Abstract
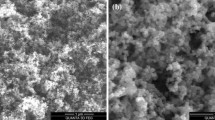
In this study, WC-Al2O3 ceramic composite was incorporated into Al5083 to produce a surface composite by friction stir processing (FSP), and the microstructure, hardness and wear properties of Al5083-WC-Al2O3 surface composite were evaluated. Optical microscopy of FSPed samples showed grain refinement in the stir zone. The addition of WC-Al2O3 particles as well as increase in FSP pass number had a considerable effect on grain refinement, and the grain size of Al5083 base metal of 36 µm reduced to 11 µm for Al5083-WC-Al2O3 surface composite after four passes. The SEM observation of the surface composite revealed that the WC-Al2O3 particles distributed homogenously in the matrix and by increasing the FSP passes, the initial agglomerates of mechanochemically synthesized WC-Al2O3 powders could be fractured. Microhardness evaluation showed a substantial improvement by adding WC-Al2O3 particles and increase in FSP pass number. The maximum microhardness value of 101 HV belonged to surface composite after four passes, while the microhardness of the base metal was 65 HV. Wear test results revealed enhanced tribological behavior with a similar trend of microhardness values. Scanning electron microscopy tests revealed both adhesive and abrasive wear mechanisms on the surface of the wear test specimens.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Polmear, D.S. John, J.F. Nie, and M. Qian, Light Alloys: Metallurgy of the Light Metals, 5th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Chennai, 2017
F.C. Campbell, Manufacturing Technology for Aerospace Structural Materials, Manuf. Technol. Aerosp. Struct. Mater., 2006, https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-185617495-4/50002-0
M. Akbari, M.H. Shojaeefard, P. Asadi, and A. Khalkhali, Wear and Mechanical Properties of Surface Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites on Al-Si Aluminum Alloys Fabricated by Friction Stir Processing, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl., 2017, 233, p 790–799. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420717702413
M. Tavoosi, S. Arjmand, and B. Adelimoghaddam, Surface Alloying of Commercially Pure Titanium with Aluminium and Nitrogen Using GTAW Processing, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 311, p 314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.12.115
M. Tavoosi and S. Arjmand, In Situ Formation of Al/Al3Ti Composite Coating on Pure Ti Surface by TIG Surfacing Process, Surf. Interfaces, 2017, 8, p 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2017.04.002
F. Ghadami, M. Heydarzadeh Sohi, and S. Ghadami, Effect of TIG Surface Melting on Structure and Wear Properties of Air Plasma-Sprayed WC-Co Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 261, p 108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.11.050
V. Kishan, A. Devaraju, and K.P. Lakshmi, Tribological Properties of Nano TiB2 Particle Reinforced 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy Surface Composites via Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5(1, Part 1), p 1615–1619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.254
K.A. Habib, J.J. Saura, C. Ferrer, M.S. Damra, E. Giménez, and L. Cabedo, Comparison of Flame Sprayed Al2O3/TiO2 Coatings: Their Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Tribology Behavior, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 201(3-4), p 1436–1443
D. Chaliampalias, S. Andronis, N. Pliatsikas, E. Pavlidou, D. Tsipas, S. Skolianos, K. Chrissafis, G. Stergioudis, P. Patsalas, and G. Vourlias, Formation and Oxidation Resistance of Al/Ni Coatings on Low Carbon Steel by Flame Spray, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 255, p 62–68
N. Kahraman and B. Gülenç, Abrasive Wear Behaviour of Powder Flame Sprayed Coatings on Steel Substrates, Mater. Des., 2002, 23(8), p 721–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-3069(02)00075-4
A. Kurt, I. Uygur, and E. Cete, Surface Modification of Aluminium by Friction Stir Processing, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, 211(3), p 313–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.09.020
H.S. Arora, H. Singh, and B.K. Dhindaw, Composite Fabrication Using Friction Stir Processing—A Review, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2012, 61(9–12), p 1043–1055
R.S. Mishra and Z.Y. Ma, Friction Stir Welding and Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep., 2005, 50, p 1–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2005.07.001
V.K.S. Jain, P.M. Muhammed, S. Muthukumaran, and S.P.K. Babu, Microstructure, Mechanical and Sliding Wear Behavior of AA5083-B4C/SiC/TiC Surface Composites Fabricated Using Friction Stir Processing, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2018, 71(6), p 1519–1529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1287-y
N. Yuvaraj and S. Aravindan, Wear Characteristics of Al5083 Surface Hybrid Nano-Composites by Friction Stir Processing, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2017, 70(4), p 1111–1129
D. Yadav and R. Bauri, Friction Stir Processing of Al-TiB2 In Situ Composite: Effect on Particle Distribution, Microstructure and Properties, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(3), p 1116–1124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1404-6
H.C. Madhu, P. Ajay Kumar, C.S. Perugu, and S.V. Kailas, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Process Derived Al-TiO2 Nanocomposite, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3188-y
G.K. Padhy, C.S. Wu, and S. Gao, Friction Stir Based Welding and Processing Technologies-Processes, Parameters, Microstructures and Applications: A Review, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34, p 1–38
F. Humphreys and M. Matherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed., Elsevier, New York, 1995, p 173–178
F.J. Humphreys, P.B. Prangnell, and R. Priestner, Fine-Grained Alloys by Thermomechanical Processing, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2001, 5(1), p 15–21
S. Swaminathan, K. Oh-Ishi, A.P. Zhilyaev, C.B. Fuller, B. London, M.W. Mahoney, and T.R. McNelley, Peak Stir Zone Temperatures during Friction Stir Processing, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 2010, 41(3), p 631–640
