Abstract
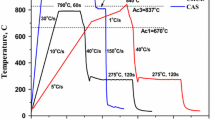
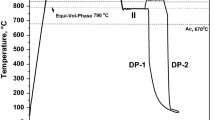
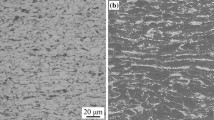
The controlled phase transformation approach is a new generation of microstructure engineering for enhancing ductility in ultrafine-grained materials. The present study aims to extend this concept to dual-phase steel for enhanced tensile ductility at high strength. In this study, cold-rolled steel was subjected to annealing at different processing conditions to develop the core–shell microstructure constituting martensite core and ferrite as shell in the matrix. Controlled austenite decomposition was adopted in designing a core–shell-type structure. The evolved microstructure was characterized using a scanning electron microscope and electron backscatter diffraction technique. The results showed that the uniaxial tensile deformation of dual-phase structured steels had a remarkable strength–ductility trade-off. The ductility was increased anomalously at high martensite fractions. Further, the mechanism of damage activity leading to void nucleation and microcrack formation was studied in post-tensile fractured specimens to establish a correlation with tensile deformation characteristics. The possibility and outcomes of this approach are also reported here.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Ameyama, H. Fujiwara, K. Ameyama, and H. Fujiwara, Creation of Harmonic Structure Materials with Outstanding Mechanical Properties, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2012, 706–709, p 9–16
D. Orlov, H. Fujiwara, and K. Ameyama, Obtaining Copper with Harmonic Structure for the Optimal Balance of Structure-Performance Relationship, Mater. Trans., 2013, 54, p 1549–1553
C. Sawangrat, O. Yamaguchi, S.K. Vajpai, and K. Ameyama, Application of Harmonic Structure Design to Biomedical Co-Cr-Mo Alloy for Improved Mechanical Properties, Mater. Trans., 2014, 55, p 99–105
N.J. Khalil, S.K. Vajpai, M. Ota, and K. Ameyama, Application of Al–Si Semi-Solid Reaction for Fabricating Harmonic Structured Al Based Alloy, Mater. Trans., 2016, 57, p 1433–1439
H. Fujiwara, R. Akada, Y. Yoshita, and K. Ameyama, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Nano-Duplex Materials Produced by HRS Process, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2013, 503–504, p 227–232
S.K. Vajpai, K. Ameyama, M. Ota, T. Watanabe, R. Maeda, T. Sekiguchi, G. Dirras, and D. Tingaud, High Performance Ti-6Al-4V Alloy by Creation of Harmonic Structure Design, IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2014, 63, p 012030
O.P. Ciuca, M. Ota, S. Deng, and K. Ameyama, Harmonic Structure Design of a SUS329J1 Two Phase Stainless Steel and Its Mechanical Properties, Mater. Trans., 2013, 54, p 1629–1633
G. Thomas, and J. Y. Koo, Structure and Properties of Dual Phase Steels, in AIME Symposium, R.A. Kot, J.W. Morris, Eds., Feb 19–21, Metallurgical Society of AIME, 1979, p. 183
Z. Jiang, Z. Guan, and J. Lian, Effects of Microstructural Variables on the Deformation Behaviour of Dual-phase Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, 190, p 55–64
A. Bag, K.K. Ray, and E.S. Dwarakadasa, Influence of Martensite Content and Morphology of Tensile and Impact Properties of High-martensite Dual-phase Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1990, 30, p 1193–1202
Q. Meng, J. Li, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, and L. Zhang, Effect of Water Quenching Process on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Low Alloy Cold Rolled Dual-phase Steel, Mater. Des., 2009, 30, p 2379–2385
K.B. Ravi, N.K. Patel, K. Mukherjee, M. Walunj, G.K. Mandal, and T. Venugopalan, Ferrite Channel Effect on Ductility and Strain Hardenability of Ultra High Strength Dual Phase Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 685, p 187–193
H.A. Alizamini, M. Militzer, and W.J. Poole, Formation of Ultrafine Grained Dual Phase Steels through Rapid Heating, ISIJ Int., 2011, 51(6), p 958–964
N. Nakada, Y. Arakawa, K.-S. Park, T. Tsuchiyama, and S. Takaki, Dual Phase Structure Formed by Partial Reversion of Cold-Deformed Martensite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 553, p 128–133
M. Nouroozi, H. Mirzadeh, and M. Zamani, Effect of Microstructural Refinement and Intercritical Annealing Time on Mechanical Properties of High-Formability Dual Phase Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 736, p 22–26
Y. Mazaheri, A. Kermanpur, and A. Najafizadeh, A Novel Route for Development of Ultrahigh Strength Dual Phase Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 619, p 1–11
J. Zhang, H. Di, Y. Deng, and R.D.K. Misra, Effect of Martensite Morphology and Volume Fraction on Strain Hardening and Fracture Behavior of Martensite-Ferrite Dual Phase Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 627, p 230–240
C.C. Tasan, M. Diehl, D. Yan, M. Bechtold, F. Roters, L. Schemmann, C. Zheng, N. Peranio, D. Ponge, M. Koyama, K. Tsuzaki, and D. Raabe, An Overview of Dual-phase Steels: Advances in Microstructure-Oriented Processing and Micromechanically Guided Design, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2015, 45, p 391–491
