Abstract
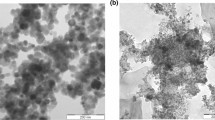
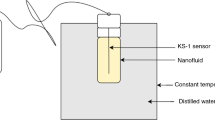
In the present work, the practicability of Fe2O3 nanofluids for heat transfer applications has been examined. Nanofluids performance, in terms of modulation of thermal conductivity, has been investigated with increasing concentration of Fe2O3 nanoparticles in water and ethylene glycol base fluids at 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 and 70 °C. Fe2O3 nanoparticles have been synthesized using the wet chemical method and characterized using TEM, SEM, XRD and UV–Vis. The characterization results revealed a face-centered cubic structure having alpha phase and particle size in the range of 40-55 nm for the synthesized Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Thermal conductivity measurement results show increases in thermal conductivity with the increase in concentration and temperature of nanofluids. 16.45 and 19.76% enhancement in thermal conductivity have been observed for Fe2O3–water and Fe2O3–ethylene glycol nanofluids of 2 vol.% at 70 °C compared to water and ethylene glycol base fluids at 10 °C, respectively. Results of the ANN approach are in good agreement with experimental results, and H–C model gives better predictions compared to other standard models. The study gives clear insights into improved heat transfer performance by material engineering.












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
23 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06145-w
References
T.K. Hong, H.S. Yang, and C.J. Choi, Study of the Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Fe Nanofluids, J. Appl. Phys., 2005, 97(6), p 1–4
K. Hong, T.K. Hong, and H.S. Yang, Thermal Conductivity of Fe Nanofluids Depending on the Cluster Size of Nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 88(3), p 31901
H.E. Patel, S.K. Das, T. Sundararagan, A.S. Nair, B. Geoge, and T. Pradeep, Thermal Conductivities of Naked and Monolayer Protected Metal Nanoparticles Based Nanofluids: Manifestation of Anomalous Enhancement and Chemical Effects, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 83, p 2931–2933
J.A. Eastman, S.U.S. Choi, S. Li, W. Yu, and L.J. Thompson, Anomalously Increased Effective Thermal Conductivities of Ethylene Glycol-Based Nanofluids Containing Copper Nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 78(6), p 718–720
X. Wang, X. Xu, and S.U.S. Choi, Thermal Conductivity of Nanoparticle-Fluid Mixture, J. Thermophys. Heat Transf., 1999, 13(4), p 474–480
H. Masuda, A. Ebata, K. Teramae, and N. Hishinuma, Alteration of Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Liquid by Dispersing Ultra-Fine Particles (Dispersion of 7-Al2O3, SiO2, and TiO2 Ultra-Fine Particles), Netsu Bus-Sei (Japan), 1993, 7(4), p 227–233
S. Lee, S.U.S. Choi, S. Li, and J.A. Eastman, Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles, J. Heat Transf., 1999, 121, p 280–289
S.M.S. Murshed, K.C. Leong, and C. Yang, Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of TiO2—Water Based Nanofluids, Int. J. Therm. Sci., 2005, 44(4), p 367–373
S. Iijima, Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon, Nature, 1991, 354(6348), p 56–57
M.S. Liu, M. Ching, L. Cheng, I.T. Huang, and C.C. Wang, Enhancement of Thermal Conductivity with Carbon Nanotube for Nanofluids, Int. Commun. Heat Mass, 2005, 32(9), p 1202–1210
J.C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, 3rd ed, Vol 435, Claredon Press, Oxford, 1904
W. Yu and S.U.S. Choi, The Role of Interfacial Layers in the Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluids, a Renovated Maxwell Model, J. Nanopart. Res., 2003, 5, p 167–171
D.A.G. Bruggeman, Berechnung Verschiedener Physikalischer Konstanten von Heterogenen Substanzen I. Dielektrizitatskonstanten and Leitfanigkeitender Mischkorper aus isotropen Substanzen, Ann. Phys., 1935, 24, p 636–679
R.L. Hamilton and O.K. Crosser, Thermal Conductivity of Heterogeneous Two Component Systems, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 1962, 1(3), p 187–191
K. Verma, S. Kumar, A. Upadhyay, and R. Singh, Prediction of Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluids Containing Metal Oxide Nanoparticles, Adv. Sci. Eng. Med., 2015, 7, p 378–384
Y. Xuan, Q. Li, and W. Hu, Aggregation Structure and Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluids, AIChE J., 2003, 49, p 1038–1043
J. Koo and C. Kleinstreuer, A New Thermal Conductivity Model for Nanofluids, J. Nanopart. Res., 2004, 6, p 577–588
K. Verma, M. Dabas, A. Upadhyay, and R. Singh, Effective Thermal Conductivity of Lithium Multipurpose Grease Filled with Metal Particles, J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 2014, 33(19), p 1794–1801
