B. Tait, C. Laurant, and J.S. Boabaid, Improving the Fatigue Crack Resistance of Waspaloy by Shot Peening, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1998, 21(12), p 1513–1524
M.Z. Wu, J.W. Zhang, G.M. Mei, J.X. Zhang, and X. Li, Effects of Fine Particle Shot Peening Treatment on Fatigue Properties of Al-7Si-0.3Mg Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28(5), p 2600–2609
N. Li, H.T. Li, J.Y. Zhou, H.T. Liu, C.K. Liu, and S.Y. Qu, Influence of Different Surface Treatments on Fatigue Life of 7050 Al Alloy, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2019, 944, p 142–148
K. Dalaei, B. Karlsson, and L.E. Svensson, Stability of Shot Peening Induced Residual STRESSES and Their Influence on Fatigue Lifetime, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(3), p 1008–1015
Kodama, S., The Behavior of Residual Stress during Fatigue Stress Cycles, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical Behavior of Metals II, Society of Material Science, Kyoto, 1972, vol. 2, pp. 111–118.
P. Li, P.D. Lee, D.M. Maijer, and T.C. Lindley, Quantification of the Interaction Within Defect Populations on Fatigue Behavior in an Aluminum Alloy, Acta Mater., 2009, 57(12), p 3539–3548
I. Serrano-Munoz, J.Y. Buffiere, R. Mokso, C. Verdu, and Y. Nadot, Location, Location & Size: Defects Close to Surfaces Dominate Fatigue Crack Initiation, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, p 45239
S.E. Stanzl-Tschegg, H.R. Mayer, A. Beste, and S. Kroll, Fatigue and Fatigue Crack Propagation in AlSi7Mg Cast Alloys under In-Service Loading Conditions, Int. J. Fatigue, 1995, 17(2), p 149–155
Q.G. Wang, D. Apelian, and D.A. Lados, Fatigue Behavior of A356-T6 Aluminum Cast Alloys: Part I—Effect of Casting Defects, J. Light Met., 2001, 1(1), p 73–84
M.E. Seniw, M.E. Fine, E.Y. Chen, M. Meshii, and J. Gray, Relation of Defect Size and Location to Fatigue Failure in Al Alloy A356 Cast Specimens (No. CONF-970980-). The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 1997, Warrendale, PA
S. Jana, R.S. Mishra, J.B. Baumann, and G. Grant, Effect of Friction Stir Processing on Fatigue Behavior of an Investment Cast Al-7Si-0.6Mg Alloy, Acta Mater., 2010, 58(3), p 989–1003
A. Rotella, Y. Nadot, M. Piellard, R. Augustin, and M. Fleuriot, Fatigue Limit of a Cast Al-Si-Mg Alloy (A357-T6) with Natural Casting Shrinkages Using ASTM Standard X-Ray Inspection, Int. J. Fatigue, 2018, 114, p 177–188
J. Zhang, W. Li, H. Wang, Q. Song, L. Lu, W. Wang, and Z. Liu, A Comparison of the Effects of Traditional Shot Peening and Micro-shot Peening on the Scuffing Resistance of Carburized and Quenched Gear Steel, Wear, 2016, 368, p 253–257
J.W. Zhang, L.T. Lu, K. Shiozawa, X.L. Shen, H.F. Yi, and W.H. Zhang, Analysis on Fatigue Property of Microshot Peened Railway Axle Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(3), p 1615–1622
J.C. Kim, S.K. Cheong, and H. Noguchi, Evolution of Residual Stress Redistribution Associated with Localized Surface Microcracking in Shot-Peened Medium-Carbon Steel during Fatigue Test, Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, 55, p 147–157
B. Skallerud, T. Iveland, and G. Härkegård, Fatigue Life Assessment of Aluminum Alloys with Casting Defects, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1993, 44(6), p 857–874
S. Barter, L. Molent, N. Goldsmith, and R. Jones, An Experimental Evaluation of Fatigue Crack Growth, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2005, 12(1), p 99–128
Q.G. Wang, P.N. Crepeau, C.J. Davidson, and J.R. Griffiths, Oxide Films, Pores and the Fatigue Lives of Cast Aluminum Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, 37(6), p 887–895
B.R. Crawford, C. Loader, A.R. Ward, C. Urbani, M.R. Bache, S.H. Spence, and A.J. Stonham, The EIFS Distribution for Anodized and Pre-corroded 7010–T7651 under Constant Amplitude Loading, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 2005, 28(9), p 795–808
Y.K. Gao and X.R. Wu, Experimental Investigation and Fatigue Life PREDICTION for 7475-t7351 Aluminum Alloy With and Without Shot Peening-Induced Residual Stresses, Acta Mater., 2011, 59(9), p 3737–3747
A.J. McEvily, Current Aspects of Fatigue, Met. Sci., 1977, 11(8–9), p 274–284
H.U. Staal and J.D. Elen, Crack Closure and Influence of Cycle Ratio R on Fatigue Crack Growth in Type 304 Stainless Steel at Room Temperature, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1979, 11(2), p 275–283