W.J. Dan, Z.Q. Lin, S.H. Li, and W.G. Zhang, Study on the Mixture Strain Hardening of Multi-Phase Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 552, p 1–8
A. Ramazani, K. Mukherjee, U. Prahl, and W. Bleck, Transformation-Induced, Geometrically Necessary, Dislocation-Based Flow Curve Modeling of Dual-Phase Steels: Effect of Grain Size, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43, p 3850–3869
M. Calcagnotto, D. Ponge, E. Demir, and D. Raabe, Orientation Gradients and Geometrically Necessary Dislocations in Ultrafine Grained Dual-Phase Steels Studied by 2D and 3D EBSD, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 2738–2746
H. Mirzadeh, M. Alibeyki, and M. Najafi, Unraveling the Initial Microstructure Effects on Mechanical Properties and Work-Hardening Capacity of Dual-Phase Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, 48(10), p 4565–4573
A. Karmakar, M. Mandal, A. Mandal, M.B. Sk, S. Mukherjee, and D. Chakrabarti, Effect of Starting Microstructure on the Grain Refinement in Cold-Rolled Low-Carbon Steel During Annealing at Two Different Heating Rates, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 47(1), p 268–281
M. Zamani, H. Mirzadeh, and M. Maleki, Enhancement of Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Dual Phase Steel via Natural Aging, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 734, p 178–183
L.J. Chai, S.Y. Wang, H. Wu, Z. Yang, H. Pan, B. Song, and N. Guo, Bimodal Plate Structures Induced by Pulsed Laser in Duplex-Phase Zr Alloy, Sci. China Technol. Sci., 2017, 60, p 587–592
L. Chai, J. Xia, Y. Zhi, K. Chen, T. Wang, B. Song, and N. Guo, Strengthening or Weakening Texture Intensity of Zr Alloy by Modifying Cooling Rates From α + β Region, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2018, 213, p 414–421
J. Xia, L. Chai, H. Woo, Y. Zhi, Y.N. Guo, W.J. Huang, and N. Guo, EBSD Study of Microstructural and Textural Changes of Hot-Rolled Ti–6Al–4V Sheet After Annealing at 800 °C, Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.), 2018, 31, p 1215–1223
M. Hillert, K. Nilsson, and L.E. Torndahl, Effect of Alloying Elements on the Formation of Austenite and Dissolution of Cementite, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1971, 209, p 49–66
Y. Duan, Peeling Stress Model and Analysis of Single-L Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic/Polymer/Al Composite Component, Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2012, 201248, p 44
J.W. Cahn, The Kinetics of Grain Boundary Nucleated Reactions, Acta Met., 1956, 4, p 449–459
M. Enomoto, W.F. Lange, and H.I. Aaronson, The Kinetics of Ferrite Nucleation at Austenite Grain Edges in Fe-C and Fe-C-X alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1986, 17, p 1399–1407
J.R. Bradley, H.I. Aaronson, K.C. Russell, and W.C. Jonshson, Effects of Austenitizing Temperature on the Kinetics of the Proeutectoid Ferrite Reaction at Constant Austenite Grain Size in an Fe-C Alloy, Metall. Trans. A, 1977, 8, p 1955–1961
T.T. Huang, R.B. Gou, W.J. Dan, and W.G. Zhang, Strain-Hardening Behaviors of Dual Phase Steels with Microstructure Features, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 672, p 88–97
Y. Bergstrom, Y. Granbom, and D. Sterkenburg, A Dislocation-based Theory for the Deformation Hardening Behavior of DP Steels: Impact of Martensite Content and Ferrite Grain Size, J. Metall., 2010, 2010, p 1–16
Z.P. Xiong, A.G. Kostryzhev, N.E. Stanford, and E.V. Pereloma, Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dual Phase Steel Produced by Laboratory Simulated Strip Casting, Mater. Des., 2015, 88, p 537–549
G.R. Speich, V.A. Demarest, and R.L. Miller, Formation of Austenite during Intercritical Annealing of Dual-Phase Steels, Metall. Trans. A, 1981, 12A, p 1419–1428
A. Sharma, M.H. Roh, D.H. Jung, and J.P. Jung, Effect of ZrO2 Nanoparticles on the Microstructure of Al-Si-Cu Filler for Low-Temperature Al Brazing Applications, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, 47A, p 510–521
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Elsevier, Oxford, 2004
N. Peranio, Y.J. Li, F. Roters, and D. Raabe, Microstructure and Texture Evolution in Dual-Phase Steels: Competition between Recovery, Recrystallization, and Phase Transformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 4161–4168
W.F. Hosford, Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2005, p 128
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge their gratitude to Director, CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory, Jamshedpur, in support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, A.K., Patel, N.K., Ravi Kumar, B. et al. Strength–Ductility Trade-Off in Dual-Phase Steel Tailored via Controlled Phase Transformation. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 2783–2791 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04799-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04799-6