Abstract
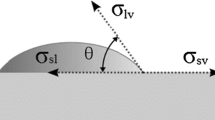
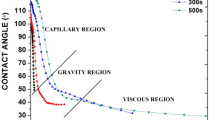
The “degree of wetting,” which is related to the contact angle (θ) between the molten solder and the substrate, is a useful parameter on the solderability process control. The contact angle, however, is strongly dependent on the type of substrate surface finish and used atmosphere (inert or non-inert). Furthermore, the surface tension, being an important parameter on the solderability process and performance, can also be achieved if the contact angle is known. In this study, the SAC405 [Sn4.0Ag0.5Cu (in wt.%)] solder paste contact angle was measured, by the “sessile drop” method, as a function of the temperature, surface pad finish and used atmosphere. The results are discussed, and the contact angles obtained for the different conditions are compared and discussed. Then, the surface tension (experimental) was obtained from the measured contact angle and compared with the obtained by using computation models (theoretical). The experiments performed in high vacuum conditions, i.e., low oxygen content, over a temperature range, allowed the evaluation and understanding of the surface oxides layers role on the solder wettability. The present study shows that in the soldering process, even in an inert atmosphere, usually used in industry, occurs the formation of superficial oxides, over the liquid solder and/or at the pad surfaces, that strongly affects the solder paste wettability, specially with Sn and OSP (organic solderability preservative) finishing. Differences in contact angle of ≥ 10° were determined between the two types of used atmospheres. The experimental surface tension and theoretical surface tension obtained, for the NiAu substrate type, present good correlation. The lower contact angle values were obtained for the NiAu and OSP finish types, independently of the atmosphere type.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Arenas and V.L. Acoff, Contact Angle Measurements of Sn-Ag and Sn-Cu Lead-Free Solders on Copper Substrates, J. Electron. Mater., 2004, 33(12), p 1452–1458
S. Amore, E. Ricci, G. Borzone, and R. Novakovic, Wetting Behaviour of Lead-Free Sn-Based Alloys on Cu and Ni Substrates, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, 495(1–2), p 108–112
V. Vuorinen, T. Laurila, H. Yu, and J.K. Kivilahti, Phase Formation Between Lead-Free Sn-Ag-Cu Solder and Ni(P)/Au Finishes, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 99(2), p 023530
C. Leinenbach, F. Valenza, D. Giuranno, H.R. Elsener, S. Jin, and R. Novakovic, Wetting and Soldering Behavior of Eutectic Au-Ge Alloy on Cu and Ni Substrates, J. Electron. Mater., 2011, 40(7), p 1533–1541
T. Chellaih, G. Kumar, and K.N. Prabhu, Effect of Thermal Contact Heat Transfer on Solidification of Pb-Sn and Pb-Free Solders, Mater. Des., 2007, 28(3), p 1006–1011
C.-T. Lin and K.-L. Lin, Contact Angle of 63Sn-37Pb and Pb-Free Solder on Cu Plating, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2003, 214(1-4), p 243–258
L. Boinovich and A. Emelyanenko, Wetting and Surface Forces, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 165(2), p 60–69
F. Guo, S. Choi, J.P. Lucas, and K.N. Subramanian, Effects of Reflow on Wettability, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Lead-Free Solders, J. Electron. Mater., 2000, 29(10), p 1241–1248
J. Lee, S. Chen, H. Chang, and C. Chen, Reactive Wetting Between Molten Sn-Bi and Ni Substrate, J. Electron. Mater., 2003, 32(3), p 13–17
C. Gonçalves, H. Leitão, C.S. Lau, J.C. Teixeira, L. Ribas, S. Teixeira, M.F. Cerqueira, F. Macedo, and D. Soares, Wetting Behaviour of SAC305 Solder on Different Substrates in High Vacuum and Inert Atmosphere, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2015, 26(7), p 5106–5112
