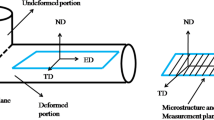
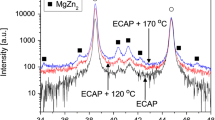
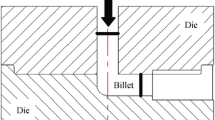
Abstract
Microstructural features and mechanical properties of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) have been investigated. The equivalent plastic strain obtained from the simulation agrees well with that from the analytical calculation in a way that both increase with an increase in deformation, but the strain distribution is non-uniform, appearing as a strain gradient along the norm direction. Microstructure investigation shows that grain refinement is achieved in frequency of low-angle grain boundaries fabricated by ECAP. The pole density is reduced by ECAP, during which the Brass and Goss type textures are introduced. TEM results show chain-like recrystallized grains formed at the grain boundaries and broken second-phase particles come into being due to the heavy shear force. After ECAP, the hardness and strength increase significantly while the elongation is reduced. Besides, an extreme strengthening is confirmed because of the balance between dynamic hardening and softening. The microstructure evolution mechanism is revealed in terms of grain refinement, precipitate phase breakage and texture evolution.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.Y. Ng and A.H.W. Ngan, Effects of Pore-Channel Ordering on the Mechanical Properties of Anodic Aluminum Oxide Nano-honeycombs, Scr. Mater., 2012, 66(7), p 439–442
P. Lehto et al., Influence of Grain Size Distribution on the Hall–Petch Relationship of Welded Structural Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 592(3), p 28–39
K. Ma et al., Mechanical Behavior and Strengthening Mechanisms in Ultrafine Grain Precipitation-Strengthened Aluminum Alloy, Acta Mater., 2014, 62(5), p 141–155
Y. Estrina, Extreme Grain Refinement by Severe Plastic Deformation: A Wealth of Challenging Science, Acta Mater., 2013, 61(3), p 782–817
R.Z. Valiev and T.G. Langdon, Achieving Exceptional Grain Refinement Through Severe Plastic Deformation: New Approaches for Improving the Processing Technology, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, 42(10), p 2942–2951
R.Z. Valiev, R.K. Islamgaliev, and I.V. Alexandrov, Bulk Nanostructured Materials from Severe Plastic Deformation, Prog. Mater. Sci., 1999, 45(2), p 103–189
E.A. El-Danaf, Mechanical Properties, Microstructure and Texture of Single Pass Equal Channel Angular Pressed 1050, 5083, 6082 and 7010 Aluminum Alloys with Different Dies, Mater. Des., 2011, 32(7), p 3838–3853
N. Haghdadi et al., The Semisolid Microstructural Evolution of a Severely Deformed A356 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Des., 2013, 49, p 878–887
G. Ramu and R. Bauri, Effect of Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP) on Microstructure and Properties of Al-SiC Composites, Mater. Des., 2009, 30(9), p 3554–3559
C.M. Cepeda-Jiménez et al., High Strain Rate Superplasticity at Intermediate Temperatures of the Al 7075 Alloy Severely Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, J. Alloy. Compd., 2011, 509(40), p 9589–9597
M.H. Shaeri et al., Characterization of Microstructure and Deformation Texture During Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 576(5), p 350–357
M.H. Shaeri et al., Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-7075 Alloy Processed by Equal Channel Angular Pressing Combined with Aging Treatment, Mater. Des., 2014, 57(5), p 250–257
S.K. Panigrahi et al., Development of Ultrafine Grained High Strength Age Hardenable Al 7075 Alloy by Cryorolling, Mater. Des., 2011, 32(6), p 3150–3160
Z.C. Duan et al., Influence of High-Pressure Torsion on Microstructural Evolution in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45(17), p 4621–4630
Y. Duan et al., Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 7005 Aluminum Alloy Processed by Room Temperature ECAP and Subsequent Annealing, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 664, p 518–529
R.Z. Valiev and T.G. Langdon, Principles of Equal-Channel Angular Pressing as a Processing Tool for Grain Refinement, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2006, 51(7), p 881–981
L. Bao et al., Simulation of Multi-Pass ECAP by 3D Finite Element Method, 5th International Conference on Nanomaterials by Severe Plastic Deformation, Materials Science Forum, vol. 667–669, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, People’s Republic of China, Mar 21–25, 2011, p 115–120
T. Guo et al., Study on the Materials Flowing and Deformation Behavior by Equal Channel Angular Pressing (ECAP), Mater. Rev., 2009, 23(18), p 93–96
V.L. Sordi, C.A. Feliciano, and M. Ferrante, The Influence of Deformation by Equal-Channel Angular Pressing on the Ageing Response and Precipitate Fracturing: Case of the Al-Ag Alloy, J. Mater. Sci., 2015, 50(1), p 138–143
C. Xu et al., Using ECAP to Achieve Grain Refinement, Precipitate Fragmentation and High Strain Rate Superplasticity in a Spray-Cast Aluminum Alloy, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(20), p 6139–6149
C. Xu et al., Influence of ECAP on Precipitate Distributions in a Spray-Cast Aluminum Alloy, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(3), p 749–758
K.T. Park et al., Size and Distribution of Particles and Voids Pre-existing in Equal Channel Angular Pressed 5083 Al Alloy: Their Effect on Cavitation During Low-Temperature Superplastic Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 371(1–2), p 178–186
I. Sabirov et al., Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Metal Matrix Composites: Effect on Particle Distribution and Fracture Toughness, Acta Mater., 2005, 53(18), p 4919–4930
J.M. García-Infanta et al., Effect of the Deformation Path on the Ductility of a Hypoeutectic Al-Si Casting Alloy Subjected to Equal-Channel Angular Pressing by Routes A, B, B and C, Scr. Mater., 2008, 58(2), p 138–141
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks for the research grants supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51275414, 51605387), Project supported by the Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing (NWPU), China (Grant No. 130-QP-2015), Province Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi (2015JM5204) and the Graduate Starting Seed Fund of Northwestern Polytechnical University (No. Z2017098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, F., Wang, W. et al. Achieving Grain Refinement and Related Mechanical Property Improvement of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy Through Severe Plastic Deformation. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6690–6700 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3758-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3758-z