S. Ahmadifard, S. Kazemi, and A. Heidarpour, Production and Characterization of A5083-Al2O3-TiO2 Hybrid Surface Nanocomposite by Friction Stir Processing, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl., 2018, 232(4), p 287–293. https://doi.org/10.1177/1464420715623977
N. Yuvaraj and S. Aravindan, Fabrication of Al5083/B4C Surface Composite by Friction Stir Processing and Its Tribological Characterization, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2015, 4(4), p 398–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2015.02.006
Y. Mazaheri, F. Karimzadeh, and M.H. Enayati, Tribological Behavior of A356/Al2O3 Surface Nanocomposite Prepared by Friction Stir Processing, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, 45(4), p 2250–2259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-2140-x
S. Shahraki, S. Khorasani, R. Abdi Behnagh, Y. Fotouhi, and H. Bisadi, Producing of AA5083/ZrO2 Nanocomposite by Friction Stir Processing (FSP), Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, 44(6), p 1546–1553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9914-9
S.A. Hosseini, K. Ranjbar, R. Dehmolaei, and A.R. Amirani, Fabrication of Al5083 Surface Composites Reinforced by CNTs and Cerium Oxide Nano Particles via Friction Stir Processing, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 622, p 725–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.158
M. Amra, K. Ranjbar, and R. Dehmolaei, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of CeO2 and SiC Incorporated Al5083 Alloy Surface Composites, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(8), p 3169–3179
C.N. Shyam Kumar, R. Bauri, and D. Yadav, Wear Properties of 5083 Al-W Surface Composite Fabricated by Friction Stir Processing, Tribol. Int., 2016, 101, p 284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.04.033
R. Bauri, D. Yadav, C.N. Shyam Kumar, and B. Balaji, Tungsten Particle Reinforced Al 5083 Composite with High Strength and Ductility, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 620, p 67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.09.108
R. Bauri, G.D. Janaki Ram, D. Yadav, and C.N. Shyam Kumar, Effect of Process Parameters and Tool Geometry on Fabrication of Ni Particles Reinforced 5083 Al Composite by Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Today Proc., 2015, 2(4-5), p 3203–3211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.115
H.I. Kurt, Influence of Hybrid Ratio and Friction Stir Processing Parameters on Ultimate Tensile Strength of 5083 Aluminum Matrix Hybrid Composites, Compos. Part B Eng., 2016, 93, p 26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.02.056
A. Heidarpour, S. Ahmadifard, and S. Kazemi, On the Al5083-Al2O3-TiO2 Hybrid Surface Nanocomposite Produced by Friction Stir Processing, Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf., 2018, 54(3), p 409–415. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205118030279
A. Heidarpour, N. Shahin, and S. Kazemi, A Novel Approach to in Situ Synthesis of WC-Al2O3 Composite by High Energy Reactive Milling, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2017, 64, p 1–6
T.R. McNelley, Friction Stir Processing (FSP): Refining Microstructures and Improving Properties, Rev. Metal., 2010, 46, p 149–156. https://doi.org/10.3989/revmetalmadrid.19XIIPMS
R. Abdi Behnagh, M.K. Besharati Givi, and M. Akbari, Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Resistance, and Microstructural Changes during Friction Stir Processing of 5083 Aluminum Rolled Plates, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2012, 27(6), p 636–640
Y. Chen, H. Ding, J. Li, Z. Cai, J. Zhao, and W. Yang, Influence of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-5083 Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 650, p 281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.10.057
J.F. Guo, J. Liu, C.N. Sun, S. Maleksaeedi, G. Bi, M.J. Tan, and J. Wei, Effects of Nano-Al2O3 Particle Addition on Grain Structure Evolution and Mechanical Behaviour of Friction-Stir-Processed Al, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 602, p 143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.02.022
I.S. Lee, C.J. Hsu, C.F. Chen, N.J. Ho, and P.W. Kao, Particle-Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites Produced from Powder Mixtures via Friction Stir Processing, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2011, 71(5), p 693–698
R. Yang, Z. Zhang, Y. Zhao, G. Chen, Y. Guo, M. Liu, and J. Zhang, Effect of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processing on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al3Ti/A356 Composites, Mater. Charact., 2015, 106, p 62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2015.05.019
K.-M. Lee, D.-K. Oh, W.-S. Choi, T. Weissgärber, and B. Kieback, Thermomechanical Properties of AlN-Cu Composite Materials Prepared by Solid State Processing, J. Alloys Compd., 2007, 434-435, p 375–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.08.176
S. Rathee, S. Maheshwari, and A.N. Siddiquee, Issues and Strategies in Composite Fabrication via Friction Stir Processing: A Review, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2018, 33, p 239–261
R.S. Mishra, Z.Y. Ma, and I. Charit, Friction Stir Processing: A Novel Technique for Fabrication of Surface Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 341(5), p 307–310
N. Yuvaraj and S. Aravindan, Comparison Studies on Mechanical and Wear Behavior of Fabricated Aluminum Surface Nano Composites by Fusion and Solid State Processing, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 309, p 309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2016.11.076
T.S. Mahmoud, O.M. Shaban, H.M. Zakaria, and T.A. Khalifa, On Effect of FSP on Microstructural and Mechanical Characteristics of A390 Hypereutectic Al-Si Alloy, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(9), p 1120–1124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heidarpour, A. Fabrication and Characterization of A5083-WC-Al2O3 Surface Composite by Friction Stir Processing. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 2747–2753 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04093-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04093-0