V. Bachmann and D. Munz, Fatigue Crack Closure Evaluation with the Potential Method, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1979, 11(1), p 61–71
Y. Murakami, and M. Endo, Effects of Hardness and Crack Geometries on μ/Cth of Small Cracks Emanating from Small Defects, 1986
Y. Murakami, Metal Fatigue: Effects of Small Defects and Nonmetallic Inclusions, vol. 70(7), Elsevier, London, 2002, p 1197–1200
Y. Murakami and E. Masahiro, Quantitative Evaluation of Fatigue Strength of Metals Containing Various Small Defects or Cracks, Eng. Fract. Mech., 1983, 17(1), p 1–15
Y. Murakami, T. Toriyama, and E.M. Coudert, Instructions for a New Method of Inclusion Rating and Correlations with the Fatigue Limit, J. Test. Eval., 1994, 22(4), p 318–326
S. Beretta and Y. Murakami, Statistical Analysis of Defects for Fatigue Strength Prediction and Quality Control of Materials, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1998, 21(9), p 1049–1065
H. Mayer, M. Papakyriacou, B. Zettl, and S.E. Stanzl-Tschegg, Influence of Porosity on the Fatigue Limit of Die Cast Magnesium and Aluminium Alloys, Int. J. Fatigue, 2003, 25(3), p 245–256
H. Mayer, M. Papakyriacou, B. Zettl, and S. Vacic, Endurance Limit and Threshold Stress Intensity of Die Cast Magnesium and Aluminium Alloys at Elevated Temperatures, Int. J. Fatigue, 2005, 27(9), p 1076–1088
P. White, L. Molent, and S. Barter, Interpreting Fatigue Test Results Using a Probabilistic Fracture Approach, Int. J. Fatigue, 2005, 27(7), p 752–767
M. Tiryakioğlu, Statistical Distributions for the Size of Fatigue-Initiating Defects in Al-7%Si-0.3%Mg Alloy Castings: A Comparative Study, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 497(1-2), p 119–125
S.S. Manson, Behavior of Materials under Conditions of Thermal Stress, vol. 2933, 1953, National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
L.F. Coffin, Jr., A Study of the Effects of Cyclic Thermal Stresses on a Ductile Metal, Trans. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. N. Y., 1954, 76, p 931–950
J. Morrow, Fatigue Design Handbook, Adv. Eng., 1968, 4, p 21–29
M.Z. Wu, J.W. Zhang, Y.B. Zhang et al., Effects of Mg Content on the Fatigue Strength and Fracture Behavior of Al-Si-Mg Casting Alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018
M.T.A. El-Khair, Microstructure Characterization and Tensile Properties of Squeeze-Cast AlSiMg ALLOYS, Mater. Lett., 2005, 59(8/9), p 894–900
ASM International. Handbook Committee. ASM Handbook, vol. 19. ASM international, 1990
SAE Standard, J443—Procedures for Using Standard Shot Peening Test Strip, 2003
SAE international, Shot Peening Coverage Determination, SAE J2277, 2013
J. Lin, N. Ma, Y. Lei, and H. Murakawa, Measurement of Residual Stress in Arc Welded Lap Joints by cosα X-Ray Diffraction Method, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, 243, p 387–394
M.G. Moore and W.P. Evans, Mathematical Correction for Stress in Removed Layers in X-Ray Diffraction Residual Stress Analysis (No. 580035). SAE Technical Paper, 1958
Y.L. Lee, J. Pan, R.B. Hathaway, and M. Barkey, Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice, Elsevier, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2005
A. Khalili and K. Kromp, Statistical Properties of Weibull Estimators, J. Mater. Sci., 1991, 26(24), p 6741–6752
J.Z. Yi, P.D. Lee, T.C. Lindley, and T. Fukui, Statistical Modeling of Microstructure and Defect Population Effects on the Fatigue Performance of Cast A356-T6 Automotive Components, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 432(1–2), p 59–68
M.A. Meggiolaro and J.T.P. Castro, Statistical Evaluation of Strain-Life Fatigue Crack Initiation Predictions, Int. J. Fatigue, 2004, 26(5), p 463–476
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51675445, U1534209) and Independent Research Project of State Key Laboratory of Traction Power (No. 2019TPL-T06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, K., Zhang, J., Li, H. et al. Analysis on the Fatigue Properties of Shot-Peened Al-Si-Mg Alloy and Its Fatigue Life Prediction. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 5114–5125 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05001-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05001-7