H. Kurt and M. Kayfeci, Prediction of Thermal Conductivity of Ethylene Glycol-Water Solutions by Using Artificial Neural Networks, Appl. Energy, 2006, 86, p 2244–2248
J.Z. Liang and G.S. Liu, A New Heat Transfer Model of Inorganic Particulate-Filled Polymer Composites, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44, p 4715–4720
R. Agarwal, K. Verma, N.K. Agrawal, R.K. Duchaniya, and R. Singh, Synthesis, Characterization, Thermal Conductivity and Sensitivity of CuO Nanofluids, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2016, 102, p 1024–1036
G. Huminic, A. Huminic, F. Dumitrache, C. Fleaca, and I. Morjan, Experimental Study of Thermo-Physical Properties of Nanofluids Based on γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles for Heat Transfer Applications, Heat Transfer Eng., 2017, 38(17), p 1496–1505
R. Agarwal, K. Verma, N.K. Agrawal, and R. Singh, Sensitivity of Thermal Conductivity for Al2O3 Nanofluids, Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci., 2017, 80(1), p 19–26
S.Z. Guo, Y. Li, J.S. Jiang, and H.Q. Xie, Nanofluids Containing γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles and Their Heat Transfer Enhancements, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2010, 5(7), p 1222
E. Ahmadloo and S. Azizi, Prediction of Thermal Conductivity of Various Nanofluids Using Artificial Neural Network, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 2016, 74(1), p 69–75
L. Motte, What are the Current Advances Regarding Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Nanomedicine?, J. Bioanal. Biomed., 2012, 4(6), p 1–2
C. Montferrand, Y. Lalatonne, D. Bonnin, L. Motte, and P. Monod, Non Linear Magnetic Behavior Around Zero Field of an Assembly of Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles, Analyst, 2012, 137(1), p 2304–2308
W. Yu and S.U.S. Choi, The Role of Interfacial Layers in the Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Nanofluids: A Renovated Maxwell Model, J. Nanopart. Res., 2003, 5(1), p 167–171
C.J. Yu, A.G. Richter, A. Datta, M.K. Durbin, and P. Dutta, Molecular Layering in a Liquid on a Solid Substrate: An X-ray Reflectivity Study, Phys. B, 2000, 283(1), p 27–31
N. Kumar and S.S. Sonawane, Experimental Study of Fe2O3/Water and Fe2O3/Ethylene Glycol Nanofluid Heat Transfer Enhancement in a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger, Int. Commun. Heat Mass, 2016, 78(1), p 277–284
N. Zouli, I.A. Said, and M. Al-Dahhan, Enhancement of Thermal Conductivity and Local Heat Transfer Coefficients Using Fe2O3/Water Nanofluid for Improved Thermal Desalination Processes, J. Nanofluids, 2019, 8(5), p 1103–1122
S.Z. Guo, Y. Li, J.S. Jiang, and H.Q. Xie, Nanofluids Containing γ-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles and Their Heat Transfer Enhancements, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2010, 5(1), p 1222–1227
L. Colla, L. Fedele, M. Scattolini, and S. Bobbo, Water-Based Fe2O3 Nanofluid Characterization: Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity Measurements and Correlation, Adv. Mech. Eng., 2012, 4(1), p 1–8
G. Huminic, A. Huminic, F. Dumitrache, C. Fleaca, and I. Morjan, Experimental Study of Thermo-Physical Properties of Nanofluids Based on γ- Fe2O3 Nanoparticles for Heat Transfer Applications, Heat Transf. Eng., 2017, 38(17), p 1496–1505
I. Nurdin, M.R. Johan, and B.C. Ang, Experimental Investigation on Thermal Conductivity and Viscosity of Maghemite (γ–Fe2O3) Water-based Nanofluids, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2018, 334(1), p 1–7
Acknowledgments
Research Associateship by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) to Ravi Agarwal and Senior Research Fellowship by University Grant Commission (conducted by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research) to Kamalesh Verma are gratefully acknowledged. Authors are also thankful to the UR-DBT-IPLS (BUILDER) of Centre for Converging Technologies, University of Rajasthan, for allowing using their facilities. KD2 Thermal Properties Analyzer provided by Dr. R. K. Duchaniya (Department of Metallurgical and Material Engineering, Malaviya National Institute of Technology (MNIT), Jaipur, Rajasthan) is also gratefully acknowledged. We thank Keiron O’Shea from Aberystwyth University, UK, for improving the language of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, R., Verma, K., Agrawal, N.K. et al. Comparison of Experimental Measurements of Thermal Conductivity of Fe2O3 Nanofluids Against Standard Theoretical Models and Artificial Neural Network Approach. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 4602–4609 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04202-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04202-z