Abstract
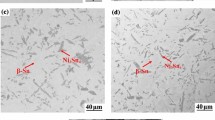
The addition of Ni on lead-free solder alloys Sn0.7Cu was tested in this study. A small amount of Ni was added to the solder alloys to evaluate the thermal behavior, microstructure, and mechanical properties of the composite solders after sintering and isothermal aging for 3 days and then compared with the results of the binary Sn0.7Cu solder. The results indicated that the ultimate tensile strength and yield tensile strength changed when adding 0.25 wt.% of Ni. The tested results of the differential scanning calorimeter showed that the addition of Ni (such as 0.5 and 1 wt.%) could obviously increase the solidification temperature of Sn0.7Cu alloys in the cooling process. When the Ni content was increased to 0.25 wt.% in the ternary condition, which includes the Sn0.7Cu-xNi (x = 0, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, and 1 wt.%) solder alloys for the indentation creep test, the minimum creep rate reached the maximum; however, the trend was reversed as the Ni content was higher than this level. In addition, the microstructure of Sn-0.7Cu-xNi solder alloys was obviously different with the eutectic Sn-0.7Cu solder, such that the Ni gradually accumulated in the (Cu, Ni)6Sn5 IMCs within the Ni-containing solder alloys. Additionally, this process refined the microstructure of the Sn-0.7Cu solder. The fracture surface of the eutectic Sn-0.7Cu solder revealed ductile fracture modes; however, there was no mixed ductile–brittle fracture mode occurred when the Ni content was in the range of 0-1 wt.%.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Chang and S.K. Wu, Damping Characteristics of Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu and Sn-37Pb Solders Studied by Dynamic Mechanical Analysis, Scr. Mater., 2010, 63, p 957–960
M. He, Z. Chen, and G.J. Qi, Solid State Interfacial Reaction of Sn-37Pb and Sn-3.5Ag Solders with Ni-P Under Bump Metallization, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 2047–2056
A.F. Abd El-Rehim and H.Y. Zahran, Investigation of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sn-xCu Solder Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 695, p 3666–3673
A.A. El-Daly, Y. Swilem, and A.E. Hammad, Creep Properties of Sn-Sb Based Lead-Free Solder Alloys, J. Alloys Comp., 2009, 471, p 98–104
M.L. Huang, N. Kang, Q. Zhou, and Y.Z. Huang, Effect of Ni Content on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion, Behavior of Al/Sn-9Zn-xNi/Cu Joints, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2012, 28, p 844–852
X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, and Z.X. Min, Interfacial Reaction and IMC Growth Between Bi-Containing Sn0.7Cu Solders and Cu Substrate During Soldering and Aging, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 582, p 341–347
H. Nishikawa and N. Iwata, Formation and Growth of Intermetallic Compound Layers at the Interface During Laser Soldering Using Sn-Ag Cu Solder on a Cu Pad, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, 215, p 6–11
H. Kang, M. Lee, D. Sun, S. Pae, and J. Park, Formation of Octahedral Corrosion Products in Sn-Ag Flip Chip Solder Bump, Scr. Mater., 2015, 108, p 126–129
W.Y. Chen, T.C. Chiu, K.L. Lin, and Y.S. Lai, Electrorecrystallization of Intermetallic Compound in the Sn0.7Cu Solder Joint, Intermetallics, 2012, 26, p 40–43
X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, Y. Liu, and Z.X. Min, Developments of High Strength Bi-Containing Sn0.7Cu Lead-Free Solder Alloys Prepared by Directional Solidification, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 625, p 241–250
J.W. Yoon, S.W. Kim, Ja.M. Koo, D.G. Kim, and S.B. Jung, Reliability Investigation and Interfacial Reaction of Ball-Grid-Array Packages Using the Lead-Free Sn-Cu Solder, J. Electron. Microsc., 2004, 33, p 1190–1199
C.K. Shin, Y.J. Baik, and J.Y. Huh, Effects of Microstructural Evolution and Intermetallic Layer Growth on Shear Strength Of Ball-Grid-Array Sn-Cu Solder Joints, J. Electron. Microsc., 2001, 30, p 1323–1331
Satyanarayan and K.N. Prabhu, Reactive Wetting, Evolution of Interfacial and Bulk IMCs and Their Effect on Mechanical Properties of Eutectic Sn-Cu Solder Alloy, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 166, p 87–118
M.I.I. Ramli, N. Saud, M.A.A. MohdSalleh, M.N. Derman, and R. MohdSaid, Effect of TiO2 Additions on Sn-0.7Cu-0.05Ni Lead-Free Composite Solder, Microelectron. Reliab., 2016, 65, p 255–264
