Abstract
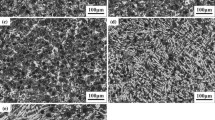
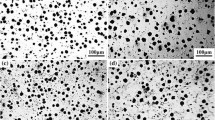
In this paper, we investigated the effect of titanium modification on microstructures and properties of carbidic austempered ductile iron (CADI) containing 3.72 wt.% C, 2.77 wt.% Si, and 0.51 wt.% Mn. The results showed that with the addition of 0.1 wt.% Ti, TiC particles were formed, and distributed in carbides and matrix. Microstructural observation indicated that the maximum diameter of graphite nodules decreased from 58 to 40 μm, and the shape of carbides transformed from network to fragmentation, which was related to the nucleation of the eutectic structure (γ + (Fe, Cr)3C) where TiC particles act as the nucleus. After isothermal quenching at 300 °C, the hardness of Ti-bearing CADI was 3.5 HRC higher than ordinary CADI, and the impact toughness was increased by 14.3%. Additionally, due to the decrease in exfoliation, the wear loss of Ti-bearing CADI was 14.8% lower than ordinary CADI during the block-on-ring wear test at the surface load of 300 N.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Laino, J.A. Sikora, and R.C. Dommarco, Development of Wear Resistant Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron (CADI), Wear, 2008, 265, p 1–7
M. Lagarde, A. Basso, J.A. Sikora, and R.C. Dommarco, Development and Characterization of a New Type of Ductile Iron with a Novel Multiphase Microstructure, ISIJ Int., 2011, 51, p 645–650
S. Laino, J.A. Sikora, and R.C. Dommarco, Wear Behavior of CADI, Operating Under Different Tribosystems, ISIJ Int., 2010, 50, p 418–424
H.Q. Cheng, H.G. Fu, J. Lin, and Y. Lei, Effect of Cr Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron, Materialprufung, 2018, 60, p 31–39
K. Muhammad Yusof, B. Abdullah, M.F. Idham, and N.H. Saad, The Effects on Microstructure and Hardness of 0.28% Vanadium and 0.87% Nickel Alloyed Ductile Iron After Boronizing Process, Key Eng. Mater., 2017, 740, p 65–69
A. Refaey and N. Fatahalla, Effect of Microstructure on Properties of ADI, and Low Alloyed Ductile Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 2003, 38, p 351–362
C.F. Han, Y.F. Sun, Y. Wu, and Y.H. Ma, Effects of Vanadium and Austempering Temperature on Microstructure and Properties of CADI, Metall. Mater. Trans., 2015, 4, p 135–145
A.S.O. Pimentel and W.L. Guesser, Tratamento térmico de austêmpera em ferro fundido nodular com adições de nióbio e de cromo, Matéria, 2017, 2, p 22–28
C.F. Han, Q.Q. Wang, Y.F. Sun, and J. Li, Effects of Molybdenum on the Wear Resistance and Corrosion Resistance of Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron, Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal., 2015, 4, p 298–304
S. Laino, J. Sikora, and R.C. Dommarco, Advances in the Development of Carbidic ADI, Key Eng. Mater., 2011, 457, p 187–192
X. Sun, Y. Wang, D.Y. Li, C. Wang, X. Li, and Z.W. Zou, Solid Particle Erosion Behavior of Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron Modified by Nanoscale Ceria Particles, Mater. Des., 2014, 10, p 367–374
X. Sun, Y. Wang, D.Y. Li, and G. Wang, Modification of Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron with Nano Ceria for Improved Mechanical Properties and Abrasive Wear Resistance, Wear, 2013, 301, p 116–121
X.H. Zhi, J.Z. Liu, J.D. Xing, and S.Q. Ma, Effect of Cerium Modification on Microstructure and Properties of Hypereutectic High Chromium Cast Iron, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 603, p 98–103
J.T. Duan, Z.Q. Jiang, and H.G. Fu, Effect of RE-Mg Complex Modifier on Structure and Performance of High-Speed Steel Roll, J. Rare Earths, 2007, 25, p 259–263
C. Wang, H. Hsu, and Q. Ma, Formation of Spheroidal Carbide in Vanadium White Cast Iron by Rare Earth Modification, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1990, 6, p 905–910