V.H. López and A.R. Kennedy, Flux-Assisted Wetting and Spreading of Al on TiC, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2006, 298(1), p 356–362
K.N. Prabhu, Reactive Wetting, Evolution of Interfacial and Bulk IMCs and Their Effect on Mechanical Properties of Eutectic Sn-Cu Solder Alloy, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 166(1–2), p 87–118
G. Humpston and D.M. Jacobson, Principles of Soldering, ASM International, Ohio, 2004
N. Eustathopoulos, M.G. Nicholas, and B. Drevet, Wettability at High Temperatures, Pergamon, Oxford, 1999
J.A. Warren, W.J. Boettinger, and A.R. Roosen, Modelling Reative Wetting, Acta Mater., 1998, 46(9), p 3247–3264
D. Bonn, J. Eggers, J. Indekeu, J. Meunier, and E. Rolley, Wetting and Spreading, Rev. Mod. Phys., 2009, 81(2), p 739–805
E.E.M. Noor, N.M. Sharif, C.K. Yew, T. Ariga, A.B. Ismail, and Z. Hussain, Wettability and Strength of In-Bi-Sn Lead-Free Solder Alloy on Copper Substrate, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 507(1), p 290–296
L. Zang, Z. Yuan, H. Xu, and B. Xu, Wetting Process and Interfacial Characteristic of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu on Different Substrates at Temperatures Ranging From 503 K to 673 K, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257(11), p 4877–4884
F. Gnecco, E. Ricci, S. Amore, D. Giuranno, G. Borzone, G. Zanicchi, and R. Novakovic, Wetting Behaviour and Reactivity of Lead Free Au-In-Sn and Bi-In-Sn Alloys on Copper Substrates, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes., 2007, 27(5), p 409–416
R. Voitovitch, A. Mortensen, F. Hodaj, and N. Eustathopoulos, Diffusion-Limited Reactive Wetting: Study of Spreading Kinetics of Cu-Cr Alloys on Carbon, Acta Mater., 1999, 47(4), p 1117–1128
G.W. Liu, F. Valenza, M.L. Muolo, G.J. Qiao, and A. Passerone, Wetting and Interfacial Behavior of Ni-Si Alloy on Different Substrates, J. Mater. Sci., 2009, 44(22), p 5990–5997
L. Zang, Z. Yuan, H. Zhao, and X. Zhang, Wettability of Molten Sn-Bi-Cu Solder on Cu Substrate, Mater. Lett., 2009, 63(23), p 2067–2069
J. Drelich, C. Fang, and C.L. White, Measurement of Interfacial Tension in Fluid–Fluid Systems, Encycl. Surf. Colloid Sci., 2002, 3, p 3158–3163
L. Zang, Z. Yuan, H. Xu, and B. Xu, Wetting Process and Interfacial Characteristics of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu on Different Substrates at Temperatures Ranging From 503 K to 673 K, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, p 4877–4884
N. Sobczak, A. Kudyba, R. Nowak, W. Radziwill, and K. Pietrzak, Factors Affecting Wettability and Bond Strength of Solder Joint Couples, Pure Appl. Chem., 2007, 79(10), p 1755–1769
J.D. Malcolm and D.D. Elliot, Interfacial Tension from Height and Diameter of a Single Sessile Drop or Captive Bubble, J. Chem. Eng., 1980, 58, p 151
J.C. Bashforth and F. Adams, An Attempt to Test the Theory of Capillary Action, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1892
O. Río and A. Neumann, Axisymmetric Drop Shape Analysis: Computational Methods for the Measurement of Interfacial Properties from the Shape and Dimensions of Pendant and Sessile Drops, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1997, 196(2), p 136–147
J.J. Sundelin, S.T. Nurmi, T.K. Lepistö, and E.O. Ristolainen, Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of SnAgCu Solder Joints, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 420(1–2), p 55–62
J. Görlich, C. Oberdorfer, D. Baither, G. Schmitza, C. Reinke, and U. Wilke, The Role of Oxide Layers in Solder Joints, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 490, p 336–341
M. Ramireza, L. Henneken, and S. Virtanen, Oxidation Kinetics of Thin Copper Films and Wetting Behaviour of Copper and Organic Solderability Preservatives (OSP) with Lead-Free Solder, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, p 6481–6488
