Abstract
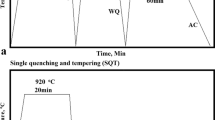
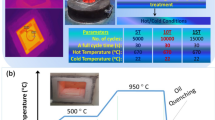
H13 steel is a typical hot work die steel with good strength and toughness that is often used to manufacture high-temperature disk springs. However, disk springs occasionally fail after use in the petrochemical industry. Therefore, the effects of the quenching and tempering temperatures on the microstructure and mechanical properties of H13 steel after quenching and tempering processes are investigated herein. The results show that the lath width (lath) controls the strength of the H13 steel. The precipitated phases mainly comprise Cr23C6, Cr7C3 and VC. The coarsening of the Cr23C6 phase reduces the hardness, while reducing the dislocation density improves the toughness of the H13 steels after quenching and tempering. When the quenching temperature is 1040 °C and the tempering temperature is 570 °C, the H13 steel after quenching and tempering has a uniform microstructure with good strength and toughness.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.A. Dobrzanski, J. Mazurkiewicz, E. Hajduczek, and J. Madejski, Comparison of the Thermal Fatigue Resistance and Structure of the 47CrMoWVTiCeZr16-26-8 Hot-Work Tool Steel with X40CrMoV5-1 Type One, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, 113(1–3), p 527–538
A. Persson, S. Hogmark, and J. Bergstrom, Simulation and Evaluation of Thermal Fatigue Cracking of Hot Work Tool Steels, Int. J. Fatigue, 2004, 26(10), p 1095–1107
A. Persson, S. Hogmark, and J. Bergstrom, Failure Modes in Field-Tested Brass Die Casting Dies, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, 148(1), p 108–118
Y.F. Wang, Z.C. Liu, and W.B. Fan, The Band Structure of H13 Steel and Its Elimination Method, Shanghai Met., 2005, 06, p 43–45
H. Jimenez, D.M. Devia, V. Benavides, A. Devia, Y.C. Arango, and P.J. Arando, Thermal Protection of H13 Steel by Growth of (TiAl)N Films by PAPVD Pulsed arc Technique, Mater Charact., 2008, 59, p 1070–1077
Q. Tong, X.C. Wu, and N. Min, Research on Hot-Working Die Steel SDH3 with High Hot Strength, J. Iron Steel, 2010, 22, p 50–54
S. Li, X.C. Wu, X.X. Li, J.W. Li, and X.J. He, Wear Characteristics of Mo-W-Type Hot-Work Steel at High Temperature, Tribol. Lett., 2016, 64(32), p 1–12
S. Li, X.C. Wu, S.H. Chen, and J.W. Li, Wear Resistance of H13 and a New Hot-Work Die Steel at High Temperature, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 2993–3006
X.H. Pan and Z.C. Zhou, The Study of the Chemical Composition and Improvement and Development for the H13 Hot Work Die & Mold Steel, Mold Manuf., 2006, 4, p 78–85.
P.S. Babu, Effects of Cryogenic Treatment on H13 Tool Steel–An Experimental Investigation, Int. J. Metall. Mater., 2013, 3, p 53–58
C. Xie, X. Wu, N. Min, and Y. Shen, Carbon Segregation Behavior of High Carbon High-Alloy Steel During Deep Cryogenic Treatment Using 3DAP, Acta Metall. Sin., 2015, 15, p 325–332
M. Pérez and F.J. Belzunce, The Effect of Deep Cryogenic Treatments on the Mechanical Properties of an AISI, H13 Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 624, p 32–40
G.H. Yan, X.M. Huang, Y.Q. Wang et al., Effects of Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of H13 Steel, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2010, 52, p 393–395
J. Li, J. Li, L.L. Wang, and L.F. Li, Study on Carbide in Forged and Annealed H13 Hot Work Die Steel, High Temp. Mater. Proc., 2015, 34, p 593–598
L.A. Norstrom and N. Ohrberg, Development of Hot-Work Tool Steel for High-Temperature Applications, Met. Technol., 1981, 8, p 22–26
S.J. Fu, Influence of Quenching Temperature on Microstructure and Properties of 25MnV Steel, Therm. Process., 2010, 39(20), p 156–157
Y.R. Liu, D. Ye, Q.L. Yong, J. Su, K.Y. Zhao, and W. Jiang, Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Property of Cr13 Super Martensitic Stainless Steel, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2011, 18(11), p 60–66
D.W. Smith and R.F. Hehemann, Influence of Structural Parameters on the Yield Strength of Tempered Martensite and Lower Bainite, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1971, 209(5), p 478–481
H.H. Liu, P.X. Fu, H.W. Liu, C. Sun, X.P. Ma, and D.Z. Li, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties in 718H Pre-hardened Mold Steel During Tempering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 709, p 181–192
P. Yan, Z. Liu, H. Bao, Y.Q. Weng, and W. Liu, Effect of Tempering Temperature on the Toughness of 9Cr-3W-3Co Martensitic Heat Resistant Steel, Mater. Des., 2014, 54, p 874–879
T. Maki, K. Tsuzaki, and I. Tamura, The Morphology of Microstructure Composed of Lath Martensites in steels, Trans ISIJ, 1980, 20(4), p 207–214
J.M. Marder and A.R. Marder, The Morphology of Iron–Nickel Massive Martensite, Trans. Am. Soc. Met., 1969, 62(1), p 1–10
C.F. Wang, Study on Strength and Toughness Structure Control Unit of Low Alloy Martensitic Steel, Central Iron & Steel Research Institute, Beijing, 2008
S.J. Chen and Q. Yu, The Role of Angle Boundary in Deformation of Titanium and Its Size Effect, Scr. Mater., 2019, 163, p 148–151
Q.L. Yong, The Second Phase of the Steel Materials, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2006
D.L. Ye and J.H. Hu, Practical Inorganic Thermodynamic Data Manual, 2nd ed., Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 2002
N. Mebarki, D. Delagnesa, P. Lamesle et al., Relationship Between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a 5% Cr Tempered Martensitic Tool Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, 387–389, p 171–175
D. Delagnes, P. Lamesle, M.H. Mathon et al., Influence of Silicon Content on the Precipitation of Secondary Carbides and Fatigue Properties of a 5% Cr Tempered Martensitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 394, p 435–444
X.B. Hu, L. Li, X.C. Wu, and M. Zhang, Coarsening Behavior of M23C6 Carbides After Ageing or Thermal Fatigue in AISI, H13 Steel With Niobium, Int. J. Fatigue, 2006, 28, p 175–182
Q. Ma, B.C. Liu, and Z.C. Wang, Breakup of Eutectic Carbide Network of White Cast Irons at High Temperatures, J. Mater. Sci., 1995, 311, p 3383–3386
W.Y. Zhang, Ostwald Growth of Spheroidal Carbide During Isothermal Spheroidization, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1993, 1(4), p 44–48
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11772147), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (Grant No. 18KJB460016) and the Introduce Talent Special Funding for Scientific Research at Nanjing Tech University (Grant No. 39802124).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Xu, Z. & Lu, X. Effect of the Quenching and Tempering Temperatures on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of H13 Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 1849–1859 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04686-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04686-0