K.S. Cho, I.K. Sang, S.S. Park, W.S. Choi, H.K. Moon, and H. Kwon, Effect of Ti Addition on Carbide Modification and the Microscopic Simulation of Impact Toughness in High-Carbon Cr-V tool steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, 47, p 1–7
E.J. Shin, B.S. Seong, Y.S. Han, K.P. Hong, C.H. Lee, and H.-J. Kang, Effect of Precipitate Size and Dispersion on Recrystallization Behavior in Ti-Added Ultra Low Carbon Steels, J. Appl. Cryst., 2010, 36, p 624–628
A.S. Chaus, F.I. Rudnickii, M. Boháčik, and P. Úradník, Special Features of Microstructure of W-Mo High-Speed Steel Modified with Titanium Diboride, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2011, 52, p 575–580
R.J. Chung, X. Tang, D.Y. Li, B. Hinckley, and K. Dolman, Effects of Titanium Addition on Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Hypereutectic High Chromium Cast Iron Fe-25wt.%Cr-4wt.%C, Wear, 2009, 267, p 356–361
H. Ding, S. Liu, H. Zhang, and J. Guo, Improving Impact Toughness of a High Chromium Cast Iron Regarding Joint Additive of Nitrogen and Titanium, Mater. Des., 2016, 90, p 958–968
Y.C. Peng, H.J. Jin, J.H. Liu, and G.L. Li, Influence of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure and Properties of a New Wear Resistant Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron, Mater. Charact., 2012, 72, p 53–58
W. Brandon, Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron, Int. J. Metalcast., 2015, 9, p 73–75
K.P. Surendra, B. Kuriachena, K. Nitin, and N. Raman, The Slurry Abrasive Wear Behaviour and Microstructural Analysis of A2024-SiC-ZrSiO4 Metal Matrix Composite, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, p 6426–6432
K. Nitin, S. Alok, K. Nripesh, and R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Eco-Friendly Complex Multiferroic Material: Bi(Co0.35Ti0.35Fe0.30)O3, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45, p 822–831
ISO: ISO 16112:2006(E), Compacted (Vermicular) Graphite Cast Irons—Classification, ISO, 2006, p 15–16
ASTM: ASTM A247-16A: Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of Graphite in Iron Castings, ASTM, 2016, p 7–12
J.C. Hernando, B. Domeij, D. González, J.M. Amieva, and A. Diószegi, New Experimental Technique for Nodularity and Mg Fading Control in Compacted Graphite Iron Production on Laboratory Scale, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, 48, p 5432–5441
Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, and B. Shen, Investigation of Tribological Properties of Brake Shoe Materials Phosphorous Cast Iron with Different Graphite Morphologies, Wear, 1993, 166, p 179–186
Q.S. Ma, Y.J. Li, and J. Wang, Effects of Ti Addition on Microstructure Homogenization and Wear Resistance of Wide-Band Laser Clad Ni60/WC Composite Coatings, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard. Mater., 2017, 64, p 225–233
Y. Fan, S. Xu, R. Schaller, J. Jiao, F. Chaplen, and H. Liu, Nanoparticle Decorated Anodes for Enhanced Current Generation in Microbial Electrochemical Cells, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2011, 26, p 1908–1912
A. Likhite, P. Parhad, D.R. Peshwe, and S.U. Pathak, Effect of Austenitization Temperature on Wear Behavior of Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron (CADI), Int. Sch. Sci. Res. Innov., 2014, 8, p 510–513
A. Meena and M.E. Mansori, Study of Dry and Minimum Quantity Lubrication Drilling of Novel Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) for Automotive Applications, Wear, 2010, 12, p 2412–2416
A. Meena and M.E. Mansori, Drilling Performance of Green Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) Grade Produced by Novel Manufacturing Technology, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2012, 59, p 9–19