L. Yang, Y.C. Zhang, J. Dai, Y.F. Jing, J.G. Ge, and N. Zhang, Microstructure, Interfacial IMC and Mechanical Properties of Sn-0.7Cu-xAl (x = 0–0.075) Lead-Free Solder Alloy, Mater. Des., 2015, 67, p 209–216
N. Zhao, M.L. Huang, Y. Zhong, H.T. Ma, and X.M. Pan, Effects of Rare Earth Ce Addition on the Microstructure, Wettability and Interfacial Reactions of Eutectic Sn-0.7Cu Solder, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2015, 26, p 345–352
S. Tian, S.P. Li, J. Zhou, and F. Xue, Thermodynamic Characteristics, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sn-0.7Cu-xIn Lead-Free Solder Alloy, J. Alloys Comp., 2018, 742, p 835–843
F.J. Wang, X. Ma, and Y.Y. Qian, Improvement of Microstructure and Interface Structure of Eutectic Sn-0.7Cu Solder with Small Amount of Zn Addition, Scr. Mater., 2005, 53, p 699–702
K.S. Kim, S.H. Huh, and K. Suganuma, Effects of Fourth Alloying Additive on Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Sn-Ag-Cu Alloy and Joints with Cu, Microelectron. Reliab., 2003, 43, p 259–267
Y.Q. Lai, X.W. Hu, Y.L. Li, and X.X. Jiang, Interfacial Microstructure Evolution and Shear Strength of Sn0.7Cu-xNi/Cu Solder Joints, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2018, 29, p 11314–11324
C.R. Yang, F.B. Song, and S.W. Ricky Lee, Impact of Ni Concentration on the Intermetallic Compound Formation and Brittle Fracture Strength of Sn-Cu-Ni (SCN) Lead-Free Solder Joints, Microelectron. Reliab., 2014, 54, p 435–446
P. He, J.H. Zhang, R.L. Zhou, and X.Q. Li, Diffusion Bonding Technology of a Titanium Alloy to a Stainless Steel Web with Ni Interlayer, Mater. Charact., 1999, 43, p 289–292
P. He and D. Liu, Mechanism of Forming Interfacial Intermetallic Compounds at Interface for Solid State Diffusion Bonding of Dissimilar Materials, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 437, p 430–435
R.K. Chinnam, C. Fauteux, J. Neuenschwander, and J. Janczak-Rusch, Evolution of the Microstructure of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Joints Exposed to Ultrasonic Waves During Solidification, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 1474–1481
A.G. Atkins, The Science of Hardness Testing and its Research Applications, ASM, Metal Park, 1971, p 223
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, H. Khanbareh, and N. Jahangiri, Indentation Creep of Lead-Free Sn-9Zn and Sn-8Zn-3Bi Solder Alloys, Mater. Des., 2009, 30, p 574–580
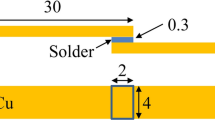
M.J. Rizvi, C. Bailey, Y.C. Chan, M.N. Islam, and H. Lu, Effect of adding 0.3 wt.% Ni into the Sn-0.7 wt.% Cu Solder: Part II. Growth of Intermetallic Layer with Cu During Wetting and Aging, J. Alloys Compd., 2007, 438, p 122–128
K. Nogita, J. Read, T. Nishimura, K. Sweatman, S. Suenaga, and A.K. Dahle, Microstructure Control in Sn-0.7 Cu Alloys, Mater. Trans., 2005, 46, p 2419–2425
C.H. Wang and H.T. Shen, Effects of Ni Addition on the Interfacial Reactions Between Sn-Cu Solders and Ni Substrate, Intermetallics, 2010, 18, p 616–622
P.M. Sargent and M.F. Ashby, Indentation Creep, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1992, 8, p 594
G. Cseh, J. Bar, H.J. Gudladt, J. Lendvai, and A. Juhasz, Indentation Creep in a Short Fibre-Reinforced Metal Matrix Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1999, 272, p 145
P. Yao, P. Liu, and J. Liu, Interfacial Reaction and Shear Strength of SnAgCu-xNi/Ni Solder Joints During Aging at 150 °C, Microelectron. Eng., 2009, 86, p 1969–1974
X.W. Hu, W.J. Chen, and B. Wu, Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Sn-1Cu Lead-Free Solder Alloy Produced by Directional Solidification, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 556, p 816–823
X.W. Hu, K. Li, and Z.X. Min, Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Sn0.7Cu0.7Bi Lead-Free Solders Produced by Directional Solidification, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 566, p 239–245
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51465039 and 51765040), Nature Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20161BAB206122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, Y., Hu, X., Jiang, X. et al. Effect of Ni Addition to Sn0.7Cu Solder Alloy on Thermal Behavior, Microstructure, and Mechanical Properties. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 6564–6576 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3734-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3734-7