Abstract
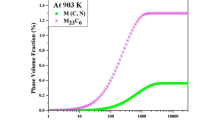
In this study, the effect of microstructure evolution, especially that involving the proeutectoid carbides, on hardness distribution of ledeburite steel containing 8% chromium content was investigated at different cooling rates after hot deformation. The continuous cooling transformation was carried out using a fully automatic transformation measuring apparatus under cooling rates in the range of 0.03-80 °C/s. The transformation temperatures, Ac1, Ac3 and Ms, were measured by dilatometry. A nanoindentation test was employed to evaluate the mechanical properties of the cooled specimens. The evolution of microstructure indicated that the proportion trend of the precipitated carbides was dependent on the cooling rates. In addition, a mixture of pearlite and proeutectoid carbides was observed under slow cooling rates in the range of 0.03-0.2 °C/s, for which only a martensite transformation took place in austenite, and the proeutectoid carbides precipitated negligibly at cooling rates greater than or equal to 10 °C/s. The results also showed that the nanohardness significantly decreased and then slowly increased to a stable value with increasing cooling rates, which was similar to the content trend of the carbides that precipitated during the cooling process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.X. Wei, S.Q. Wang, L. Wang et al., Selection of Heat Treatment Process and Wear Mechanism of High Wear Resistant Cast Hot-Forging Die Steel, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2012, 19(5), p 50–57
D. Toboła, W. Brostow, K. Czechowski et al., Improvement of Wear Resistance of Some Cold Working Tool Steels, Wear, 2017, 382–383, p 29–39
S. Huth, N. Krasokha, and W. Theisen, Development of Wear and Corrosion Resistant Cold-Work Tool Steels Produced by Diffusion Alloying, Wear, 2009, 267(1), p 449–457
O. Hentschel, C. Scheitler, A. Fedorov et al., Experimental Investigations of Processing the High Carbon Cold-Work Tool Steel 1.2358 by Laser Metal Deposition for the Additive Manufacturing of Cold Forging Tools, J. Laser Appl., 2017, 29(2), p 022307
G. Ramesh, R. Rahul, M. Pradeep et al., Evolution of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of D2 Tool Steel during Annealing Heat Treatment, Mater. Today, 2018, 5, p 2733–2737
P. Schaaf, A. Kraemer, S. Wiesen et al., Mössbauer Study of Iron Carbides: Mixed Carbides M7C3 and M23C6, Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, 42(9), p 3077–3081
D.W. Hetzner, Refining Carbide Size Distributions in M1 High Speed Steel by Processing and Alloying, Mater. Charact., 2001, 46(2), p 175–182
T. Večko Pirtovšek, G. Kugler, M. Godec et al., Microstructural Characterization during the Hot Deformation of 1.17C-11.3Cr-1.48 V-2.24 W-1.35Mo Ledeburitic Tool Steel, Mater. Charact., 2011, 62(2), p 189–197
S. Kheirandish, Effect of Ti and Nb on the Formation of Carbides and the Mechanical Properties in As-cast AISI-M7 High-speed Steel, Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 2007, 41(3), p 187–195
S. Kheirandish and A. Noorian, Effect of Niobium on Microstructure of Cast AISI, H13 Hot Work Tool Steel, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2008, 15(4), p 61–66
R.A. Mesquita and C.A. Schuh, Tool Steel Coatings Based on Niobium Carbide and Carbonitride Compounds, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2012, 207(207), p 472–479
F. Meurling, A. Melander, M. Tidesten et al., Influence of Carbide and Inclusion Contents on the Fatigue Properties of High Speed Steels and Tool Steels, Int. J. Fatigue, 2001, 23(3), p 215–224
K. Wieczerzak, P. Bala, R. Dziurka et al., The Effect of Temperature on the Evolution of Eutectic Carbides and M7C3 → M23C6 Carbides Reaction in the Rapidly Solidified Fe-Cr-C Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 698, p 673–684
K. Wieczerzak, P. Bala, M. Stepien et al., Formation of Eutectic Carbides in Fe-Cr-Mo-C Alloy during Non-Equilibrium Crystallization, Mater. Des., 2016, 94, p 61–68
Y. Yang, Y.R. Chen, K. Sridharan et al., Evolution of Carbide Precipitates in 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel during Long-Term Service in a Power Plant, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, 41(6), p 1441–1447
M.R. Ghomashchi and C.M. Sellars, Microstructural Changes in As-cast M2 Grade High Speed Steel during Hot Forging, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1993, 24a, p 10
M. Momeni, S. Kheirandish, H. Saghafian et al., Effects of Heat Treatment on Mechanical Properties of Modified Cast AISI, D3 Tool Steel, Mater. Des., 2014, 54(2), p 742–747
T. Večko Pirtovšek, G. Kugler, and M. Terčelj, The Behaviour of the Carbides of Ledeburitic AISI, D2 Tool Steel during Multiple Hot Deformation Cycles, Mater. Charact., 2013, 83(3), p 97–108
S. Salunkhe, D. Fabijanic, J. Nayak et al., Effect of Single and Double Austenitization Treatments on the Microstructure and Hardness of AISI, D2 Tool Steel, Mater. Today Proc., 2015, 2(4–5), p 1901–1906
S. Pitois, G. Millot, and S. Wabnitz, Phase Transformation under Continuous Cooling Conditions in Medium Carbon Microalloyed Steels, J. Mater. Sci. Tech., 2014, 30(5), p 511–516
Z.Q. Li, Z. Wen, F.Y. Su et al., Modeling Research on Pearlite-to-Austenite Transformation in Hypereutectoid Steel Containing Cr, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 727, p 1050–1056
G. Miyamoto, Y. Karube, and T. Furuhara, Formation of Grain Boundary Ferrite in Eutectoid and Hypereutectoid Pearlitic Steels, Acta Mater., 2016, 103, p 370–381
R.C. Chen, Z.Z. Zheng, N. Li et al., In-situ Investigation of Phase Transformation Behaviors of 300 M Steel in Continuous Cooling Process, Mater. Charact., 2018, 144, p 400–410
H. Kim, J.Y. Kang, D. Son et al., Evolution of Carbides in Cold-Work Tool Steels, Mater. Charact., 2015, 107, p 376–385
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7(6), p 1564–1583
K.S. Ming, X.F. Bi, and J. Wang, Precipitation Strengthening of Ductile Cr15Fe20Co35Ni20Mo10 Alloys, Scripta Mater., 2017, 137, p 88–93
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Key Research Project of China (2016YFB0300402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, S., Li, C., Han, Y. et al. Evolution of the Microstructure and Hardness of Fe-8Cr-2.1Mo-Si-V Die Steel at Different Cooling Rates after Hot Deformation. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 4522–4530 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04210-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04210-z