J. Li, J. Karppinen, T. Laurila, and J.K. Kivilahti, Reliability of Lead-Free Solder Interconnections in Thermal and Power Cycling Tests, IEEE Trans. Compon. Pack Technol., 2009, 32(2), p 302–308
J. Han, H. Chen, and M. Li, Role of Grain Orientation in the Failure of Sn-Based Solder Joints Under Thermomechanical Fatigue, Acta Met. Sin., 2012, 25(3), p 214–224
K. Kanlayasiri, M. Mongkolwongrojn, and T. Ariga, Influence of Indium Addition on Characteristics on Sn-03-Ag-0.7Cu Solder Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 485(1/2), p 225–230
J.-W. Yoon, B.-I. Noh, B.-K. Kim, C.-C. Shur, and S.-B. Jung, Wettability and Interfacial Reaction of Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu and Sn-Ag-Ni/Cu Solder Joints, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 486(1/2), p 142–147
L. Zhang, S.B. Xue, G. Zeng, L.L. Gao, and H. Ye, Interface Reaction Between SnAgCu/SnAgCuCe Solders and Cu Substrate Subjected to Thermal Cycling and Isothermal Aging, J. Alloy. Compd., 2012, 510(1), p 38–45
T. Gancarz, Density, Surface Tension and Viscosity of Ga-Sn Alloys, J. Mol. Liq., 2017, 241, p 231–236
A. Zdziennicka, K. Szymczyk, J. Krawczyk, and B. Janczuk, Some Remarks on the Solid Surface Tension Determination From Contact Angle Measurements, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 405, p 88–101
H. Tavana and A.W. Neumann, Recent Progress in the Determination of Solid Surface Tensions from Contact Angles, Adv. Coll. Interface. Sci., 2007, 132, p 1–32
V. Sklyarchuka, Y. Plevachuka, I. Kabanb, and R. Novakovićc, Surface Properties and Wetting Behaviour of Liquid Ag-Sb-Sn Alloys, J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall., 2012, 48(3), p 443–448
Z. Moser, W. Gasior, A. Debski, and J. Pstrus, SURDAT—Database of Physical Properties of Lead-Free Solders, J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall., 2007, 43(2), p 125–130
T. Tanaka, K. Hack, T. Lida, and S. Hara, Application of Thermodynamic Databases to the Evaluation of Surface Tensions of Molten Alloys, Salt Mixtures and Oxide Mixtures, Z. Metall., 1996, 875, p 380–389
J. Lee, W. Shimoda, and T. Tanaka, Surface Tension and its Temperature Coefficient of Liquid Sn_X (X = Ag, Cu) Alloys, Mater. Trans., 2004, 45(9), p 2864–2870
T. Hetschel, K. Wolter, F. Phillipp, R.B. Gmbh, Wettability Effects of Immersion Tin Final Finishes with Lead Free Solder, in Electronics System-Integration Technology Conference, 2008. ESTC 2008, 2nd (2008)
P. Protsenko, A. Terlain, V. Traskine, and N. Eustathopoulos, The Role of Intermetallics in Wetting in Metallic Systems, Scr. Mater., 2001, 45, p 1439–1445
O. Dezellus and N. Eustathopoulos, Fundamental Issues of Reactive Wetting by Liquid Metals, J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45(16), p 4256–4264
K. Suganuma, Advances in Lead-Free Electronics Soldering, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2001, 5, p 55–64
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by FCT with the reference Project UID/EEA/04436/2013, Compete 2020 with the Code POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006941 and project in co-promotion No. 002814/2015 (iFACTORY 2015-2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited submission to JMEP selected from presentations at the Symposium “Interface Design and Modelling, Wetting and High-Temperature Capillarity,” belonging to the topic “Processing” at the European Congress and Exhibition on Advanced Materials and Processes (EUROMAT 2017), held September 17-22, 2017, in Thessaloniki, Greece, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soares, D., Leitão, H., Lau, C.S. et al. Effect of the Soldering Atmosphere on the Wettability Between Sn4.0Ag0.5Cu (in wt.%) Lead-Free Solder Paste and Various Substrates. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 5011–5017 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3419-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3419-2