G. Straffelini, M. Pellizzari, and L. Maines, Effect on Sliding Speed and Contact Pressure on the Oxidative Wear of Austempered Ductile Iron, Wear, 2011, 270, p 714–719
U.R. Kumari and P.P. Rao, Study of Wear Behaviour of Austempered Ductile Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44, p 1082–1093
K.H.Z. Gahr, Wear by Hard Particles, Tribol. Int., 1998, 31, p 587–596
J.V. Giacchi, R.A. Martínez, M.M. Gamba, and R.C. Dommarco, Abrasion and Impact Properties of Partially Chilled Gray Iron, Wear, 2007, 262, p 282–291
Y.L. Yi, J.D. Xing, Y.F. Lu, H.G. Fu, M.J. Wan, L.L. Yu, Q.L. Zheng, and C. Ya, Investigations on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Abrasion Resistance of 4 wt.%Cr-2 wt.%Mn-2 wt.%Cu-Fe-B Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2018, 137, p 222–230
Y.F. Zhou, Y.L. Yang, J. Yang, F.F. Hao, D. Li, X.J. Ren, and Q.X. Yang, Effect of Ti Additive on (Cr, Fe)7C3 Carbide in Arc Surfacing Layer and Its Refined Mechanism, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258, p 6653–6659
H.C. Li, Z.Y. Jiang, A.K. Tieu, W.H. Sun, and D.B. Wei, Experimental Study on Wear and Friction of Work Roll Material with 4% Cr and Added Ti in Cold Rolling, Wear, 2011, 9, p 2500–2511
A. Bedolla-Jacuinde, F.V. Guerra, I. Mejía, J. Zuno-Silva, and M. Rainforth, Abrasive Wear of V-Nb-Ti Alloyed High-Chromium White Irons, Wear, 2015, 6, p 1006–1011
Y. Gao, Z. Lv, S. Sun, M. Qu, Z. Shi, R. Zhang, and W. Fu, First Principles Study on Surface Structure and Stability of Alloyed Cementite Doped with Cr, Mater. Lett., 2013, 100, p 170–172
B. Tololi and A. Hellawell, Phase Separation and Undercooling in Al-Si Eutectic Alloy—the Influence of Freezing Rate and Temperature Gradient, Acta Metall., 1976, 24, p 565–573
S.Z. Lu and A. Hellawell, Modification of Al-Si Alloys: Microstructure, Thermal Analysis, and Mechanisms, JOM, 1995, 2, p 38–40
B.L. Bramfitt, The Effect of Carbide and Nitride Additions on the Heterogeneous Nucleation Behavior of Liquid Iron, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1970, 1, p 1987–1990
Y.H. Qu, J.D. Xing, X.H. Zhi, J.Y. Peng, and H.G. Fu, Effect of Cerium on the As-Cast Microstructure of a Hypereutectic High Chromium Cast Iron, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, p 3024–3027
X. Yun, Y. Zhou, J. Yang, X. Xing, X. Ren, Y.L. Yang, and Q.X. Yang, Refinement of Nano-Y2O3 on Microstructure of Hypereutectic Fe-Cr-C Hardfacing Coatings, J. Rare Earths, 2015, 33, p 671–678
Y. Zhou, Y. Yang, J. Yang, F. Hao, D. Li, X. Ren, and Q.X. Yang, Effect of Ti Additive on (Cr, Fe)7C3 Carbide in Arc Surfacing Layer and Its Refined Mechanism, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258, p 6653–6659
Z. Shi, S. Liu, Y. Gao, Y. Zhou, X. Xing, X. Ren, and Q.X. Yang, Mechanism of Y2O3 as Heterogeneous Nucleus of TiC in Hypereutectic Fe-CrC-Ti-Y2O3 Coating: First Principle Calculation and Experiment Research, Mater. Today Commun., 2017, 13, p 80–91
Z. Ni, Y. Sun, F. Xue, J. Bai, and Y. Lu, Microstructure and Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel Reinforced With In Situ TiC Particulate, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 1462–1467
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial support for this work from National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (51775006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P., Fu, H., Nan, R. et al. Effect of Ti Modification on Microstructures and Properties of Carbidic Austempered Ductile Iron. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 2335–2347 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03986-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03986-4