Abstract
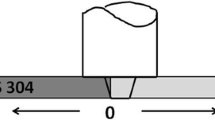
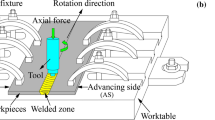
Three-millimeter-thick Q235 steel plates were friction stir welded using a tool made of tungsten-rhenium alloy in the present study. The microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joints at various traverse speeds from 50 to 150 mm/min were analyzed. It was demonstrated that traverse speed had great impacts on microstructure and mechanical properties of the joints. Phase transformation accompanied with recrystallization occurred during FSW process which resulted in different microstructures in the WNZ, and the grain size in other zones was significantly affected by traverse speed. The highest hardness was located in the nugget zone, while the lowest hardness was found in the heat-affected zone. The transverse tensile test suggested that all the joints showed slightly lower tensile strength than that of the base material, and the tensile strength increased with increasing traverse speed. All the joints fractured in the heat-affected zone with ductile fracture mode. The impact test showed that the impact toughness decreased with the increasing traverse speed and the impact fracture surface could be divided into shear lip zone and fibrous zone which showed a typical ductile fracture.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.S. Sato, T.W. Nelson, C.J. Sterling, R.J. Steel, and C.O. Pettersson, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded SAF 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 397(1–2), p 376–384
H.H. Cho, H.N. Han, S.T. Hong, J.H. Park, and Y.J. Kwon, Microstructural Analysis of Friction Stir Welded Ferritic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(6), p 2889–2894
R.S. Mishra, Z.Y. Ma, Y. Sato, Y. Hovanski, and R. Verma, Friction Stir Welding and Processing VII, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2005, 50(1), p 1–78
Y.S. Sato, H. Yamanoi, H. Kokawa, and T. Furuhara, Microstructural Evolution of Ultrahigh Carbon Steel During Friction Stir Welding, Scr. Mater., 2007, 57(6), p 557–560
R. Ramesh, I. Dinaharan, R. Kumar, and E.T. Akinlabi, Microstructure and Mechanical Characterization of Friction Stir Welded High Strength Low Alloy Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 687, p 39–46
S.H.C. Park, Y.S. Sato, and H. Kokawa, Microstructural Evolution and Its Effect on Hall–Petch Relationship in Friction Stir Welding of Thixomolded Mg Alloy AZ91D, J. Mater. Sci., 2003, 38(21), p 4379–4383
J. Teimurnezhad, H. Pashazadeh, and A. Masumi, Effect of Shoulder Plunge Depth on the Weld Morphology, Macrograph and Microstructure of Copper FSW Joints, J. Manuf. Process., 2016, 22, p 254–259
S. Mironov, Y. Zhang, Y.S. Sato, and H. Kokawa, Crystallography of Transformed β Microstructure in Friction Stir Welded Ti–6Al–4V Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2008, 59(5), p 511–514
A. Scialpi, M.D. Giorgi, L.A.C.D. Filippis, R. Nobile, and F.W. Panella, Mechanical Analysis of Ultra-Thin Friction Stir Welding Joined Sheets with Dissimilar and Similar Materials, Mater. Des., 2008, 29(5), p 928–936
P. Carlone, A. Astarita, G.S. Palazzo, V. Paradiso, and A. Squillace, Microstructural Aspects in Al–Cu Dissimilar Joining by FSW, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2015, 79(5–8), p 1109–1116
A. De, H.K.D.H. Bhadeshia, and T. Debroy, Friction Stir Welding of Mild Steel: Tool Durability and Steel Microstructure, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, 30(9), p 1050–1056
Y. Sun, H. Fujii, H. Imai, and K. Kondoh, Suppression of Hydrogen-Induced Damage in Friction Stir Welded Low Carbon Steel Joints, Corros. Sci., 2015, 94, p 88–98
Y. Azuma, Y. Kameno, and T. Takasugi, Friction Stir Welding in Stainless Steel Sheet of Type 430 Using Ni-Based Dual Two-Phase Intermetallic Alloy Tool, Weld. Int., 2013, 27(12), p 929–935
W.M. Thomas, P.L. Threadgill, and E.D. Nicholas, Feasibility of Friction Stir Welding Steel, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 1999, 4(6), p 365–372
H. Fujii, L. Cui, N. Tsuji, M. Maeda, and K. Nakata, Friction Stir Welding of Carbon Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 429(1), p 50–57
L. Cui, H. Fujii, N. Tsuji, K. Nakata, and K. Nogi, Transformation in Stir Zone of Friction Stir Welded Carbon Steels with Different Carbon Contents, ISIJ Int., 2007, 47(2), p 299–306
H. Fujii, L. Cui, K. Nakata, and K. Nogi, Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Carbon Steel Joints—Friction Stir Welding With and Without Transformation, Weld. World, 2013, 52(9–10), p 75–81
M. Ghosh, M. Hussain, and G.R. Kumar, Effect of Welding Parameters on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Plain Carbon Steel, ISIJ Int., 2012, 52(3), p 477–482
T.J. Lienert, W.L. Stellwag, B.B. Grimmett, and R.W. Warke, Friction Stir Welding Studies on Mild Steel—Process Results, Microstructures, and Mechanical Properties are Reported, Weld. J., 2003, 82(1), p 1S–9S
S. Karami, H. Jafarian, A.R. Eivani, and S. Kheirandish, Engineering Tensile Properties by Controlling Welding Parameters and Microstructure in a Mild Steel Processed by Friction Stir Welding, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 670, p 68–74
R. Nandan, G.G. Roy, T.J. Lienert, and T. Debroy, Three-Dimensional Heat and Material Flow During Friction Stir Welding of Mild Steel, Acta Mater., 2007, 55(3), p 883–895
D. Micallef, D. Camilleri, A. Toumpis, A. Galloway, and L. Arbaoui, Local Heat Generation and Material Flow in Friction Stir Welding of Mild Steel Assemblies, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. L J. Mater., 2016, 230(2), p 586–602
A.K. Lakshminarayanan and V. Balasubramanian, Tensile and Impact Toughness Properties of Gas Tungsten Arc Welded and Friction Stir Welded Interstitial Free Steel Joints, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, 20(1), p 82–89
H. Li, S. Yang, S. Zhang, B. Zhang, and Z. Jiang, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welding Super-Austenitic Stainless Steel S32654, Mater. Des., 2017, 118, p 207–217
M.H. Razmpoosh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and A. Imandoust, Effect of the Zener–Hollomon Parameter on the Microstructure Evolution of Dual Phase TWIP Steel Subjected to Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 638, p 15–19
P. Xue, B.L. Xiao, W.G. Wang, Q. Zhang, and D. Wang, Achieving Ultrafine Dual-Phase Structure with Superior Mechanical Property in Friction Stir Processed Plain Low Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 575(28), p 30–34
D.M. Sekban, S.M. Aktarer, and P. Xue, Impact Toughness of Friction Stir Processed Low Carbon Steel Used in Shipbuilding, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 672, p 40–48
Acknowledgments
The research was sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No. ZR2016EEM43) and Key Research & Development Program in Shandong Province (No. 2017CXGC0811).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Zhang, R.X., Yang, H.F. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Q235 Low-Carbon Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6709–6718 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3747-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3747-2